What is India’s Progress on Hunger and Poverty Alleviation? - Social Issues | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
What is India’s Progress on Hunger and Poverty Alleviation?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
social issues
📖 Introduction
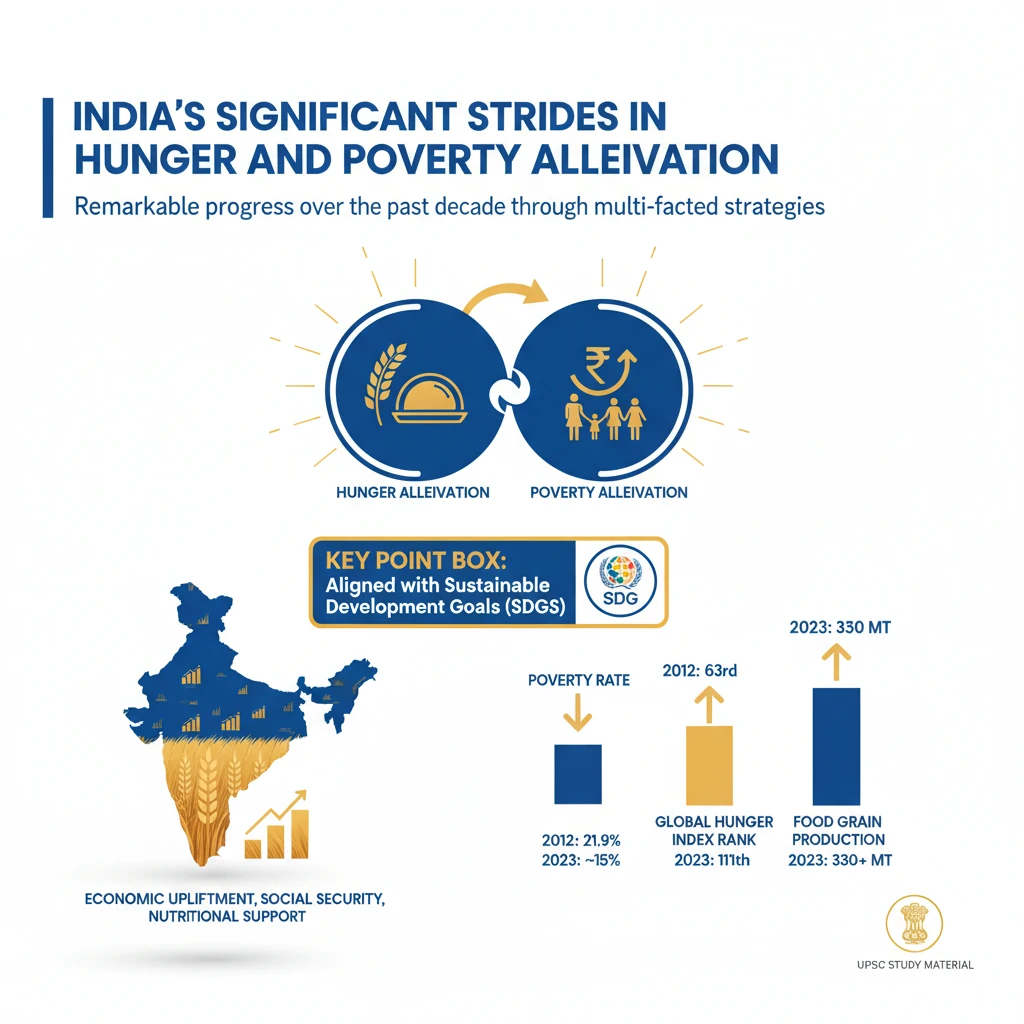
<h4>India's Significant Strides in Hunger and Poverty Alleviation</h4><p>India has demonstrated remarkable progress in addressing the critical issues of <strong>hunger</strong> and <strong>poverty alleviation</strong> over the past decade. This progress is a result of multi-faceted strategies focusing on economic upliftment, social security, and nutritional support.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The nation's commitment to these goals aligns with the <strong>Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)</strong>, particularly <strong>SDG 1 (No Poverty)</strong> and <strong>SDG 2 (Zero Hunger)</strong>.</p></div><h4>Poverty Alleviation Efforts</h4><p>A major achievement in recent years has been the substantial reduction in the number of people living in poverty. This indicates the effectiveness of various targeted interventions.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Between <strong>2014</strong> and <strong>2024</strong>, India successfully lifted approximately <strong>250 million people</strong> out of <strong>poverty</strong>, marking a significant milestone in its development journey.</p></div><h4>Ensuring Food Security for All</h4><p>Food security remains a cornerstone of India's welfare agenda, ensuring that vulnerable populations have access to adequate and nutritious food. Large-scale public distribution programs play a crucial role.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Currently, over <strong>800 million people</strong> across the country are provided with <strong>food grains free of cost</strong>, reinforcing the commitment to eliminate hunger.