Timeline of reforms for Transgender Persons - Social Issues | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
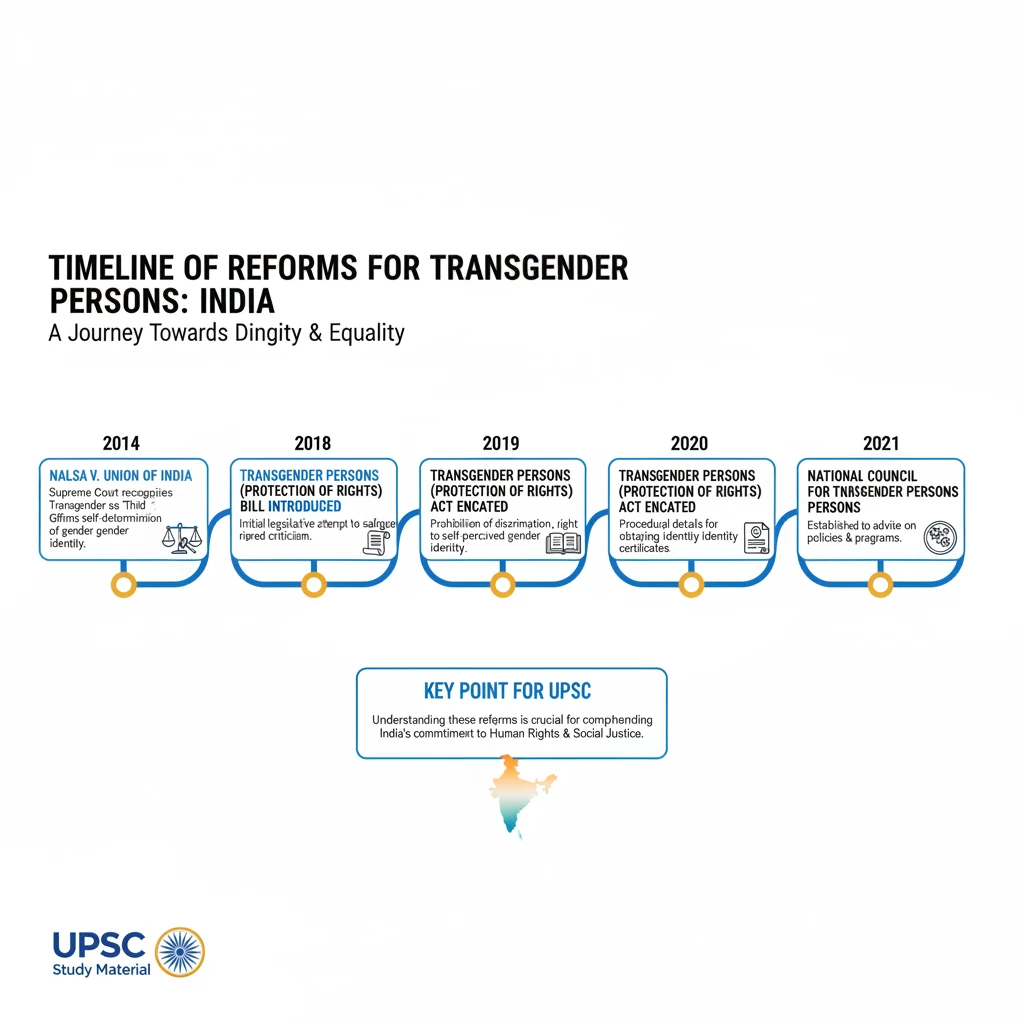
Timeline of reforms for Transgender Persons
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
social issues
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to Transgender Rights Reforms in India</h4><p>The journey towards recognizing and protecting the rights of <strong>transgender persons</strong> in India has seen significant milestones through judicial pronouncements and legislative actions. These reforms aim to ensure dignity, equality, and non-discrimination for a community that has historically faced marginalization.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>Understanding these reforms is crucial for comprehending India's commitment to <strong>social justice</strong> and <strong>human rights</strong>, particularly for vulnerable groups.</p></div><h4>Election Commissioner's Directive (2009)</h4><p>In <strong>2009</strong>, the <strong>Election Commissioner</strong> issued a significant directive. This directive addressed the need for inclusive identification options for individuals who do not conform to binary gender categories.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The directive updated voter registration forms to include an <strong>“others” option</strong>. This allowed <strong>transsexual individuals</strong> to register without being forced to identify as either male or female.</p></div><p>This was an early administrative step towards acknowledging gender diversity within official government records.</p><h4>Supreme Court Ruling (2014): NALSA v. Union of India</h4><p>A landmark judgment came in <strong>2014</strong> from the <strong>Supreme Court of India</strong>. This ruling was in the pivotal case of <strong>National Legal Services Authority (NALSA) vs. Union of India</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The Supreme Court formally recognized <strong>transgender people</strong> as the <strong>“Third Gender.”</strong> This decision was a monumental step, emphasizing that this recognition is a fundamental <strong>human right</strong>.