What is the Financing Mechanism of the Global Alliance Against Hunger and Poverty? - Social Issues | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What is the Financing Mechanism of the Global Alliance Against Hunger and Poverty?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
social issues
📖 Introduction
<h4>Understanding the Global Alliance Against Hunger and Poverty's Financing</h4><p>The <strong>Global Alliance Against Hunger and Poverty</strong> is a significant international initiative aimed at eradicating food insecurity worldwide. Its success heavily relies on robust and innovative <strong>financing mechanisms</strong> to support member countries.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The core principle behind the Alliance's funding strategy is the encouragement of diverse and innovative <strong>financing approaches</strong>. These methods are designed to bolster a country's ability to implement effective policies against hunger and poverty.</p></div><h4>Mobilizing Resources Through Innovative Approaches</h4><p>The Alliance promotes several key strategies for <strong>mobilizing resources</strong>. These include <strong>blended financing</strong>, <strong>concessional co-financing</strong>, and strategic <strong>partnerships</strong>. These approaches aim to leverage various funding sources for maximum impact.</p><p>These innovative methods are crucial for providing the necessary financial support, especially to developing nations, to implement their national policies and programs aimed at achieving <strong>food security</strong> and reducing poverty.</p><h4>Blended Financing Explained</h4><p><strong>Blended financing</strong> is a sophisticated financial instrument that combines different types of funds. It strategically mixes <strong>concessional funds</strong> with <strong>non-concessional funds</strong> to create a more attractive and sustainable financing package.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Concessional funds</strong> typically involve low-interest loans or outright grants. These are provided on terms more favorable than market rates, often by development banks or aid agencies.</p><p><strong>Non-concessional funds</strong>, in contrast, are market-based financing. This includes commercial loans, equity investments, or other private sector capital, provided at standard market rates.</p></div><p>By blending these two types, projects that might otherwise be deemed too risky or not commercially viable can attract private capital, thereby scaling up development impact.</p><h4>Concessional Co-financing Defined</h4><p><strong>Concessional co-financing</strong> represents another vital component of the Alliance's financing strategy. It involves below-market-rate finance provided by large financial entities.</p><div class='info-box'><p>This type of financing is typically offered by <strong>major financial institutions</strong>, such as multilateral development banks (MDBs). The terms are more favorable than commercial loans, making it accessible for countries with limited fiscal space.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>For <strong>UPSC Mains GS-III (Economy)</strong>, understanding these financing terms is crucial. Questions on development finance, international aid, and sustainable development goals often require knowledge of such mechanisms. Be prepared to explain their advantages and challenges.</p></div>
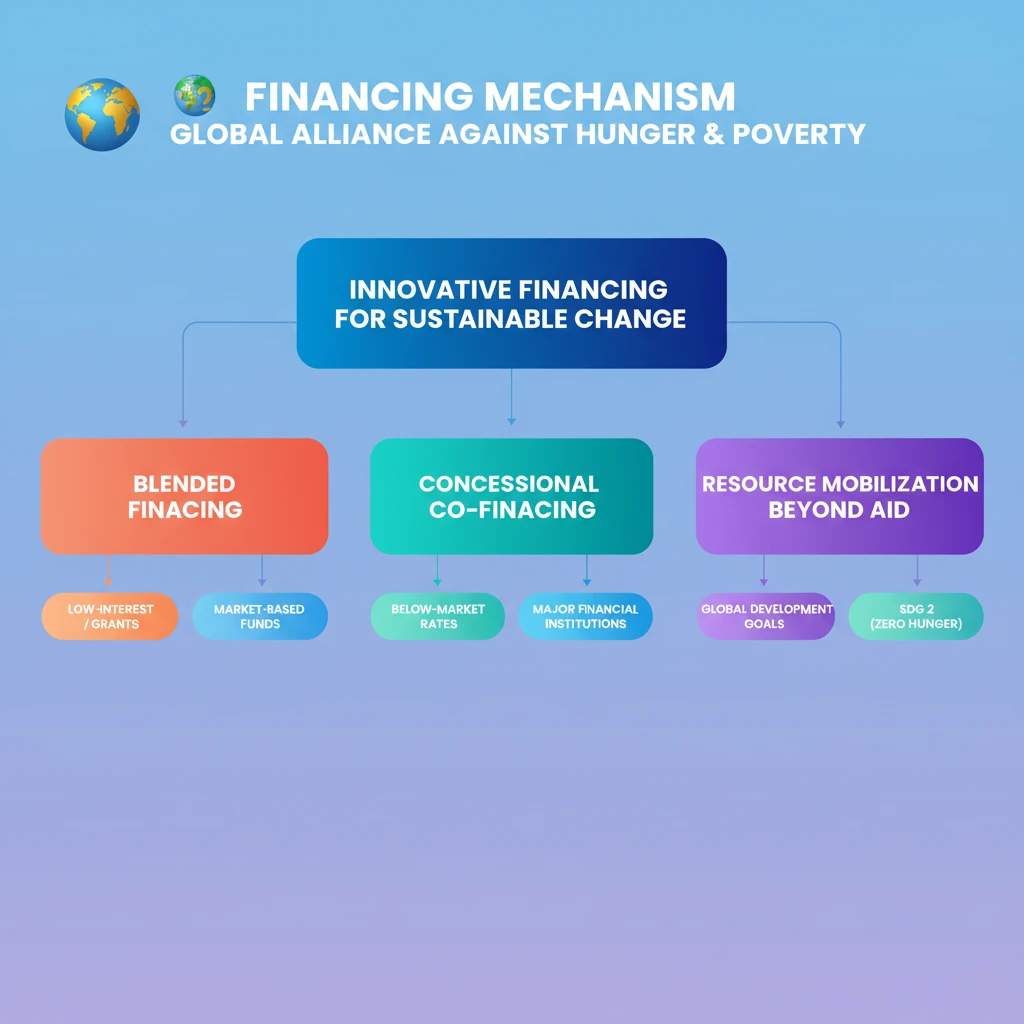
💡 Key Takeaways
- •The Global Alliance Against Hunger and Poverty relies on innovative financing.
- •Key mechanisms include blended financing and concessional co-financing.
- •Blended financing combines concessional (low-interest/grants) with non-concessional (market-based) funds.
- •Concessional co-financing is below-market-rate finance from major financial institutions.
- •These mechanisms are crucial for mobilizing resources beyond traditional aid to achieve global development goals like SDG 2.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•World Bank Group publications on Blended Finance
•UNICEF reports on financing for development
•Official UN documents on Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) financing