Black Hole Triple System - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Black Hole Triple System
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
<h4>Recent Discovery: The First Black Hole Triple System</h4><p>A groundbreaking study recently announced the discovery of the <strong>first black hole triple system</strong>. This unique celestial arrangement is situated approximately <strong>8,000 light-years (LY)</strong> away from Earth, marking a significant find in astrophysics.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>What is a Light-Year (LY)?</strong></p><ul><li>A <strong>light-year</strong> is a unit of distance, not time.</li><li>It represents the distance that light travels in one Earth year.</li><li>This distance is approximately <strong>5.9 trillion miles (9.5 trillion km)</strong>.</li></ul></div><h4>Defining a Black Hole Triple System</h4><p>Unlike typical black holes, which are often found in isolation or as part of a <strong>binary system</strong> (two gravitationally bound objects), a <strong>black hole triple system</strong> is far more complex.</p><p>It comprises a <strong>central black hole</strong> that is gravitationally bound to <strong>two orbiting stars</strong>. These three components are held together by their mutual gravitational forces, creating a stable, intricate dance.</p><h4>Formation Mechanism: Direct Collapse</h4><p>The formation of this triple system is attributed to a unique process known as <strong>“direct collapse”</strong>. This mechanism is crucial for understanding how such a complex system can form and remain intact.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Direct Collapse (Failed Supernova) Explained:</strong></p><ul><li>A <strong>massive star</strong> collapses inwards under its own gravity.</li><li>Crucially, this collapse occurs <strong>without undergoing a supernova explosion</strong>.</li><li>This gentler formation mechanism means that nearby stars are not violently ejected.</li><li>Instead, they remain <strong>gravitationally attached</strong> to the newly formed black hole.</li></ul></div><p>This process is also referred to as a <strong>“failed supernova”</strong>. It avoids the violent expulsion of surrounding matter that typically accompanies a supernova, thus preserving the gravitational bonds with nearby stellar companions.</p><h4>Significance and Challenges to Traditional Models</h4><p>The discovery of this <strong>black hole triple system</strong> is profoundly significant for several reasons. It challenges many of the traditional models that describe how black holes form and evolve within stellar systems.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight: Implications for Astrophysics</strong></p><p>Understanding such unique structures is vital for advancements in <strong>astrophysics</strong>. It provides empirical data that can refine our theories on <strong>stellar evolution</strong>, <strong>gravitational dynamics</strong>, and the prevalence of different types of black hole systems in the universe. This topic could appear in <strong>GS Paper III (Science & Technology)</strong> under Space Technology or Developments in Physics.</p></div><p>It demonstrates the intricate and complex <strong>gravitational dynamics</strong> that can exist in stellar environments, pushing the boundaries of our current astrophysical understanding.</p>
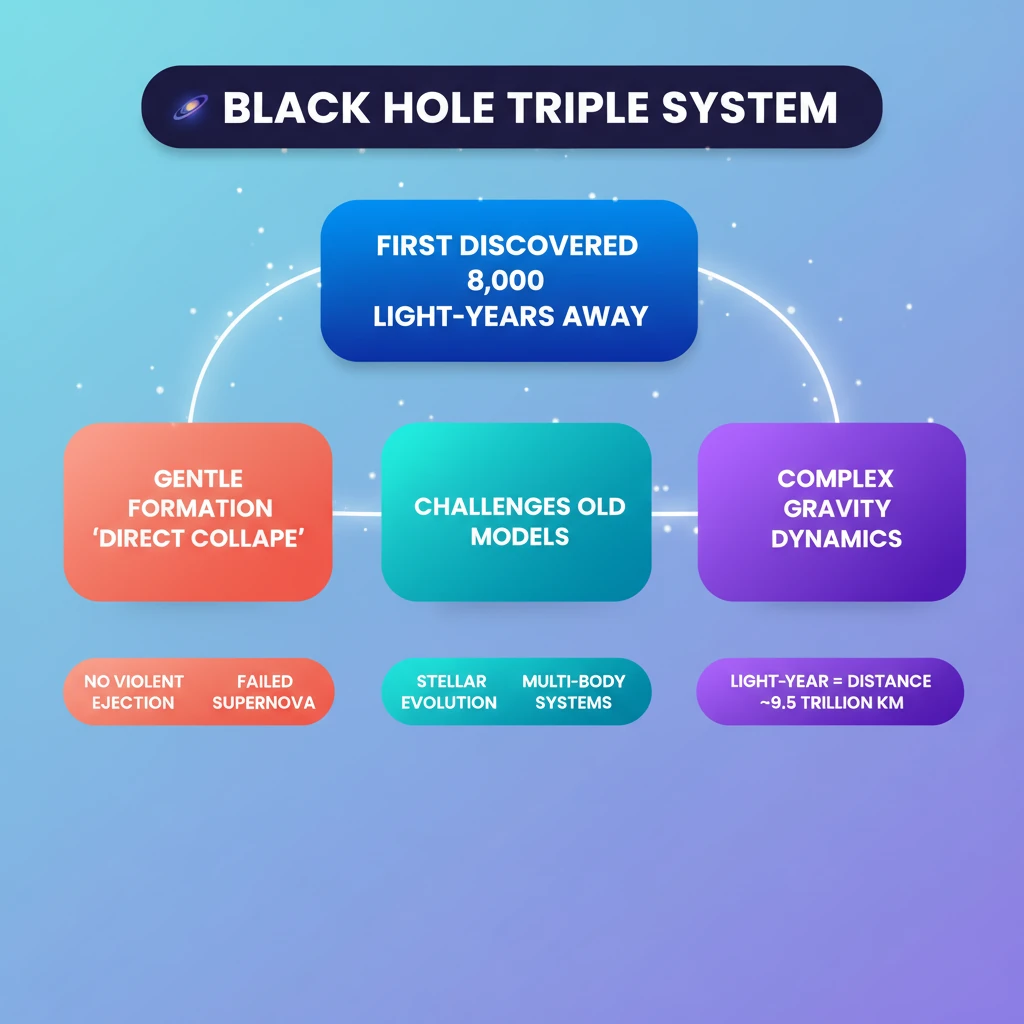
💡 Key Takeaways
- •First black hole triple system discovered 8,000 LY away, featuring a central black hole and two orbiting stars.
- •Formed via 'direct collapse' or 'failed supernova', a gentler process avoiding violent ejection of matter.
- •Challenges traditional black hole formation models and highlights complex gravitational dynamics.
- •A light-year is a unit of distance (approx. 9.5 trillion km), not time.
- •Significantly advances understanding of stellar evolution and multi-body gravitational systems.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•General Astrophysical Research on Black Holes and Stellar Systems (for historical context and conceptual framework)