Deletion of MGNREGA Job Cards - Social Issues | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Deletion of MGNREGA Job Cards
Medium⏱️ 10 min read
social issues
📖 Introduction
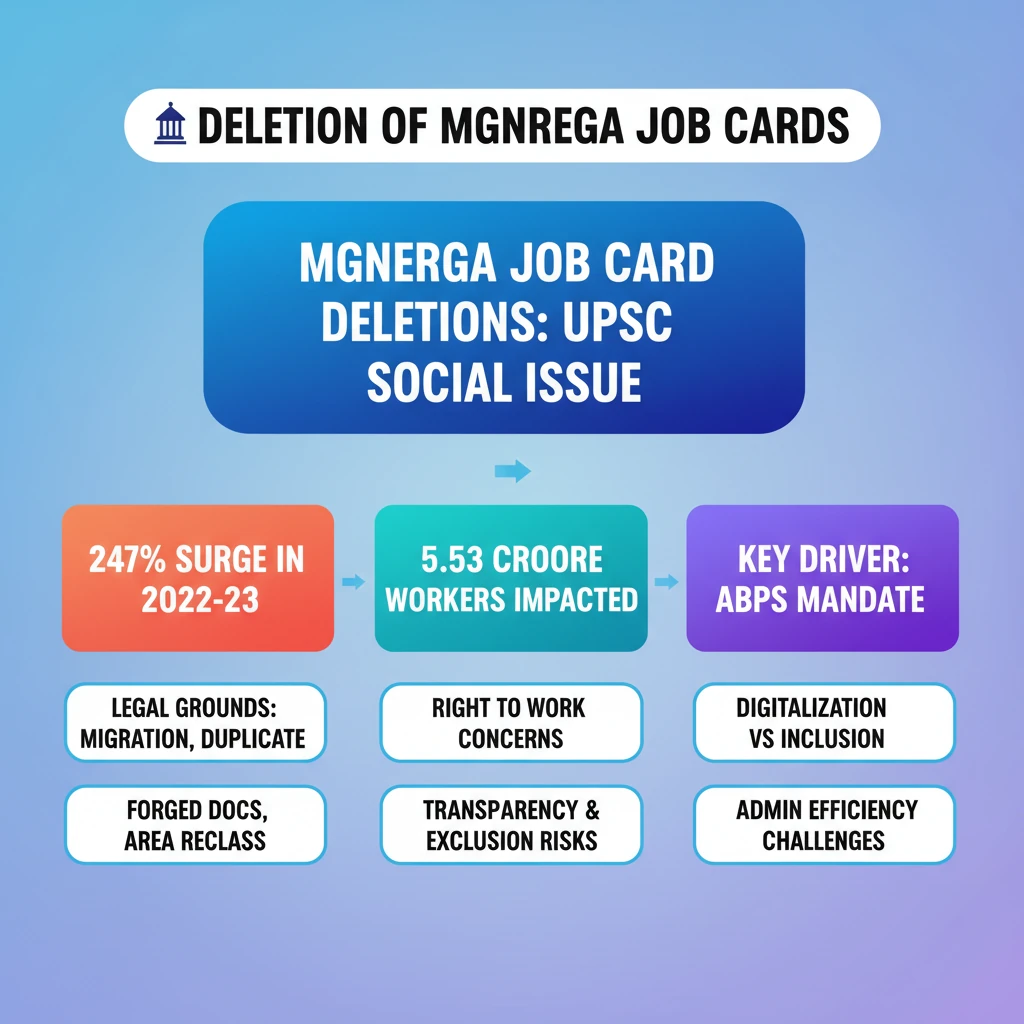
<h4>Introduction to MGNREGA Job Card Deletions</h4><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Note:</strong> The source content included information on unrelated technologies at the beginning. This information is presented here as found in the source, but it is not directly related to MGNREGA job card deletions.</p><ul><li><strong>Endobot & Swath AI:</strong> These technologies diagnose pipelines to detect and mitigate water contamination, wastage, and sewer overflows.</li><li><strong>Robo-Drain System:</strong> This refers to automated robotic technology specifically designed for cleaning underground sewers.</li><li><strong>Vacuum Trucks:</strong> These vehicles utilize powerful pumps to remove sewage waste, eliminating the need for human entry into sewers.</li></ul></div><p>The <strong>Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, 2005 (MGNREGA)</strong> is a crucial social security measure. Recently, there has been a significant increase in the deletion of workers from job cards under this Act.</p><p>This surge has raised serious concerns regarding the fundamental <strong>right to work</strong> for rural laborers. It also brings into question the overall <strong>transparency</strong> and effectiveness of the scheme's implementation.</p><h4>Recent Trends in Job Card Deletions</h4><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Deletion Statistics (2022-23)</strong></p><ul><li>Over <strong>5.53 crore workers</strong> were removed from MGNREGA job cards.</li><li>This represents a staggering <strong>247% increase</strong> in deletions compared to the previous financial year (2021-22).</li></ul></div><p>The unprecedented scale of these deletions highlights a critical issue affecting millions of rural households. Understanding the reasons behind this trend is essential for policy evaluation.</p><h4>Legal Grounds for Job Card Deletion</h4><div class='key-point-box'><p>As per <strong>Schedule II, Paragraph 23 of the MGNREGA Act, 2005</strong>, job cards can only be deleted under specific, clearly defined conditions. These provisions aim to ensure legitimate management of the scheme.</p></div><p>The Act outlines several valid reasons for removing a worker's job card. These are designed to prevent misuse and maintain the integrity of the program.</p><ul><li><strong>Permanent Migration:</strong> A job card can be deleted if a household permanently relocates from the concerned <strong>Gram Panchayat</strong>. This ensures benefits are tied to the local area.</li><li><strong>Duplicate Job Cards:</strong> Deletion occurs if a job card is identified as a <strong>duplicate</strong>. This prevents individuals from holding multiple cards and claiming benefits illicitly.