Transgender Rights and Related Concerns - Social Issues | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Transgender Rights and Related Concerns
Medium⏱️ 12 min read
social issues
📖 Introduction
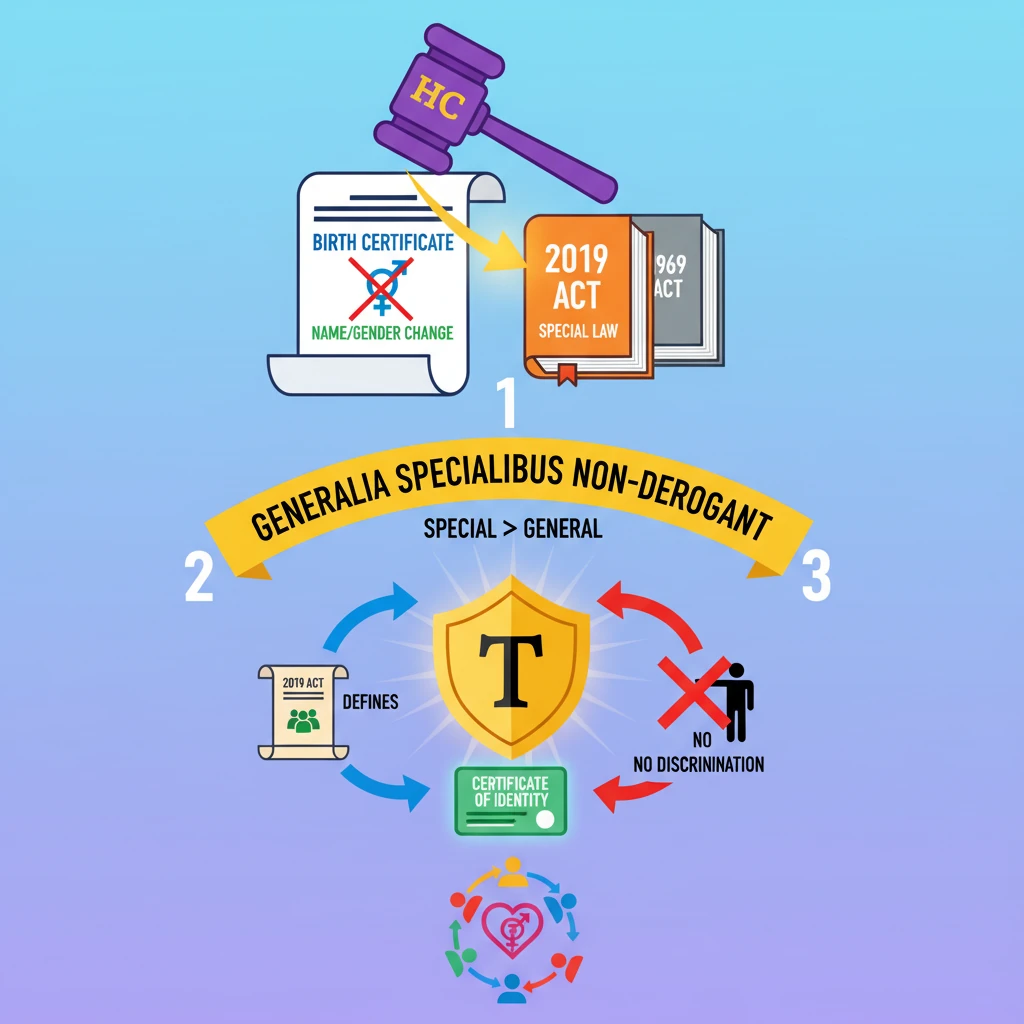
<h4>Karnataka HC Ruling: Ms. X vs State of Karnataka Case, 2024</h4><h5>Background of the Case</h5><p>The petitioner, diagnosed with <strong>gender dysphoria</strong>, underwent <strong>sex-reassignment surgery</strong>. She legally changed her name and gender identity on documents like <strong>Aadhaar card</strong>, <strong>driving license</strong>, and <strong>passport</strong>.</p><p>However, her request to change gender and name on her <strong>birth certificate</strong> was rejected.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Gender dysphoria</strong> refers to psychological distress occurring when a person’s sex assigned at birth does not match their gender identity.</p></div><h5>Legal Objection and Petitioner's Argument</h5><p>The rejection was based on <strong>Section 15 of the Registration of Births and Deaths Act, 1969</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>Registration of Births and Deaths Act, 1969</strong> permits changes to birth certificates only if the information is erroneous, fraudulent, or incorrectly entered.</p></div><p>The petitioner argued that this restrictive nature violated her <strong>right to life with dignity</strong> under <strong>Article 21</strong> of the Indian Constitution.</p><p>She highlighted that differing identities across documents lead to a <strong>dual identity</strong>, causing potential harassment and discrimination.</p><h5>The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019</h5><p>This Act allows transgender people to be issued a <strong>“certificate of identity”</strong> (<strong>Section 6</strong>). This certificate can be revised if they opt for <strong>sex-reassignment surgery</strong> (<strong>Section 7</strong>).</p><p>The law explicitly mandates that the gender of a transgender person <strong>“shall be recorded in all official documents”</strong> according to this certificate.