Tribal Development Approaches - Social Issues | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Tribal Development Approaches
Medium⏱️ 10 min read
social issues
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to Tribal Development Approaches</h4><p>The recent protest by <strong>Hana-Rawhiti Kareariki Maipi-Clarke</strong>, the youngest Member of Parliament in <strong>New Zealand</strong>, has brought global attention to the complexities of <strong>tribal development approaches</strong>. Representing a <strong>Maori tribe</strong>, her <strong>haka protest</strong> highlighted the ongoing debate.</p><p>This incident underscores the challenge of balancing the preservation of <strong>cultural heritage</strong> with the demands of <strong>modern governance</strong> in policies related to indigenous communities.</p><h4>Understanding the Haka Protest</h4><p>The <strong>haka protest</strong> was a direct response to the introduction of the <strong>Treaty Principles Bill</strong> in New Zealand. This bill seeks to reinterpret a foundational document of the nation's history.</p><p>The protest, a powerful display of <strong>Maori identity</strong>, symbolized resistance against perceived threats to indigenous rights and traditional understandings of the treaty.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>What is Haka?</strong></p><ul><li>The <strong>Haka</strong> is a traditional <strong>Maori dance</strong>.</li><li>Historically performed by <strong>warriors on the battlefield</strong> or as a <strong>welcome gesture</strong>.</li><li>Involves <strong>chanting</strong>, intense <strong>facial expressions</strong>, and vigorous <strong>hand movements</strong>.</li><li>It is a profound representation of <strong>Maori identity</strong> and has evolved into a symbol of <strong>resistance</strong>.</li></ul></div><h4>The Maori Tribe and its Significance</h4><p>The <strong>Maori tribe</strong> comprises the <strong>indigenous people</strong> who have historically inhabited <strong>New Zealand</strong>. Their culture, language, and traditions are integral to the nation's identity.</p><p>Their unique status and historical relationship with the Crown are enshrined in the <strong>Treaty of Waitangi</strong>.</p><h4>The Treaty of Waitangi (1840)</h4><p>The <strong>1840 Treaty of Waitangi</strong> is a pivotal document that established the relationship between the <strong>British Crown</strong> and <strong>Māori chiefs</strong> in New Zealand. It is considered the founding document of the nation.</p><p>Its principles and interpretations have been a continuous source of debate, forming the bedrock of <strong>Māori rights</strong> and their relationship with the state.