</li><li><strong>Forged Documents:</strong> If a job card was originally issued based on <strong>forged documents</strong>, it is subject to deletion. This combats fraud and ensures eligibility.</li><li><strong>Reclassification of Area:</strong> Should a <strong>Gram Panchayat</strong> be reclassified as a <strong>Municipal Corporation</strong>, all associated job cards are deleted. This is because MGNREGA applies to rural areas.</li></ul><h4>Additional Reasons via MGNREGA MIS</h4><p>The <strong>MGNREGA Management Information System (MIS)</strong> provides further categories for job card deletions. These reasons are often administrative in nature.</p><ul><li><strong>Duplicate Applicant:</strong> Similar to duplicate job cards, this refers to instances where the same individual applies multiple times.</li><li><strong>Fake Applicant:</strong> This category covers cases where an applicant is found to be non-existent or fraudulent.</li><li><strong>Not Willing to Work:</strong> If a registered worker consistently expresses unwillingness to participate in work, their card may be deleted.</li></ul><h4>Impact of Aadhaar-Based Payment Systems (ABPS)</h4><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>The implementation of <strong>Aadhaar-based Payment Systems (ABPS)</strong> is a critical factor in the recent surge of job card deletions. This connection is vital for UPSC Mains answers on governance and social welfare.</p></div><p>The sharp increase in MGNREGA job card deletions during <strong>2022-23</strong> coincided directly with the mandatory implementation of <strong>ABPS</strong>. This system requires workers to link their <strong>Aadhaar numbers</strong> to their job cards for wage payments.</p><p>A significant number of deletions occurred because workers had <strong>non-linked</strong> or <strong>improperly linked Aadhaar numbers</strong>. This administrative requirement inadvertently led to the exclusion of many genuine beneficiaries from the scheme.</p>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •MGNREGA job card deletions surged by 247% in 2022-23, impacting over 5.53 crore workers.
- •Legal grounds for deletion include permanent migration, duplicate cards, forged documents, and area reclassification (MGNREGA Act, Schedule II, Para 23).
- •The mandatory Aadhaar-based Payment System (ABPS) implementation was a key driver for the recent deletions.
- •Deletions raise significant concerns about the right to work, transparency, and potential exclusion of genuine beneficiaries.
- •Balancing administrative efficiency through digitalization with ensuring social inclusion remains a critical challenge for welfare schemes.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, 2005 (Schedule II, Paragraph 23)
•Reports from the Ministry of Rural Development (implied for deletion statistics and ABPS implementation)