What are India’s Initiatives to Address Hunger? - Social Issues | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What are India’s Initiatives to Address Hunger?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
social issues
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to India's Hunger Initiatives</h4><p>India, a nation committed to achieving <strong>Sustainable Development Goal 2 (Zero Hunger)</strong>, has launched a multi-pronged approach to combat hunger and malnutrition. These initiatives span various sectors, from food security and nutrition to public health and maternal care, aiming for holistic development.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Understanding these schemes is crucial for <strong>UPSC Civil Services Exam</strong>, particularly for <strong>GS Paper I (Social Issues)</strong> and <strong>GS Paper II (Governance, Social Justice)</strong>. Focus on objectives, beneficiaries, and outcomes.</p></div><h4>Eat Right India Movement</h4><p>The <strong>Eat Right India Movement</strong>, spearheaded by the <strong>Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI)</strong>, aims to improve public health by ensuring safe, healthy, and sustainable food for all citizens. It adopts a 'preventive healthcare' approach.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Objective:</strong> To nudge people towards healthier food choices and to ensure food safety standards across the country.</p><p><strong>Key Pillars:</strong> 'Eat Safe', 'Eat Healthy', 'Eat Sustainable'.</p></div><h4>POSHAN Abhiyan (National Nutrition Mission)</h4><p>The <strong>POSHAN Abhiyan</strong>, launched in <strong>2018</strong>, is the Government of India's flagship program to improve nutritional outcomes for children, adolescent girls, pregnant women, and lactating mothers. It employs a life-cycle approach to nutrition.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>This mission aims to reduce <strong>stunting</strong>, <strong>under-nutrition</strong>, <strong>anemia</strong>, and <strong>low birth weight</strong> among children, and anemia among women and adolescent girls.</p></div><h4>Mid-day Meal (MDM) Scheme</h4><p>The <strong>Mid-day Meal Scheme</strong>, now known as <strong>PM-POSHAN Scheme</strong>, is a centrally sponsored scheme providing one hot cooked meal to children in government and government-aided schools. It was launched in <strong>1995</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Dual Objectives:</strong> To enhance enrollment, retention, and attendance in schools, and to improve the nutritional status of children.</p></div><h4>Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY)</h4><p>The <strong>Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY)</strong> is a maternity benefit program launched in <strong>2017</strong>. It provides partial compensation for wage loss during pregnancy and childbirth, ensuring safe delivery and good nutrition.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>Eligible pregnant women and lactating mothers receive a cash incentive of <strong>₹5,000</strong> in three installments upon fulfilling specific health conditions.