What is the Swachh Bharat Mission? - Social Issues | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
What is the Swachh Bharat Mission?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
social issues
📖 Introduction
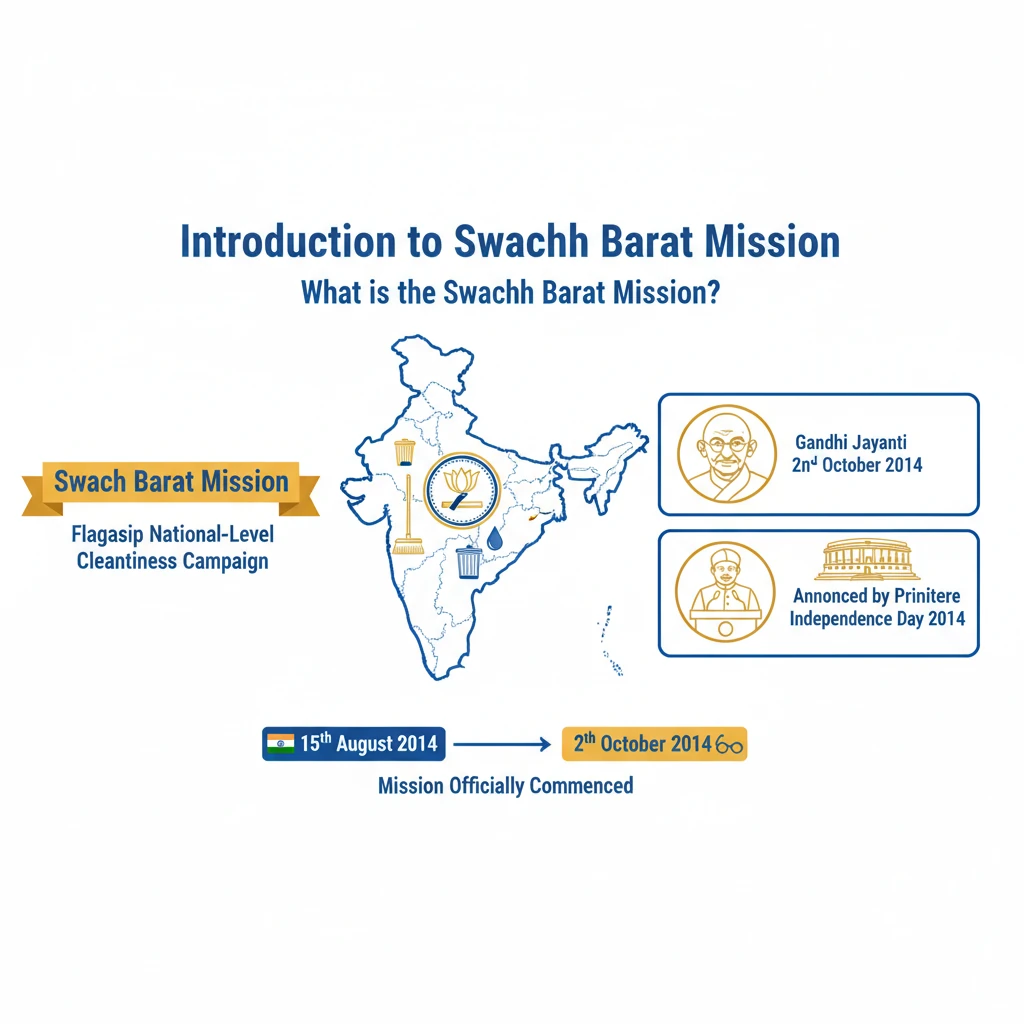
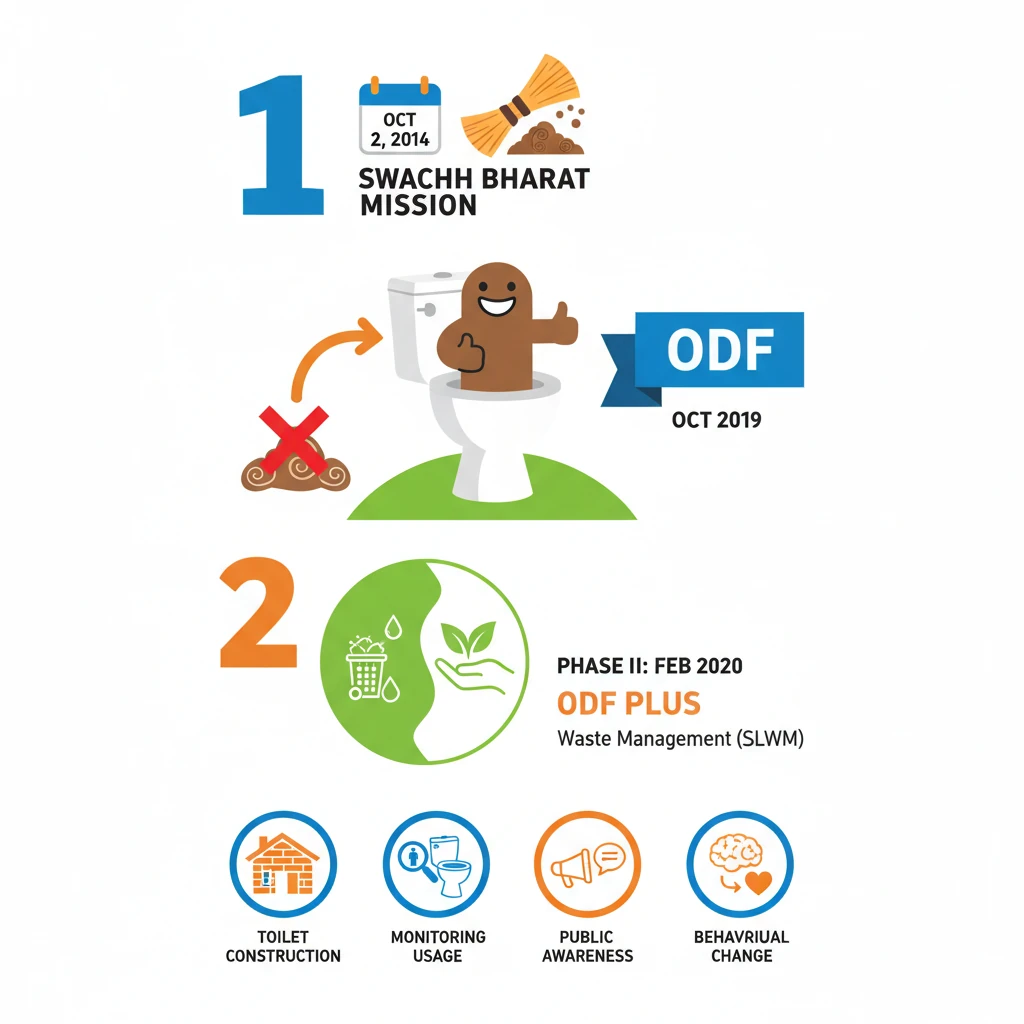
<h4>Introduction to Swachh Bharat Mission</h4><p>The <strong>Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM)</strong> is a flagship national-level cleanliness campaign launched by the Government of India. It was initially announced by the <strong>Prime Minister</strong> on <strong>Independence Day 2014</strong>.</p><p>The mission officially commenced on <strong>2nd October 2014</strong>, a date strategically chosen to coincide with <strong>Gandhi Jayanti</strong>, honoring Mahatma Gandhi's vision of cleanliness.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Scale of SBM:</strong> Considered <strong>India’s largest-ever cleanliness drive</strong>, SBM actively engaged approximately <strong>3 million government employees</strong>, along with numerous school and college students, across the nation.</p></div><h4>Evolution: Swachh Bharat Mission Phase II</h4><p>Recognizing the need for sustained efforts, <strong>Phase II</strong> of the <strong>Swachh Bharat Mission</strong> was officially approved in <strong>February 2020</strong>. This subsequent phase builds upon the achievements of Phase I.</p><p>Phase II primarily focuses on sustaining the <strong>Open Defecation Free (ODF) status</strong> achieved in the first phase. It also places a strong emphasis on comprehensive <strong>Solid and Liquid Waste Management (SLWM)</strong> in rural areas.</p><h4>Key Principles and Goals of SBM</h4><div class='key-point-box'><p>The mission is guided by several core principles aimed at transforming India's sanitation landscape:</p></div><ul><li><strong>Toilet Construction:</strong> A primary goal was the construction of <strong>individual, cluster, and community toilets</strong>. This was crucial for eliminating or significantly reducing <strong>open defecation</strong>, a major contributor to child mortality and various health issues.</li><li><strong>Monitoring Usage:</strong> Beyond mere construction, SBM established an accountable mechanism to actively <strong>monitor toilet use</strong>. The focus was on ensuring behavioral change, not just infrastructure development.</li><li><strong>Public Awareness:</strong> A significant component involved promoting widespread <strong>public awareness</strong> about the severe drawbacks of <strong>open defecation</strong>. This aimed to encourage consistent and proper toilet use.