</p></div><p>The ruling affirmed the right of transgender persons to self-identify their gender and mandated the government to ensure their rights to education, employment, and healthcare.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>The <strong>NALSA judgment</strong> is a cornerstone for social justice questions in <strong>UPSC Mains GS-II</strong>. Remember its year <strong>(2014)</strong> and its core pronouncements on <strong>gender identity</strong> and <strong>human rights</strong>.</p></div><h4>Legislative Efforts: Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019</h4><p>Building upon the judicial recognition, legislative efforts culminated in the enactment of the <strong>Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019</strong>. This Act aims to provide a legal framework for the protection of transgender rights.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>Act</strong> seeks to prohibit discrimination against transgender persons in various spheres, including employment, education, healthcare, and access to public services. It also outlines procedures for obtaining a <strong>certificate of identity</strong> as a transgender person.</p></div><p>While the Act has faced some criticism, it represents a crucial legislative step towards mainstreaming transgender rights and ensuring their protection under law.</p>
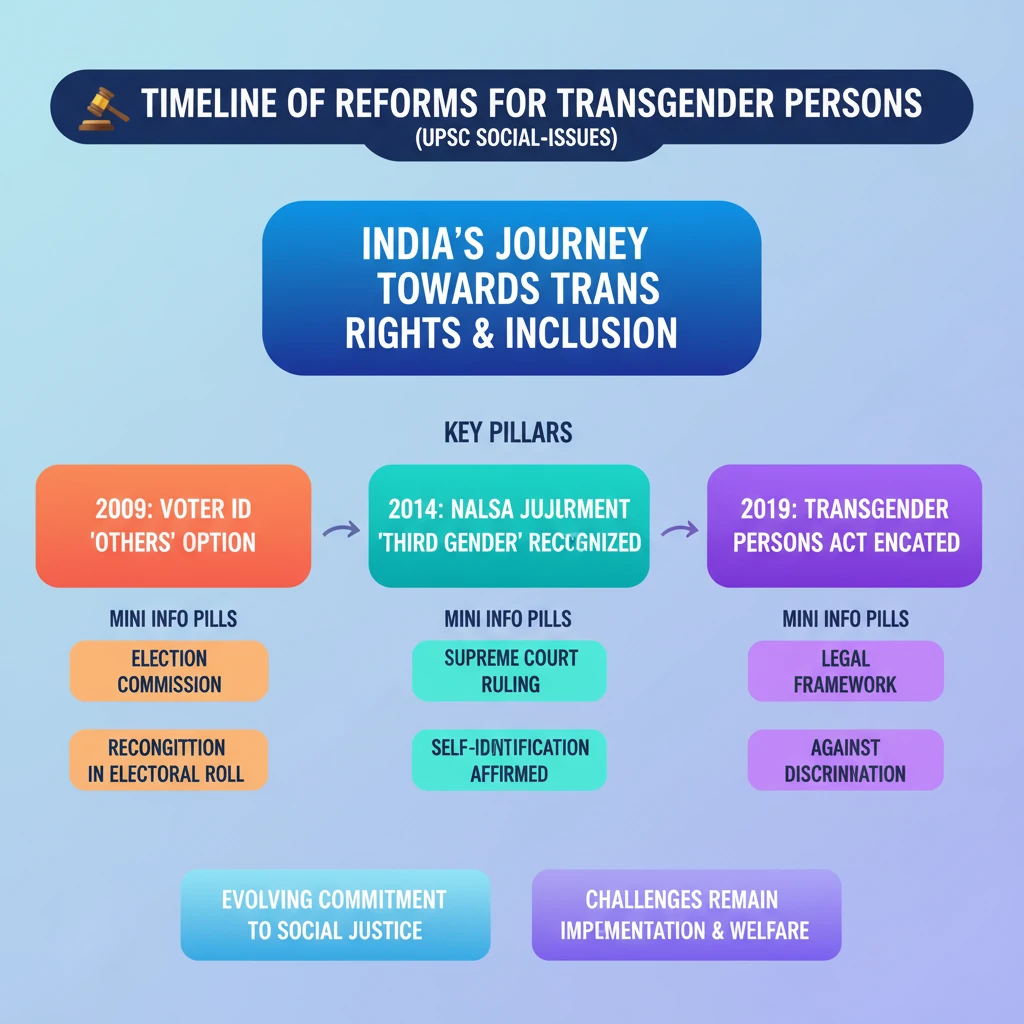
💡 Key Takeaways
- •2009: Election Commissioner's Directive introduced 'others' option for voter registration.
- •2014: Supreme Court's NALSA judgment recognized transgender persons as 'Third Gender' and affirmed self-identification as a human right.
- •2019: Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act enacted to provide a legal framework against discrimination.
- •Reforms reflect India's evolving commitment to social justice and human rights for marginalized communities.
- •Challenges remain in effective implementation and ensuring comprehensive welfare for transgender persons.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•National Legal Services Authority (NALSA) vs. Union of India, 2014 SCC OnLine SC 644
•The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019
•Election Commission of India directives (public domain information)