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The <strong>Treaty of Waitangi</strong> is crucial because it recognized <strong>Māori sovereignty</strong> and guaranteed their rights to lands, forests, fisheries, and other treasures, in exchange for British sovereignty over New Zealand.</p></div><h4>The Treaty Principles Bill</h4><p>The controversial <strong>Treaty Principles Bill</strong> aims to reinterpret the <strong>1840 Treaty of Waitangi</strong>. Its stated goal is to ensure <strong>equality for all New Zealanders</strong>.</p><p>However, critics argue that this approach, by applying treaty principles equally to all citizens, fails to acknowledge the <strong>distinct rights</strong> and historical grievances of the <strong>Māori as Indigenous people</strong>.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> This case highlights the universal challenge of <strong>reconciling indigenous rights with national governance structures</strong>. For UPSC, understand the tension between <strong>assimilationist vs. recognition-based tribal development models</strong>, relevant for <strong>GS-I Social Issues</strong> and <strong>GS-II Polity</strong>.</p></div><p>This reinterpretation is viewed by many as undermining the specific <strong>legal protections</strong> and historical recognition afforded to <strong>Māori</strong> under the original <strong>Treaty of Waitangi</strong>.</p>
💡 Key Takeaways
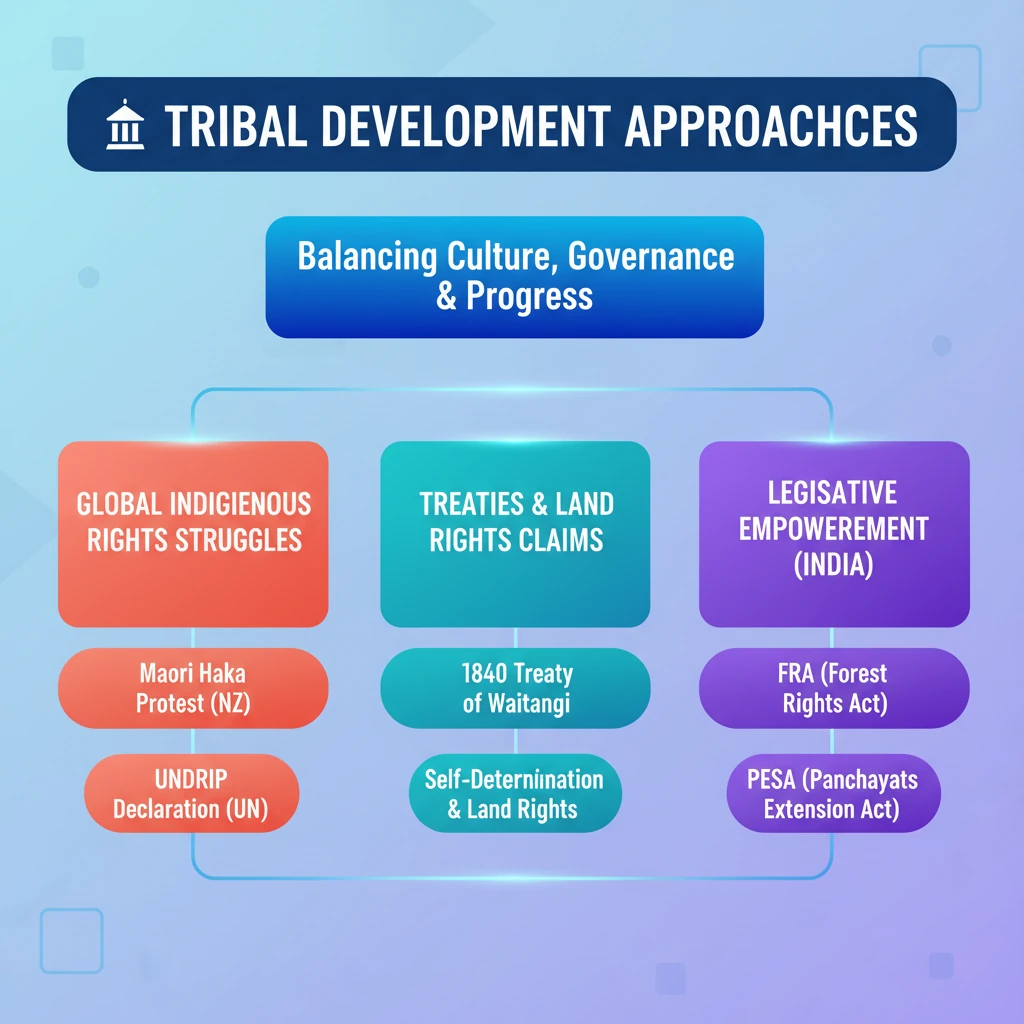
- •Tribal development involves balancing cultural preservation with modern governance and socio-economic progress.
- •The Maori Haka protest against New Zealand's Treaty Principles Bill highlights global indigenous rights struggles.
- •The 1840 Treaty of Waitangi is a foundational document whose reinterpretation is causing conflict.
- •Indigenous rights include self-determination, land rights, and cultural protection, often enshrined in international declarations like UNDRIP.
- •In India, acts like FRA and PESA are key legislative approaches to tribal empowerment and self-governance.
- •Effective tribal development requires recognizing distinct rights, not just 'equality for all,' to avoid undermining historical protections.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Official website of New Zealand Parliament (for Haka protest context)
•The Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006 (FRA)
•The Panchayats (Extension to Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996 (PESA)
•United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples (UNDRIP)