Anaemia: Causes, Impact, and Mitigation Strategies - Social Issues | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
Anaemia: Causes, Impact, and Mitigation Strategies
Easy⏱️ 10 min read
social issues
📖 Introduction
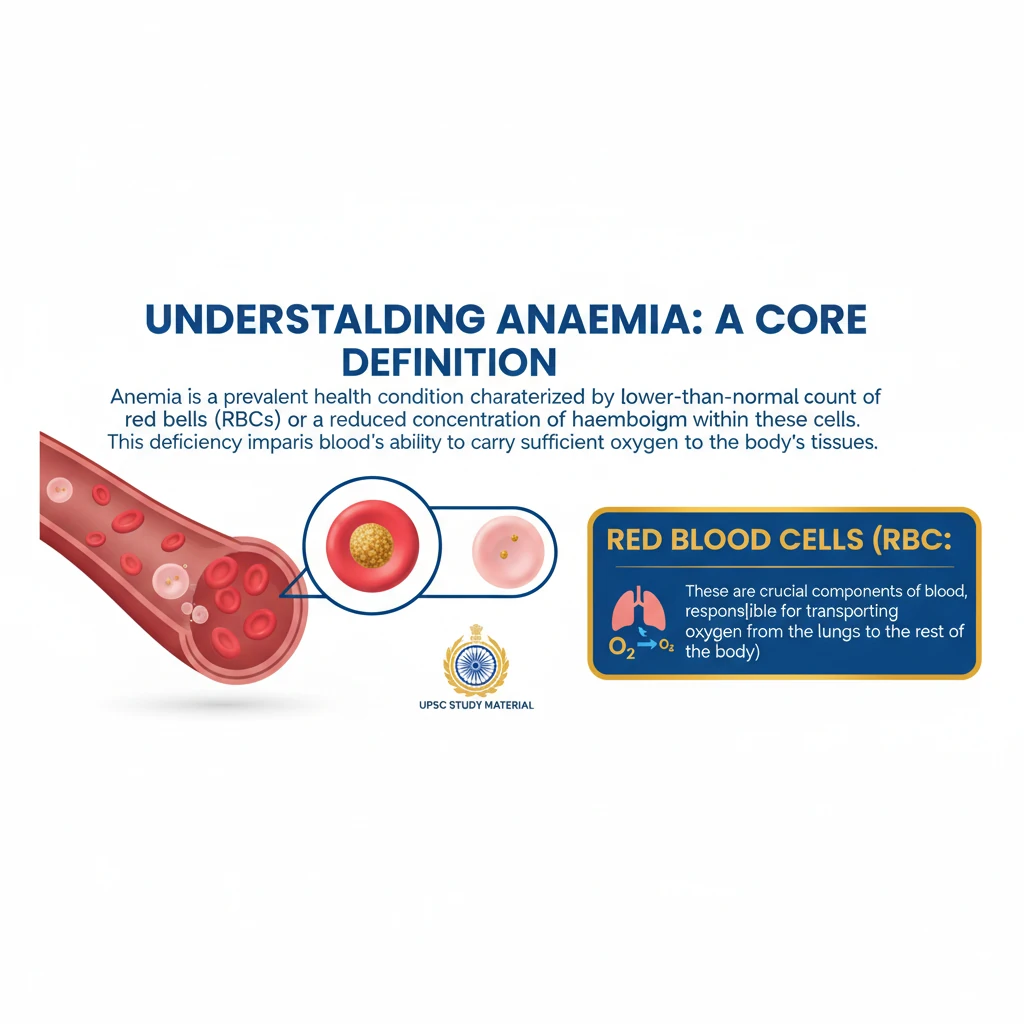
<h4>Understanding Anaemia: A Core Definition</h4><p><strong>Anaemia</strong> is a prevalent health condition characterized by a lower-than-normal count of <strong>red blood cells</strong> (RBCs) or a reduced concentration of <strong>haemoglobin</strong> within these cells. This deficiency impairs the blood's ability to carry sufficient <strong>oxygen</strong> to the body's tissues.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Red Blood Cells (RBCs):</strong> These are crucial components of blood, responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to various parts of the body and carrying carbon dioxide back to the lungs.</p></div><h4>The Role of Haemoglobin</h4><p><strong>Haemoglobin</strong> is a vital protein found within <strong>red blood cells</strong>. Its primary function is to bind with <strong>oxygen</strong> in the lungs and release it in tissues where it's needed for metabolic processes. A healthy haemoglobin level is essential for optimal bodily function.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Haemoglobin Composition:</strong> It is an iron-rich protein, giving blood its characteristic red color. The iron component is critical for its oxygen-binding capacity.</p></div><h4>Impact of Reduced Haemoglobin</h4><p>When <strong>haemoglobin</strong> levels are low, the body's tissues and organs do not receive adequate <strong>oxygen</strong>. This leads to a range of symptoms, including fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, dizziness, and pale skin. Severe anaemia can have serious health consequences.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Key Concept: Oxygen Transport.</strong> The entire pathology of anaemia revolves around the impaired capacity of blood to transport oxygen, directly impacting cellular respiration and overall energy production.</p></div><h4>Causes and Types of Anaemia</h4><p>Anaemia can stem from various causes, broadly categorized into three main groups: decreased <strong>red blood cell</strong> production, increased <strong>red blood cell</strong> destruction, or significant blood loss. Nutritional deficiencies are a major contributor, especially in developing countries.</p><ul><li><strong>Nutritional Anaemias:</strong> Often caused by deficiencies in <strong>iron</strong>, <strong>Vitamin B12</strong>, or <strong>folate</strong>.</li><li><strong>Haemolytic Anaemias:</strong> Occur when red blood cells are destroyed faster than they can be produced (e.g., <strong>Sickle Cell Anaemia</strong>, <strong>Thalassemia</strong>).</li><li><strong>Aplastic Anaemia:</strong> A rare condition where the bone marrow fails to produce enough blood cells.</li><li><strong>Anaemia of Chronic Disease:</strong> Associated with chronic inflammatory conditions, infections, or cancers.</li></ul><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> While the definition is fundamental, UPSC questions often focus on the <strong>causes, consequences, prevalence, and government initiatives</strong> related to anaemia, particularly in the context of public health and women's/child health.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Anaemia is characterized by low red blood cells or haemoglobin, impairing oxygen transport.
- •Haemoglobin is an iron-rich protein vital for oxygen binding and delivery.
- •Common causes include iron, Vitamin B12, or folate deficiencies, blood loss, and genetic disorders.
- •Symptoms range from fatigue and weakness to severe organ damage in chronic cases.
- •Anaemia is a major public health issue in India, particularly for women and children.
- •Government initiatives like Anaemia Mukt Bharat aim to reduce its prevalence and impact.
🧠 Memory Techniques
98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•World Health Organization (WHO) - Anaemia Fact Sheets
•Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India - Anaemia Mukt Bharat Guidelines
•National Family Health Survey (NFHS) data
•NCERT Biology Textbooks