What are the Key Facts About Hepatitis? - Social Issues | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What are the Key Facts About Hepatitis?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
social issues
📖 Introduction
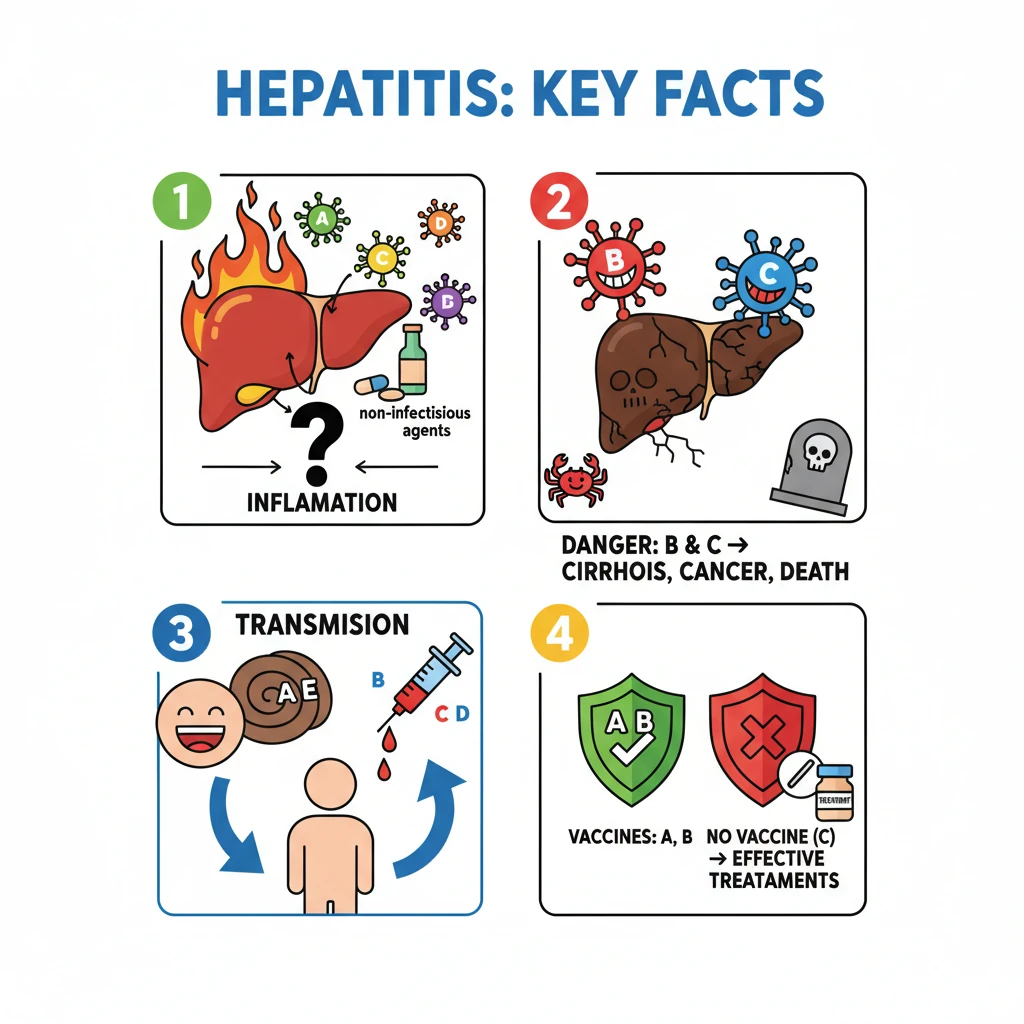
<h4>Understanding Hepatitis: An Overview</h4><p><strong>Hepatitis</strong> is an inflammation of the <strong>liver</strong>, a vital organ responsible for numerous metabolic functions. This condition can be triggered by various factors, leading to a spectrum of health issues, some of which can be life-threatening.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The term <strong>Hepatitis</strong> originates from the Greek words 'hepar' (liver) and 'itis' (inflammation). It signifies a serious health concern affecting millions globally.</p></div><h4>Causes of Hepatitis</h4><p>Hepatitis primarily arises from two main categories of agents: <strong>infectious viruses</strong> and <strong>noninfectious agents</strong>. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for prevention and treatment.</p><ul><li><strong>Viral Hepatitis:</strong> This is the most common cause, involving specific viruses that target the liver.</li><li><strong>Noninfectious Agents:</strong> These include excessive alcohol consumption, certain medications, toxins, and autoimmune diseases.</li></ul><h4>Main Strains of Hepatitis Virus</h4><p>There are five primary strains of the <strong>hepatitis virus</strong>, each designated by a letter. These strains exhibit distinct characteristics in terms of transmission, severity, global distribution, and preventive measures.</p><ul><li><strong>Hepatitis A (HAV)</strong></li><li><strong>Hepatitis B (HBV)</strong></li><li><strong>Hepatitis C (HCV)</strong></li><li><strong>Hepatitis D (HDV)</strong></li><li><strong>Hepatitis E (HEV)</strong></li></ul><div class='key-point-box'><p>Each viral strain requires a specific diagnostic approach and targeted treatment strategy, highlighting the importance of accurate identification.</p></div><h4>Severity and Impact of Hepatitis B and C</h4><p>Among the five strains, <strong>Hepatitis B</strong> and <strong>Hepatitis C</strong> are particularly concerning due to their significant health implications. They are the leading causes of severe chronic liver diseases worldwide.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Liver Cirrhosis:</strong> A condition where the <strong>liver</strong> becomes severely scarred and permanently damaged, impairing its ability to function. This is a common outcome of chronic <strong>Hepatitis B</strong> and <strong>C</strong> infections.</p></div><p>These two strains are also major contributors to <strong>liver cancer (Hepatocellular Carcinoma)</strong> and account for the majority of <strong>viral hepatitis-related deaths</strong> globally. Early detection and management are critical to prevent these severe outcomes.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>For <strong>UPSC Mains (GS-II: Health)</strong>, understanding the distinctions between Hepatitis types and their public health impact is vital. Focus on prevention strategies and government initiatives.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Hepatitis is liver inflammation caused by viruses (A, B, C, D, E) or non-infectious agents.
- •Hepatitis B and C are the most dangerous, leading to cirrhosis, liver cancer, and most hepatitis-related deaths.
- •Transmission varies: fecal-oral (A, E), blood-borne (B, C, D).
- •Vaccines exist for Hepatitis A and B, but not for C (though highly effective treatments are available).
- •India's National Viral Hepatitis Control Program aims for free screening and treatment for B and C.
- •Global goal: eliminate viral hepatitis as a public health threat by 2030 (WHO).
🧠 Memory Techniques
98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India - National Viral Hepatitis Control Program documents
•Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) - Hepatitis Information
•Drishti IAS (original source content)