</p><h5>Karnataka High Court's Ruling</h5><p>The HC held that the <strong>1969 Act</strong> is a <strong>“general enactment”</strong>. It must comply with the <strong>Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019</strong>, which is a <strong>“special enactment”</strong>.</p><p>The court invoked the legal principle: <strong>“generalia specialibus non-derogant”</strong>, meaning <strong>“the special shall prevail over the general”</strong>.</p><p>The ruling directed the Registrar to accept the <strong>transgender certificate</strong> and issue a corrected birth certificate under the 1969 Act, as amended by the special law.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>General enactments</strong> apply broadly (e.g., <strong>1969 Act</strong>), while <strong>special laws</strong> focus on specific issues (e.g., <strong>Transgender Persons Act</strong>).</p></div><h5>Significance of the Judgment</h5><p>This judgment underscores the <strong>supremacy of special laws</strong> designed to protect the rights of transgender individuals. It is a crucial step towards the recognition of <strong>gender identity</strong> in all official records for transgender persons.</p><div class='info-box'><p>As per the <strong>2011 census</strong>, the total transgender population in India is around <strong>4.88 Lakh</strong>. The top 3 states with the largest transgender population are <strong>Uttar Pradesh</strong>, <strong>Andhra Pradesh</strong>, and <strong>Maharashtra</strong>.</p></div><h4>Key Facts About the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019</h4><h5>Definition of Transgender Person</h5><p>A <strong>transgender person</strong> is defined as someone whose gender does not match the gender assigned at birth.</p><p>The Act clarifies terms like <strong>‘person with intersex variation’</strong> and <strong>‘transgender person’</strong> to include <strong>trans men and women</strong>, irrespective of surgery or therapy.