</p></div><h4>Expanding Health Insurance Coverage</h4><p>Access to affordable healthcare is vital for preventing catastrophic health expenditures that can push families into poverty. India has implemented one of the world's largest health assurance schemes.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>Ayushman Bharat-Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojna (PM-JAY)</strong> benefits <strong>550 million people</strong>, providing comprehensive health coverage. Additionally, <strong>60 million senior citizens</strong>, aged over <strong>70</strong>, are now eligible for <strong>free health insurance</strong>.</p></div><h4>Financial and Social Inclusion Initiatives</h4><p>Empowering women through financial independence and entrepreneurship is a key strategy for inclusive growth and poverty reduction. Connecting them to formal financial systems is paramount.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Over <strong>300 million women micro-entrepreneurs</strong> have been successfully linked to banks, gaining access to essential <strong>credit facilities</strong> to foster their businesses and livelihoods.</p></div><h4>Comprehensive Farmer Support</h4><p>The agricultural sector is critical for both food security and rural livelihoods. Government schemes provide financial assistance and risk mitigation to farmers, enhancing their resilience.</p><ul><li>Under the <strong>Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY)</strong>, more than <strong>40 million farmers</strong> have received benefits totaling over <strong>20 billion US dollars</strong>, safeguarding them against crop losses.</li><li>The <strong>PM-KISAN</strong> scheme has disbursed assistance worth over <strong>40 billion dollars</strong> to <strong>110 million farmers</strong>, providing direct income support.</li><li>India has also focused on agricultural innovation, developing over <strong>2000 climate-resilient crop varieties</strong> to combat environmental challenges.</li></ul><h4>Focused Nutritional Programs</h4><p>Addressing malnutrition, especially among vulnerable groups like women and children, is crucial for long-term human development. Integrated programs are designed to provide comprehensive nutritional support.