What is MGNREGA Scheme? - Social Issues | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What is MGNREGA Scheme?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
social issues
📖 Introduction
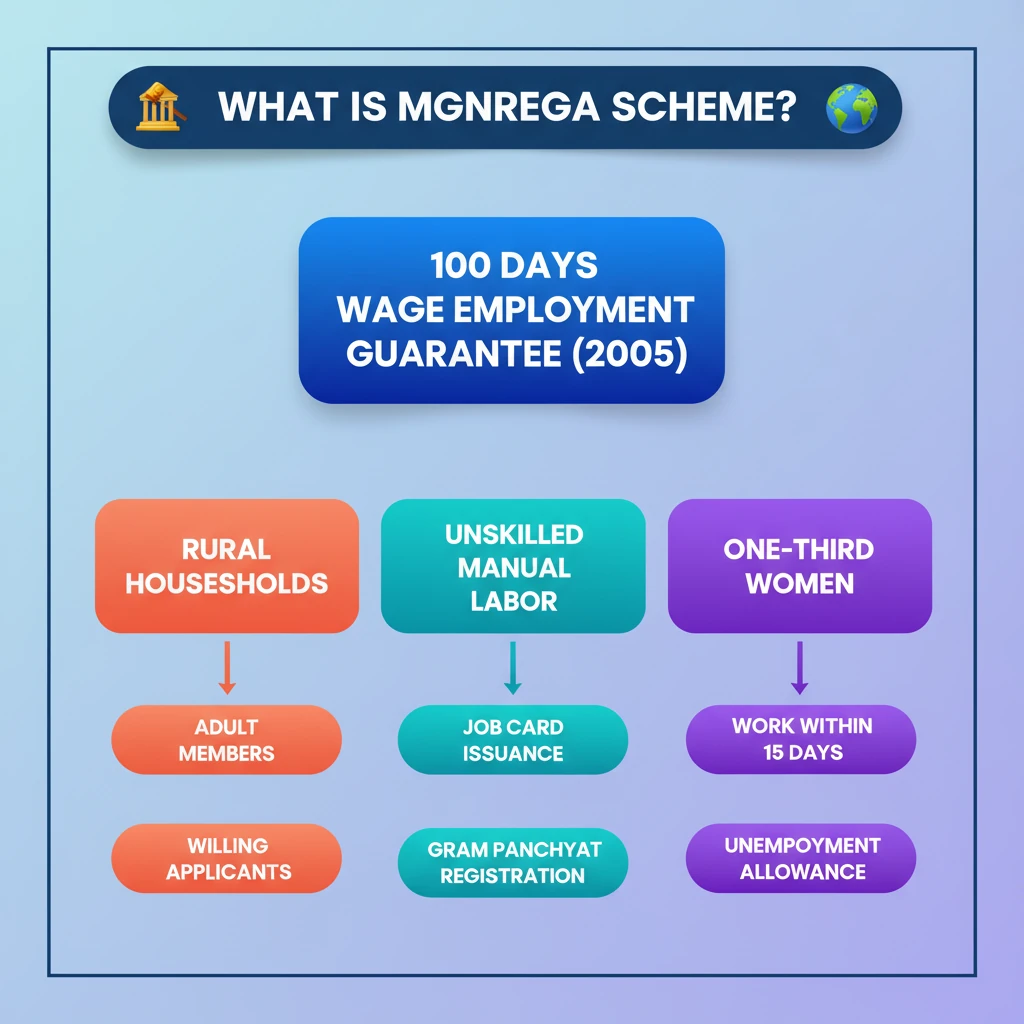
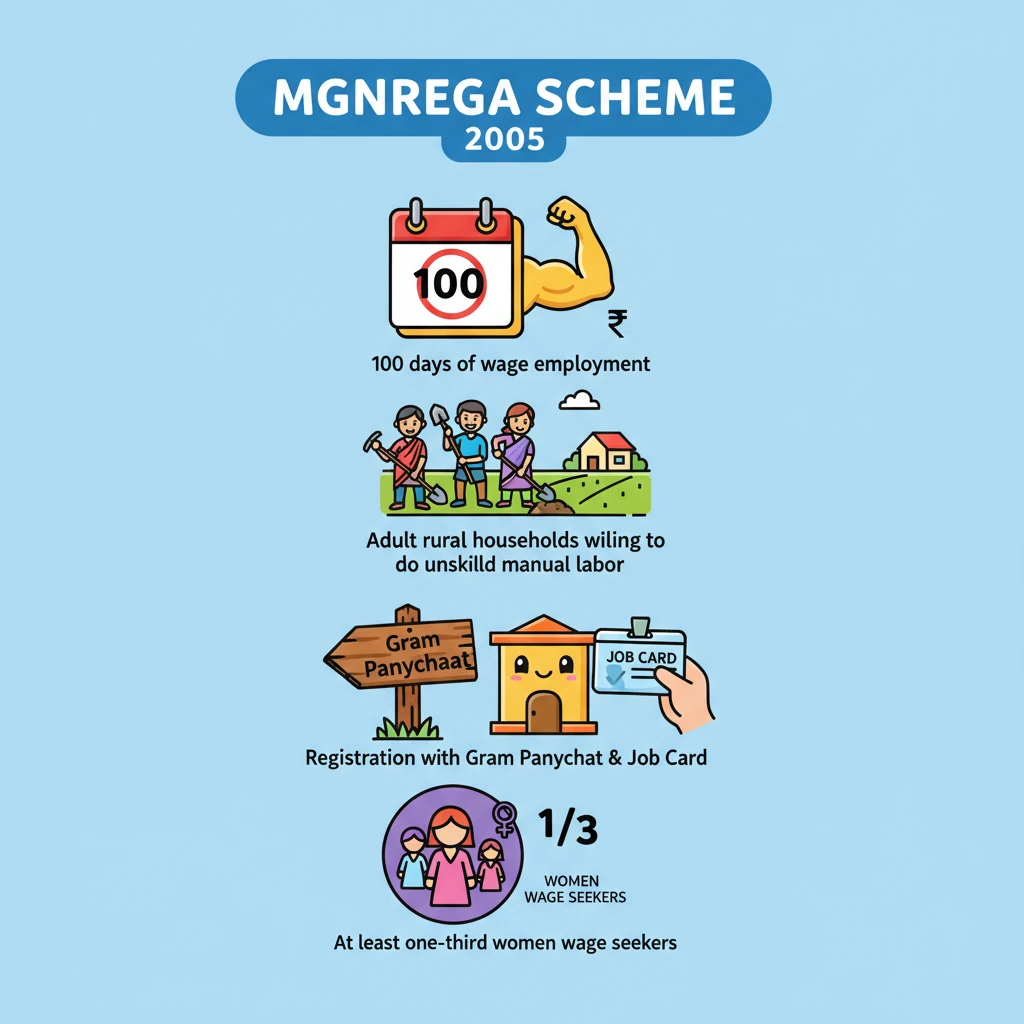
<h4>Introduction to MGNREGA</h4><p>The <strong>Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA)</strong>, enacted in <strong>September 2005</strong>, is a landmark legislation in India.</p><p>It provides a <strong>legal guarantee for wage employment</strong>, aiming to enhance the livelihood security of millions in rural areas.</p><div class="info-box"><p>The <strong>MGNREGA scheme</strong> operates under this Act, ensuring a safety net for vulnerable rural households.</p></div><h4>Core Objectives of the Scheme</h4><p>The primary objective of <strong>MGNREGA</strong> is to boost <strong>livelihood security</strong> in India's rural regions.</p><p>It achieves this by guaranteeing <strong>100 days of wage employment</strong> in a financial year to adult members of rural households.</p><p>This employment is specifically for those willing to undertake <strong>unskilled manual labor</strong>.</p><div class="key-point-box"><p>The scheme acts as a crucial social safety net and a tool for rural development.</p></div><h4>Eligibility Criteria and Registration</h4><p>The scheme targets <strong>all rural households</strong> that require employment and are willing to perform <strong>manual, unskilled work</strong>.</p><p>To access the benefits, applicants must submit their requests to the local <strong>Gram Panchayat</strong>.</p><p>Upon verification, the <strong>Gram Panchayat</strong> registers eligible households and issues them a <strong>job card</strong>.