Light Pollution - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Light Pollution
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
<h4>What is Light Pollution?</h4><p><strong>Light Pollution</strong> refers to the excessive or inappropriate use of <strong>artificial lighting</strong>. This phenomenon has emerged as a significant environmental concern in the modern era.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Definition:</strong> <strong>Light Pollution</strong> is the alteration of natural light levels in the outdoor environment due to anthropogenic sources of light.</p></div><p>It encompasses various forms, including <strong>skyglow</strong>, <strong>glare</strong>, <strong>light trespass</strong>, and <strong>clutter</strong>. These forms collectively contribute to its detrimental effects on ecosystems and human well-being.</p><h4>Significant Environmental Threats</h4><p>The presence of excessive artificial light poses substantial threats across multiple domains. These impacts are often interconnected, creating a cascade of negative consequences.</p><ul><li><strong>Human Health:</strong> Disrupts the natural <strong>circadian rhythm</strong>, leading to sleep disorders, increased risk of certain diseases, and psychological stress.</li><li><strong>Wildlife:</strong> Affects nocturnal animals' navigation, foraging, reproduction, and predator-prey dynamics. It can disorient migratory birds and sea turtles.</li><li><strong>Climate and Energy:</strong> Wasted light often means wasted energy, contributing to higher carbon emissions. Inefficient lighting systems exacerbate this issue.</li><li><strong>Astronomical Observation:</strong> <strong>Skyglow</strong> significantly reduces the visibility of stars and other celestial objects, impacting scientific research and cultural heritage.</li></ul><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding the multifaceted impacts of <strong>Light Pollution</strong> is crucial. Be prepared to discuss its environmental, social, and economic dimensions, linking it to topics like <strong>biodiversity conservation</strong>, <strong>public health</strong>, and <strong>sustainable urban planning</strong> in <strong>GS-III</strong> and <strong>GS-I (Geography)</strong>.</p></div>
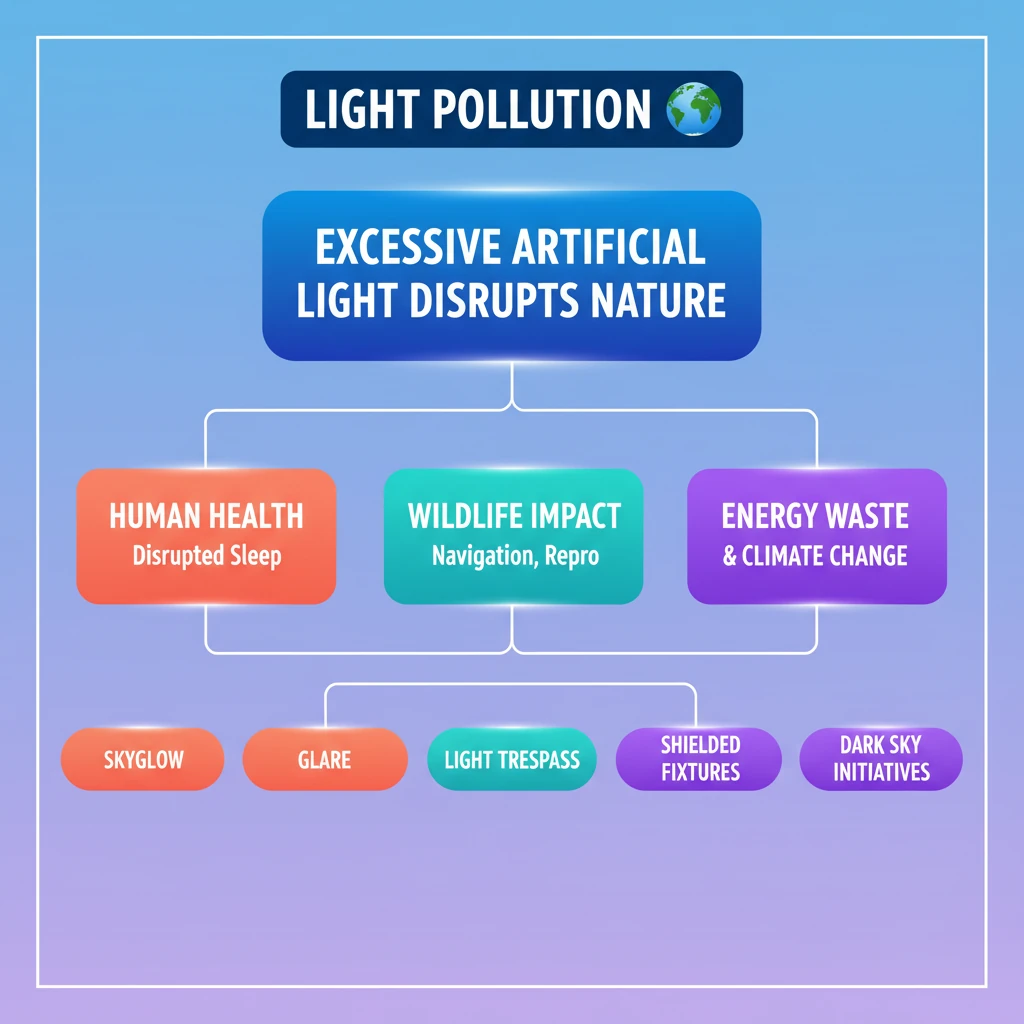
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Light Pollution is excessive or inappropriate artificial lighting disrupting natural darkness.
- •It poses significant threats to human health (circadian rhythm), wildlife (navigation, reproduction), and climate (energy waste).
- •Key forms include skyglow, glare, light trespass, and clutter.
- •Its rise is linked to widespread electrification and inefficient lighting practices.
- •Mitigation involves responsible lighting design: shielded fixtures, dimmers, warm-spectrum lights, and dark sky initiatives.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) reports on environmental issues
•Scientific journals on ecology, chronobiology, and urban planning
•Government reports on energy efficiency and environmental conservation