Tobacco Control Legislation: COTPA, NTCP & PECA - Social Issues | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Tobacco Control Legislation: COTPA, NTCP & PECA
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
social issues
📖 Introduction
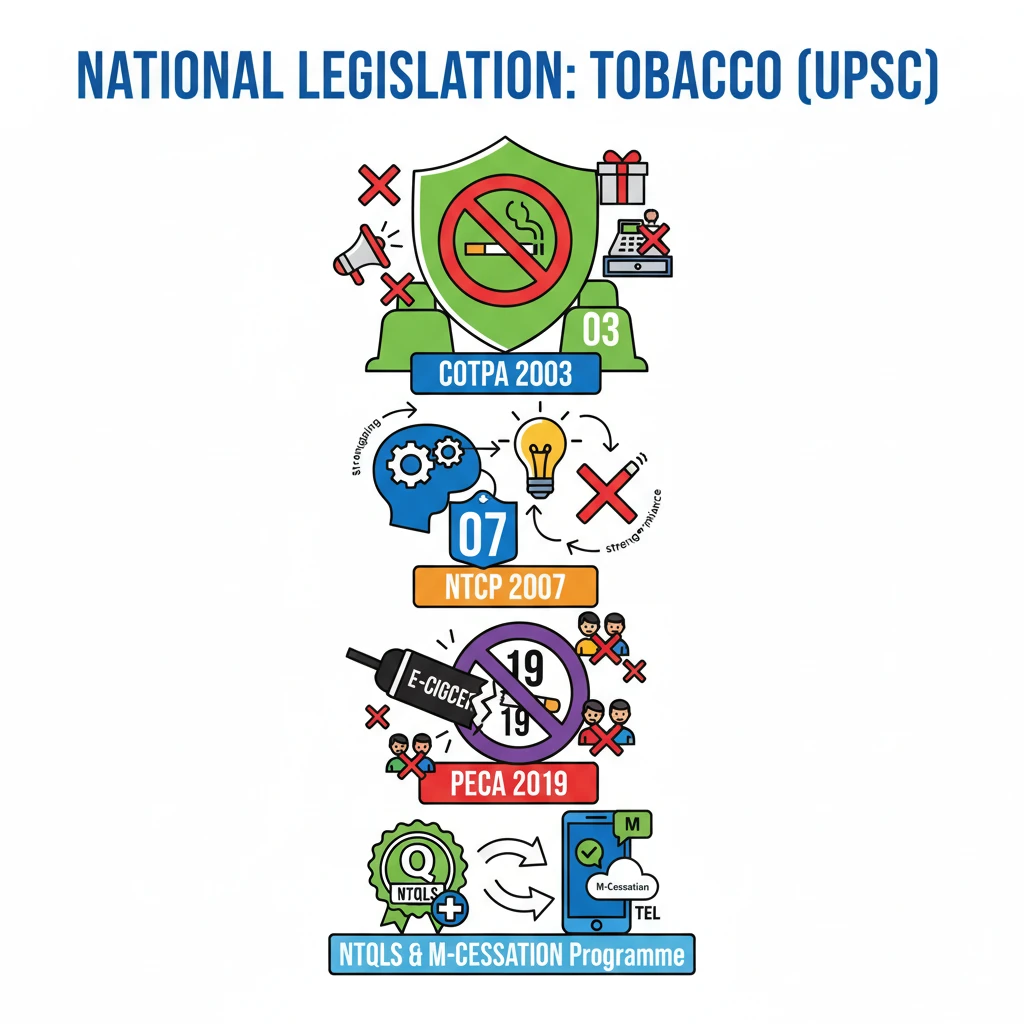
<h4>Understanding National Tobacco Control Legislation</h4><p>India has implemented a robust framework of national legislation and programs to combat tobacco use and its associated health risks. These initiatives aim to regulate the production, sale, distribution, and advertisement of tobacco products, alongside promoting public awareness and cessation.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The primary goal of these legislations is to safeguard public health by reducing tobacco consumption and protecting citizens, especially the youth, from its harmful effects.</p></div><h4>Cigarettes and Other Tobacco Products (Prohibition of Advertisement and Regulation of Trade and Commerce, Production, Supply and Distribution) Act (COTPA) 2003</h4><p>The <strong>Cigarettes and Other Tobacco Products Act (COTPA)</strong>, enacted in <strong>2003</strong>, is the cornerstone of tobacco control in India. It provides a comprehensive legal framework to regulate various aspects of tobacco products.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>COTPA 2003</strong> governs key areas:</p><ul><li><strong>Production and Supply</strong>: Regulates manufacturing standards and availability.</li><li><strong>Advertising and Promotion</strong>: Prohibits direct and indirect advertisement of tobacco products.</li><li><strong>Distribution and Sale</strong>: Specifies rules for point-of-sale, including age restrictions.</li><li><strong>Packaging and Labeling</strong>: Mandates pictorial health warnings on tobacco product packaging.</li></ul></div><h4>National Tobacco Control Program (NTCP) 2007</h4><p>The <strong>National Tobacco Control Program (NTCP)</strong> was launched in <strong>2007</strong>. Its main objective is to strengthen the implementation of <strong>COTPA 2003</strong> and ensure India's compliance with the <strong>WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC)</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Key functions of <strong>NTCP</strong> include:</p><ul><li><strong>Public Awareness Campaigns</strong>: Utilizes mass media to educate the public about the severe health risks associated with tobacco use.</li><li><strong>Smoking Cessation Initiatives</strong>: Provides support for individuals to quit tobacco through various interventions like quitlines and counseling.</li><li><strong>Enforcement Mechanisms</strong>: Strengthens the enforcement of <strong>COTPA</strong> provisions through designated authorities at national, state, and district levels.