</p><ul><li>The <strong>Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0</strong> campaign targets the nutritional needs of <strong>pregnant women</strong>, <strong>newborn babies</strong>, <strong>children under the age of 6</strong>, and <strong>adolescent girls</strong>.</li><li>The long-standing <strong>Mid-Day Meal scheme</strong> continues to pay special attention to the nutritional requirements of <strong>school-going children</strong>, improving health and educational outcomes.</li></ul><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> When discussing India's progress, always cite specific schemes and statistics. This adds credibility and depth to your answers in <strong>GS-I (Social Issues)</strong> and <strong>GS-II (Government Policies)</strong>. Remember to mention both the scale and the impact.</p></div>
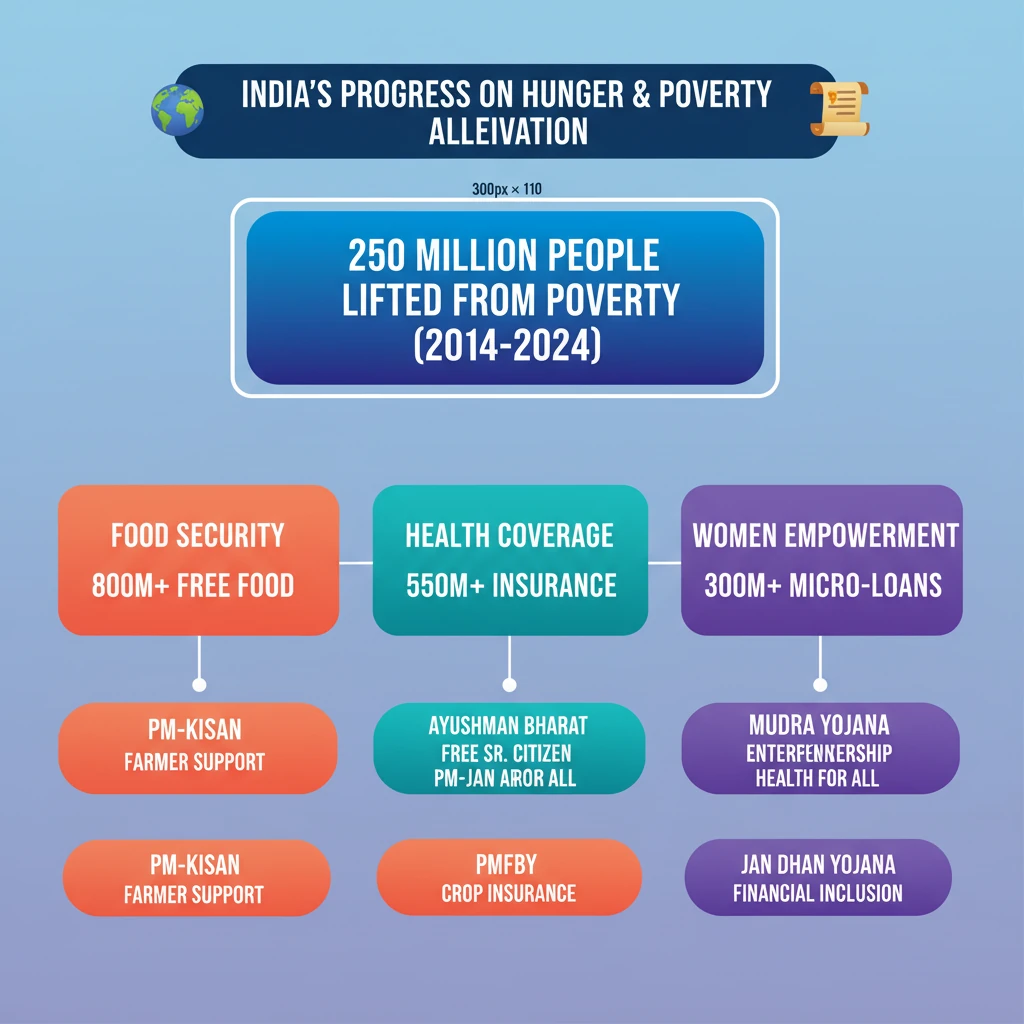
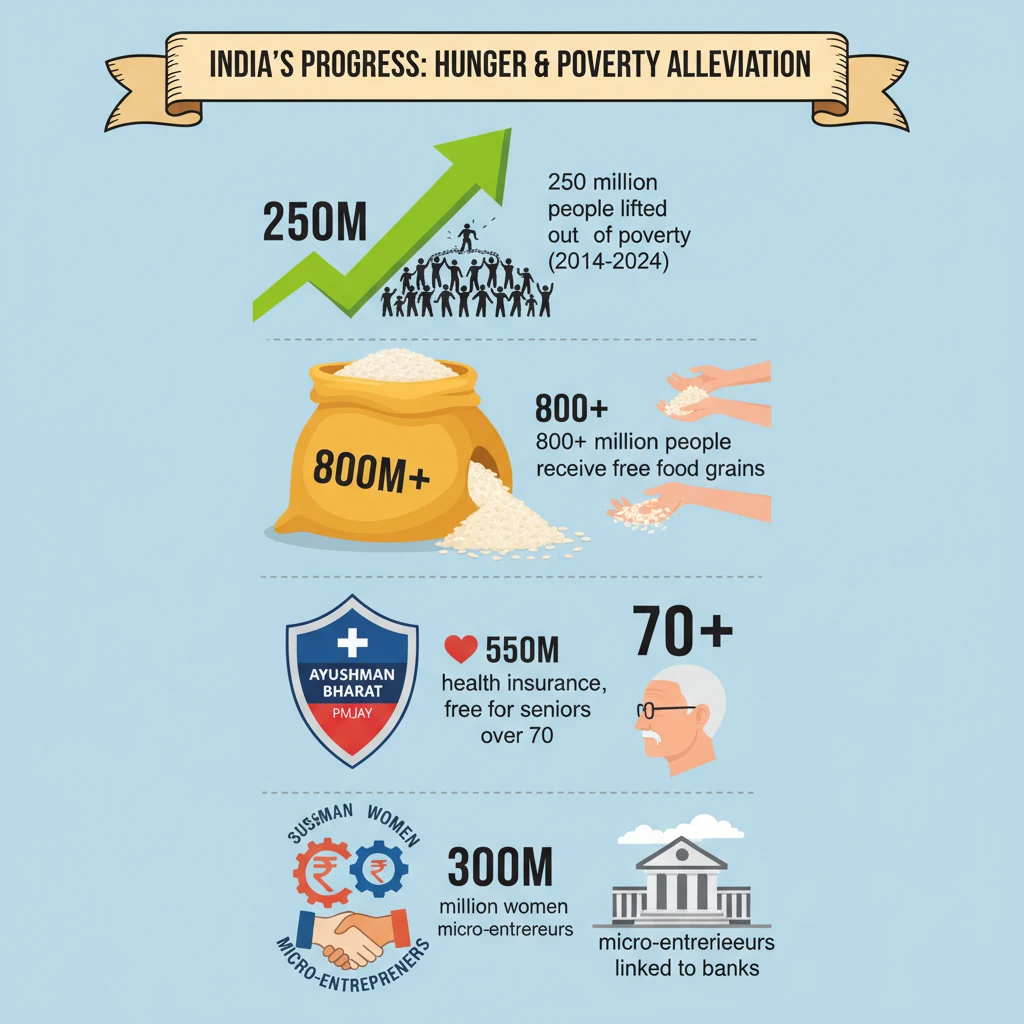
💡 Key Takeaways
- •India lifted 250 million people out of poverty between 2014-2024, a significant achievement.
- •Over 800 million people receive free food grains, ensuring widespread food security.
- •Ayushman Bharat-PMJAY provides health insurance to 550 million, including free cover for senior citizens over 70.
- •300 million women micro-entrepreneurs linked to banks, promoting financial and social inclusion.
- •PM-KISAN and PMFBY offer substantial financial support and risk coverage to over 100 million farmers.
- •Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0 focus on comprehensive nutrition for vulnerable groups, including children and pregnant women.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•NITI Aayog Reports on Poverty and Development
•Ministry of Rural Development, Government of India
•Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India
•Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, Government of India
•National Family Health Survey (NFHS) data