What is the POCSO Act? - Social Issues | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What is the POCSO Act?
Easy⏱️ 7 min read
social issues
📖 Introduction
<h4>Understanding the POCSO Act</h4><p>The <strong>Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012</strong>, is a landmark legislation in India. It specifically addresses and aims to prevent crimes related to the <strong>sexual exploitation</strong> and <strong>sexual abuse of children</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Objective:</strong> To provide a comprehensive legal framework for the protection of children from sexual offenses.</p></div><h4>Definition of 'Child' under POCSO</h4><p>A crucial aspect of the Act is its clear definition of who constitutes a child. This ensures that its protective provisions are applied uniformly across the country.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Under the <strong>POCSO Act</strong>, a <strong>child</strong> is defined as any person who is <strong>below the age of 18 years</strong>. This definition aligns with international standards for child protection.</p></div><h4>International Mandate and Enactment</h4><p>The enactment of the <strong>POCSO Act</strong> was not an isolated domestic initiative. It was a direct response to India's commitment on the global stage towards child rights.</p><p>India's ratification of the <strong>UN Convention on the Rights of the Child (UNCRC)</strong> in <strong>1992</strong> served as a primary catalyst. The <strong>POCSO Act</strong> was subsequently enacted to fulfill these international obligations.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> The connection between international conventions (like <strong>UNCRC</strong>) and domestic legislation (like <strong>POCSO</strong>) is a recurring theme in <strong>GS-II (Polity and Governance)</strong>. Understanding this link is vital.</p></div><h4>Salient Features of the POCSO Act</h4><p>The Act incorporates several progressive features designed to offer robust protection to child victims and ensure justice. These features make it a comprehensive and victim-centric law.</p><ul><li><strong>Gender-Neutral Nature:</strong> The Act acknowledges that both <strong>girls and boys</strong> can be victims of sexual abuse. It ensures that such abuse is considered a crime irrespective of the victim's gender.</li><li><strong>Confidentiality of Victim's Identity:</strong> <strong>Section 23</strong> of the <strong>POCSO Act, 2012</strong>, strictly mandates the confidentiality of a child victim's identity. This provision is critical for protecting the child's privacy and future well-being.</li><li><strong>Mandatory Reporting of Child Abuse Cases:</strong> <strong>Sections 19 to 22</strong> of the Act impose a legal obligation on individuals. Anyone with knowledge or reasonable suspicion of a <strong>POCSO offense</strong> must report it to the appropriate authorities.</li></ul><h4>Protecting Victim Identity</h4><p>The confidentiality clause is vital to prevent secondary victimization and stigmatization. It places strict restrictions on information disclosure.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Media reports</strong> are explicitly prohibited from disclosing any details that could reveal the victim’s identity. This includes their <strong>name, address, family information</strong>, or any other identifying particulars.</p></div><h4>Ensuring Accountability through Reporting</h4><p>The mandatory reporting provisions are designed to create a network of vigilance. They ensure that cases of child abuse do not go unreported.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>This legal compulsion helps in early intervention and prosecution, thereby safeguarding children more effectively. It involves various stakeholders, including teachers, doctors, and even concerned citizens.</p></div>
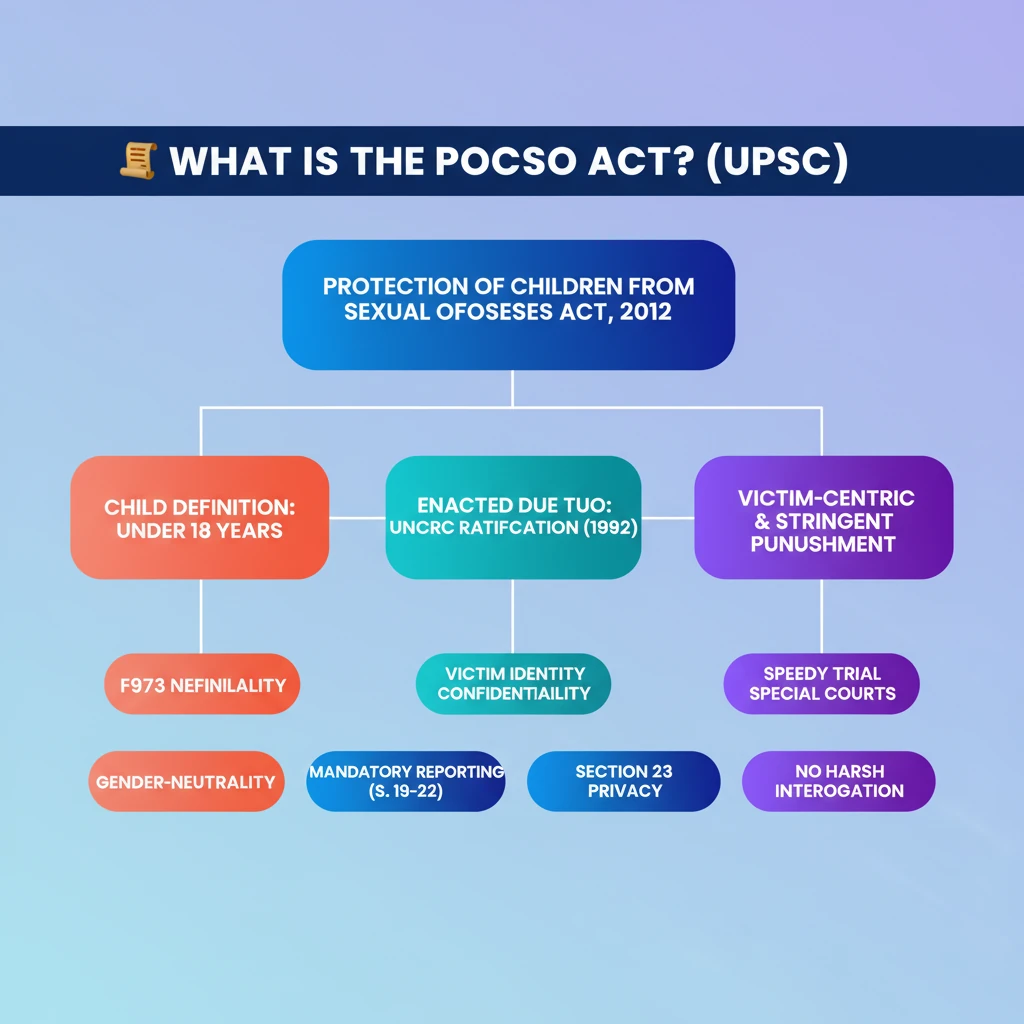
💡 Key Takeaways
- •POCSO Act, 2012, protects children from sexual offenses.
- •Defines a child as anyone under 18 years.
- •Enacted due to India's UNCRC ratification (1992).
- •Key features: gender-neutrality, victim identity confidentiality (Section 23), mandatory reporting (Sections 19-22).
- •Aims for a victim-centric approach and stringent punishment.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content