</li></ul></div><h4>The Prohibition of Electronic Cigarette Act (PECA), 2019</h4><p>Recognizing the emerging threat of new tobacco products, the <strong>Prohibition of Electronic Cigarette Act (PECA)</strong> was enacted in <strong>2019</strong>. This landmark legislation completely banned <strong>e-cigarettes</strong> in India.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>PECA 2019</strong> prohibits the production, manufacture, import, export, transport, sale, distribution, storage, and advertisement of <strong>e-cigarettes</strong> and similar devices across the country.</p></div><h4>National Tobacco Quitline Services (NTQLS)</h4><p>The <strong>National Tobacco Quitline Services (NTQLS)</strong> offers crucial support for tobacco users seeking to quit. It provides free, confidential counseling and guidance through a toll-free number.</p><h4>M-Cessation Programme</h4><p>The <strong>M-Cessation Programme</strong> is an innovative initiative leveraging mobile technology for tobacco cessation. It was launched in <strong>2016</strong> as a part of the government’s broader <strong>Digital India</strong> initiative.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>M-Cessation Programme</strong> provides support to tobacco users through:</p><ul><li><strong>Text messages</strong>: Delivers motivational and informative messages.</li><li><strong>Interactive voice response (IVR)</strong>: Offers guided cessation support.</li><li><strong>Personalized follow-ups</strong>: Helps users stay on track with their quit journey.</li></ul></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>For <strong>UPSC Mains GS-II (Social Justice - Health)</strong>, understanding these legislations and programs is crucial. Questions often revolve around their effectiveness, challenges in implementation, and their role in achieving public health goals.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •COTPA 2003 is India's comprehensive law regulating tobacco products, covering advertising, sale, and packaging.
- •NTCP 2007 strengthens COTPA implementation and FCTC compliance through awareness, cessation, and enforcement.
- •PECA 2019 completely bans e-cigarettes in India to prevent their uptake, especially among youth.
- •NTQLS and M-Cessation Programme provide crucial support for tobacco cessation, with the latter leveraging mobile technology.
- •These legislations and programs form a multi-pronged strategy to reduce tobacco burden and improve public health.
🧠 Memory Techniques
98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•The Cigarettes and Other Tobacco Products (Prohibition of Advertisement and Regulation of Trade and Commerce, Production, Supply and Distribution) Act, 2003
•The Prohibition of Electronic Cigarette Act, 2019
•Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) - National Tobacco Control Programme (NTCP) documentation