</p></div><h4>National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013</h4><p>The <strong>National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013</strong>, legally entitles up to <strong>75% of the rural population</strong> and <strong>50% of the urban population</strong> to receive subsidized food grains. It is a landmark legislation in ensuring food security.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Provisions:</strong> Provides <strong>5 kg of food grains per person per month</strong> at highly subsidized prices (rice at ₹3, wheat at ₹2, coarse grains at ₹1 per kg).</p><p>Also includes provisions for maternity benefits and child nutrition.</p></div><h4>Mission Indradhanush</h4><p><strong>Mission Indradhanush</strong>, launched in <strong>2014</strong>, is a flagship immunization program by the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare. While primarily focused on health, it indirectly addresses malnutrition by preventing diseases that exacerbate nutritional deficiencies.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>It aims to immunize all unvaccinated and partially vaccinated children and pregnant women against <strong>12 vaccine-preventable diseases</strong>.</p></div><h4>Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) Scheme</h4><p>The <strong>Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) Scheme</strong>, launched in <strong>1975</strong>, is one of the world's largest and most unique programs for early childhood development. It provides a package of services to children below 6 years and pregnant/lactating mothers.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Services include:</strong> Supplementary nutrition, immunization, health check-up, referral services, pre-school non-formal education, and nutrition & health education.</p></div>
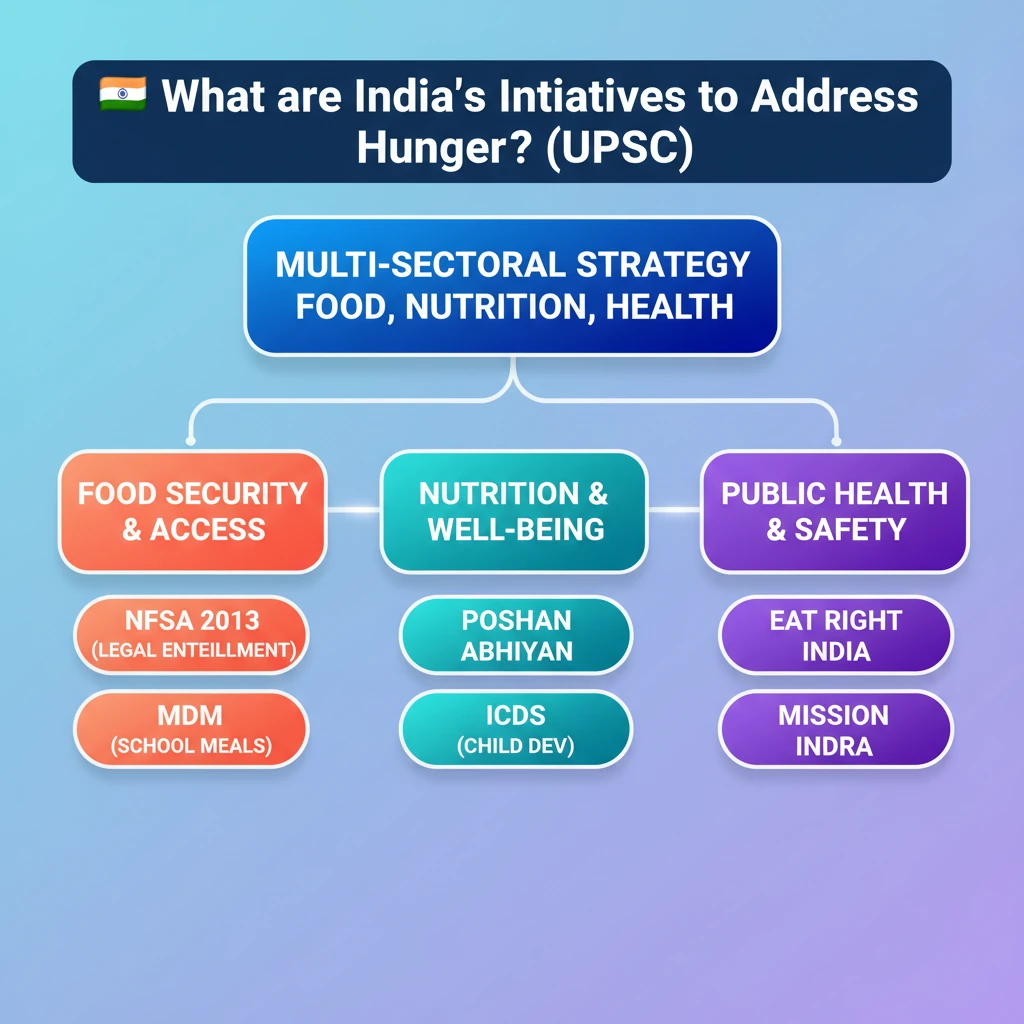
💡 Key Takeaways
- •India employs a multi-sectoral strategy to combat hunger, encompassing food security, nutrition, and public health.
- •Key initiatives include NFSA (legal food entitlement), POSHAN Abhiyan (nutrition improvement), MDM (school meals), PMMVY (maternity benefits), ICDS (early childhood development), Eat Right India (food safety), and Mission Indradhanush (immunization).
- •There's a shift from welfare-based to rights-based approach (NFSA) and a focus on holistic nutrition (POSHAN Abhiyan).
- •Convergence of ministries and technology integration are crucial for effective implementation and monitoring.
- •Challenges remain, emphasizing the need for continuous evaluation, adaptation, and community participation to achieve Zero Hunger.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (MoHFW) - Mission Indradhanush, PMMVY
•Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution - NFSA, PDS
•Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) - Eat Right India Movement
•NITI Aayog reports on nutrition and food security
•Press Information Bureau (PIB) releases