</li><li><strong>Behavioural Change:</strong> The mission sought to fundamentally change people’s attitudes, mindsets, and behaviours towards sanitation. This was achieved through dedicated ground staff and extensive awareness campaigns.</li><li><strong>Clean Villages:</strong> SBM aimed to ensure overall cleanliness in villages. This included effective implementation of <strong>Solid and Liquid Waste Management (SLWM)</strong> strategies, primarily through the involvement of <strong>Gram Panchayats</strong>.</li><li><strong>Water Supply:</strong> A crucial enabling factor was the installation of <strong>water pipelines</strong>. This initiative ensured a consistent water supply to all households, making toilet usage practical and hygienic.</li></ul><h4>Funding and Budget Allocation</h4><p>The government demonstrated substantial commitment through significant financial investment. From <strong>2015 to 2020</strong>, SBM had an average annual budget of approximately <strong>1.25 billion USD</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>This substantial investment underscored the government’s dedication to improving national sanitation and public health outcomes across the country.</p></div><p>The central government provided financial incentives and technical support to state governments. These incentives covered various sanitation efforts, including toilet construction and waste management initiatives.</p><p>The <strong>Swachh Bharat Kosh</strong> was established to facilitate broader participation. It allows for contributions from the public, corporate entities, and individuals, specifically for sanitation infrastructure purposes.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding the phases, funding mechanisms, and the shift from ODF to <strong>ODF Plus</strong> (SLWM) is crucial for both Prelims (facts) and Mains (policy analysis, socio-economic impact).</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) launched on October 2, 2014, as India's largest cleanliness drive.
- •Initial goal was to achieve Open Defecation Free (ODF) status by October 2019.
- •Phase II, approved in Feb 2020, focuses on sustaining ODF and comprehensive Solid and Liquid Waste Management (SLWM) (ODF Plus).
- •Key principles include toilet construction, monitoring usage, public awareness, and behavioural change.
- •Significant government funding (approx. $1.25 billion USD annually) and public contributions (Swachh Bharat Kosh) support the mission.
- •It has broad impacts on public health, women's safety, and environmental sustainability, aligning with SDGs.
🧠 Memory Techniques
98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Jal Shakti, Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (DDWS) - Swachh Bharat Mission (Grameen) website
•Press Information Bureau (PIB) releases on SBM Phase II
•NITI Aayog reports on sanitation and rural development