</p><div class="info-box"><p><strong>Priority for Women:</strong> A significant provision mandates that at least <strong>one-third of the wage seekers</strong> under the scheme should be <strong>women</strong>, promoting gender equity.</p></div><h4>Employment Provision and Conditions</h4><p>Once registered, the <strong>Gram Panchayat</strong> or <strong>Block Programme Officer</strong> is obligated to provide work within <strong>15 days</strong> of the application.</p><p>Ideally, work should be provided within a <strong>5-kilometer radius</strong> of the applicant’s village to minimize travel burden.</p><p>If work is assigned beyond this distance, an additional <strong>10% wage</strong> is provided to cover transportation and living costs.</p><div class="info-box"><p><strong>Work Duration:</strong> Employment provided should last for a minimum of <strong>14 consecutive days</strong>, with a maximum of <strong>six workdays per week</strong>.</p></div><h4>Unemployment Allowance</h4><p>A critical feature of the scheme is the provision for an <strong>unemployment allowance</strong>.</p><p>If employment is not provided within the stipulated <strong>15 days</strong> of application, beneficiaries are entitled to this allowance.</p><div class="info-box"><p><strong>Allowance Structure:</strong> The allowance is <strong>one-fourth of the wage rate</strong> for the first <strong>30 days</strong> and increases to at least <strong>half of the wage rate</strong> for the remaining period.</p></div><h4>Due Process for Deletion of Workers</h4><p>The scheme outlines a clear and transparent <strong>due process for deletion</strong> of workers from the rolls.</p><p>This ensures fairness and prevents arbitrary removal of beneficiaries.</p><div class="key-point-box"><ul><li><strong>Hearing:</strong> Workers proposed for deletion must be heard, with <strong>two independent persons present</strong>.