Political Representation of Women - Social Issues | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
Political Representation of Women
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
social issues
📖 Introduction
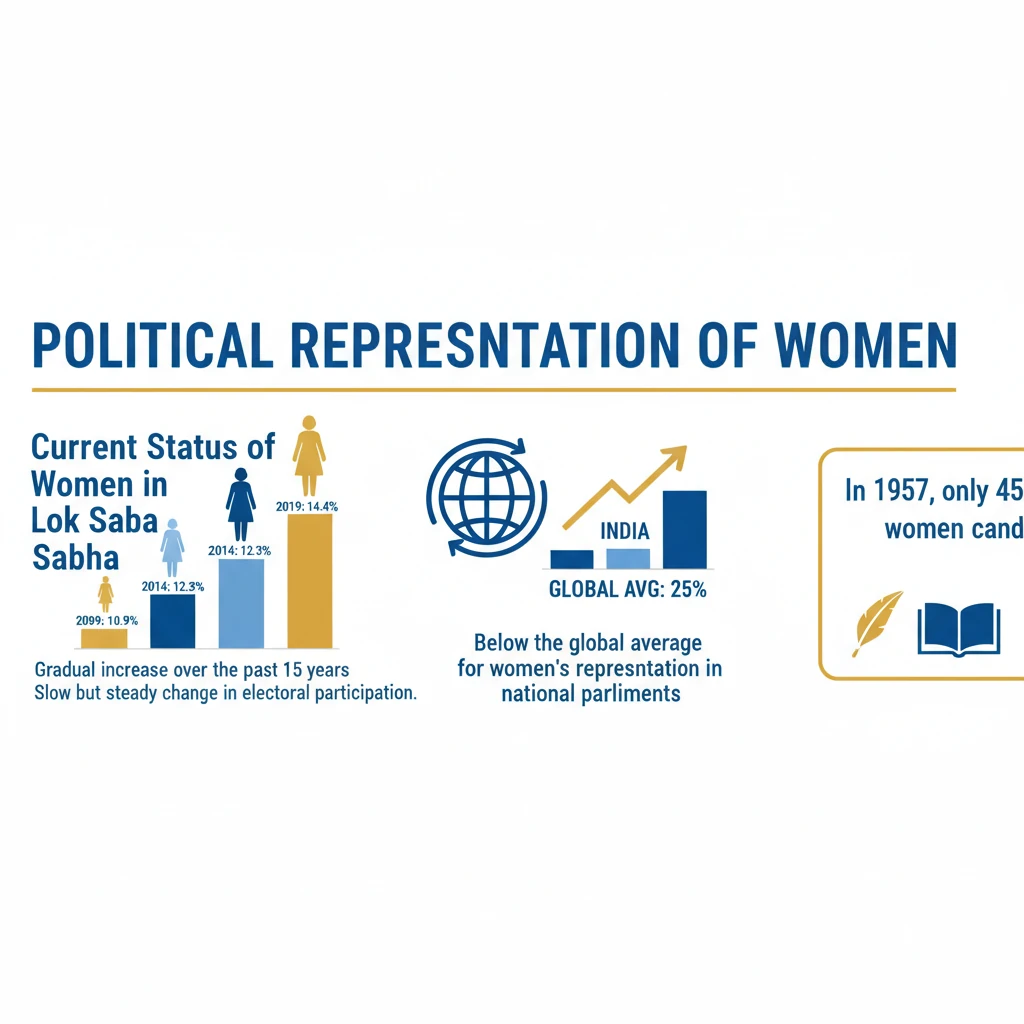
<h4>Current Status of Women in Lok Sabha</h4><p>The <strong>political representation of women</strong> in India's Lok Sabha has shown a <strong>gradual increase</strong> over the past 15 years, reflecting a slow but steady change in electoral participation.</p><p>Despite this rise, India's performance remains significantly <strong>below the global average</strong> for women's representation in national parliaments.</p><div class='info-box'><p>In <strong>1957</strong>, only <strong>45 women candidates</strong> contested the Lok Sabha election. By <strong>2024</strong>, this number surged to <strong>799 women candidates</strong>, constituting <strong>9.5%</strong> of the total candidates contested.</p></div><div class='key-point-box'><p>While the number of contesting women has grown, their overall proportion remains modest compared to the total pool of candidates.</p></div><h4>Leading States and Parties in Women's Representation</h4><p>Certain states and political parties have demonstrated better performance in electing women representatives to the Parliament.</p><p>This indicates that regional political dynamics and party ideologies can influence the extent of women's political empowerment.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>West Bengal</strong> leads among Indian states by electing the most women MPs, with <strong>11 representatives</strong> in the Lok Sabha.</p><p>The <strong>Trinamool Congress</strong> party stands out with the highest proportion of women among its Lok Sabha MPs, reaching <strong>38%</strong> in the <strong>18th Lok Sabha</strong>.</p></div><h4>Global Comparison of Women's Representation</h4><p>India's standing in global rankings for women's representation in the lower house of Parliament highlights a significant gap compared to many other nations.</p><p>This global perspective underscores the need for more concerted efforts to enhance gender parity in political spheres.</p><div class='info-box'><p>India ranks <strong>143 out of 185 countries</strong> in terms of women’s representation in its lower house of Parliament.</p><ul><li><strong>Sweden</strong> boasts <strong>46%</strong> female MPs.</li><li><strong>South Africa</strong> has <strong>45%</strong> female MPs.</li><li>The <strong>UK</strong> records <strong>40%</strong> female MPs.</li><li>The <strong>US</strong> has <strong>29%</strong> female MPs.</li></ul><p>India lags behind several developing nations, including <strong>Vietnam</strong>, the <strong>Philippines</strong>, <strong>Pakistan</strong>, and <strong>China</strong>, in gender representation.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Understanding these statistics is crucial for <strong>UPSC Mains GS Paper 1 (Social Issues)</strong> and <strong>GS Paper 2 (Polity)</strong>, especially when discussing gender justice, democratic deficits, and electoral reforms.</p></div><h4>Women’s Representation in State Legislatures</h4><p>The scenario of women's representation at the state level is even more concerning than at the national level, indicating deeper structural challenges.</p><p>The low numbers in State Legislative Assemblies reflect a broader issue of gender imbalance in regional politics.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>national average</strong> of women’s representation in <strong>State Legislative Assemblies</strong> is a mere <strong>9%</strong>.</p><p>No Indian state has more than <strong>20%</strong> women legislators. Even <strong>Chhattisgarh</strong>, the state with the highest representation, has only <strong>18%</strong> women MLAs.</p></div><div class='key-point-box'><p>This consistent underrepresentation across both national and state legislatures points to systemic barriers preventing women from entering and succeeding in political careers.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Women's representation in Lok Sabha increased from 45 candidates in 1957 to 799 in 2024 (9.5% of total).
- •India ranks 143 out of 185 countries in women's representation in the lower house, lagging behind many nations.
- •West Bengal leads in electing women MPs (11), and Trinamool Congress has the highest proportion (38%) among its MPs.
- •Representation in State Legislative Assemblies is even lower, with a national average of 9% and no state above 20%.
- •Low representation creates a democratic deficit and impacts gender-sensitive policy-making.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content