</p><h5>Prohibition of Discrimination</h5><p>The Act explicitly prohibits discrimination against transgender persons in various spheres. This includes areas such as <strong>education</strong>, <strong>employment</strong>, <strong>healthcare</strong>, and access to <strong>public facilities</strong>.</p><p>It also affirms their rights to <strong>movement</strong>, <strong>property ownership</strong>, and holding <strong>public office</strong>.</p><h5>Certificate of Identity</h5><p>The Act grants transgender individuals the right to <strong>self-perceived gender identity</strong>. It mandates district magistrates to issue <strong>certificates of identity</strong> without requiring medical examinations.</p><h4>Timeline of Reforms for Transgender Persons in India</h4><ol><li><strong>2009: Election Commission's Directive</strong> - Registration forms were updated to include an <strong>“others” option</strong>, allowing transsexual individuals to avoid binary male or female identification.</li><li><strong>2014: Supreme Court Ruling (NALSA vs. Union of India)</strong> - The Supreme Court recognized transgender people as the <strong>“Third Gender”</strong>, emphasizing their rights as a fundamental human rights issue.</li><li><strong>2019: Legislative Efforts (Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act)</strong> - This landmark Act was enacted to provide comprehensive protection of transgender rights.</li></ol>
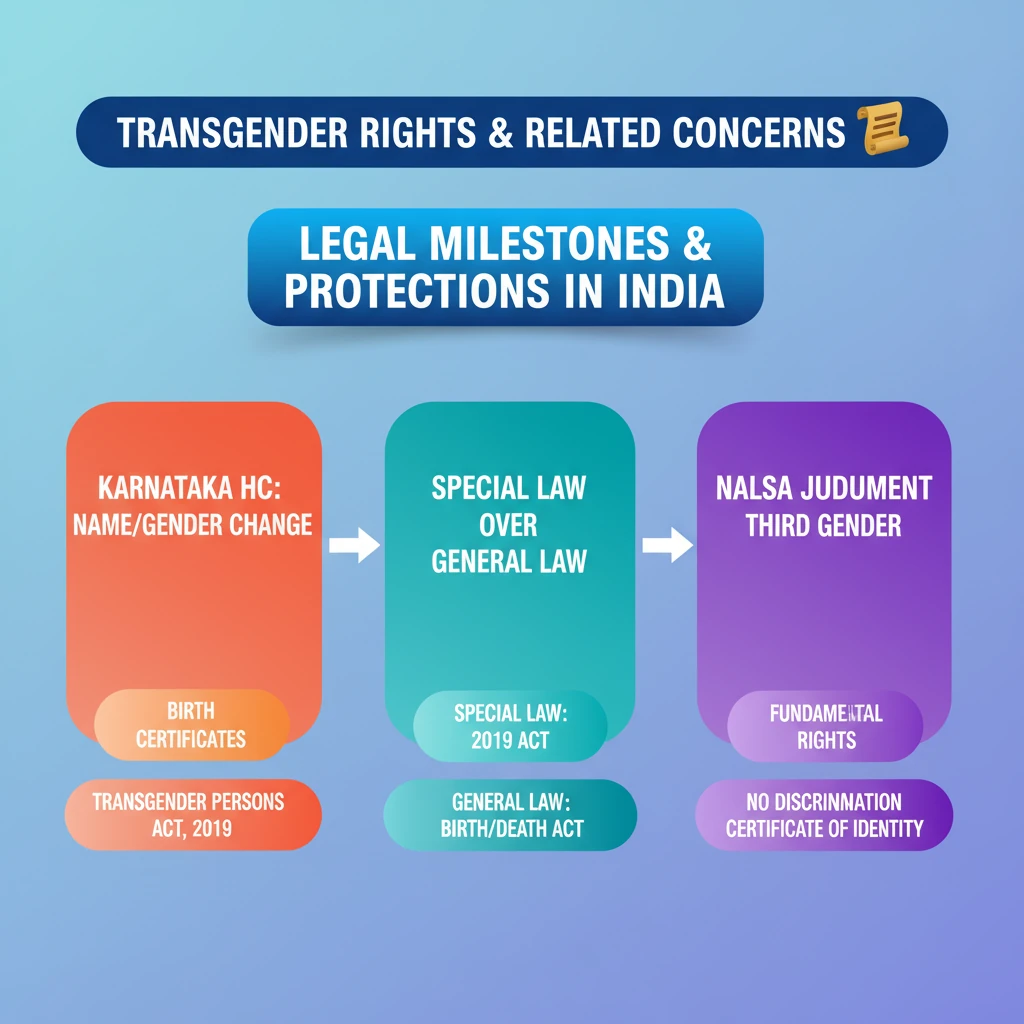
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Karnataka HC ruled transgender persons can change name/gender on birth certificates.
- •The ruling prioritizes the Transgender Persons Act, 2019 (special law) over the Registration of Births and Deaths Act, 1969 (general law).
- •Principle: "generalia specialibus non-derogant" (special prevails over general).
- •Transgender Persons Act, 2019 defines transgender and prohibits discrimination, granting a Certificate of Identity.
- •NALSA vs. Union of India (2014) recognized transgender as "Third Gender" and affirmed fundamental rights.
- •This ensures recognition of self-perceived gender identity in all official documents, upholding dignity.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content