</li><li><strong>Verification:</strong> Reasons for deletion must be <strong>independently verified</strong>.</li><li><strong>Documentation:</strong> All actions and findings must be <strong>documented</strong>.</li><li><strong>Transparency:</strong> Reports are shared with the <strong>Gram Sabha</strong> or <strong>Ward Sabha</strong> for complete transparency.</li></ul></div><h4>Aadhaar-Based Payment System (ABPS)</h4><p>The <strong>Aadhaar-Based Payment System (ABPS)</strong> is an integral part of the payment mechanism under <strong>MGNREGA</strong>.</p><p>It streamlines the transfer of wages and benefits directly to beneficiaries.</p><div class="info-box"><p><strong>ABPS Functionality:</strong> This system uses <strong>Aadhaar numbers</strong> to electronically send government subsidies and benefits to the <strong>Aadhaar-linked bank accounts</strong> of beneficiaries, ensuring direct and efficient transfers.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •MGNREGA, enacted in 2005, provides a legal guarantee for 100 days of wage employment per financial year.
- •Targets adult members of rural households willing to do unskilled manual labor.
- •Eligibility involves registration with Gram Panchayat and issuance of a job card.
- •Mandates at least one-third women wage seekers.
- •Work must be provided within 15 days; otherwise, unemployment allowance is paid.
- •Includes a transparent due process for worker deletion and uses Aadhaar-Based Payment System (ABPS).
🧠 Memory Techniques
98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Official MGNREGA Website, Ministry of Rural Development, Government of India
•Economic Survey of India (relevant years)
•Reports from NITI Aayog on rural development schemes