DBS Brain Implant Surgery for Epilepsy Treatment - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
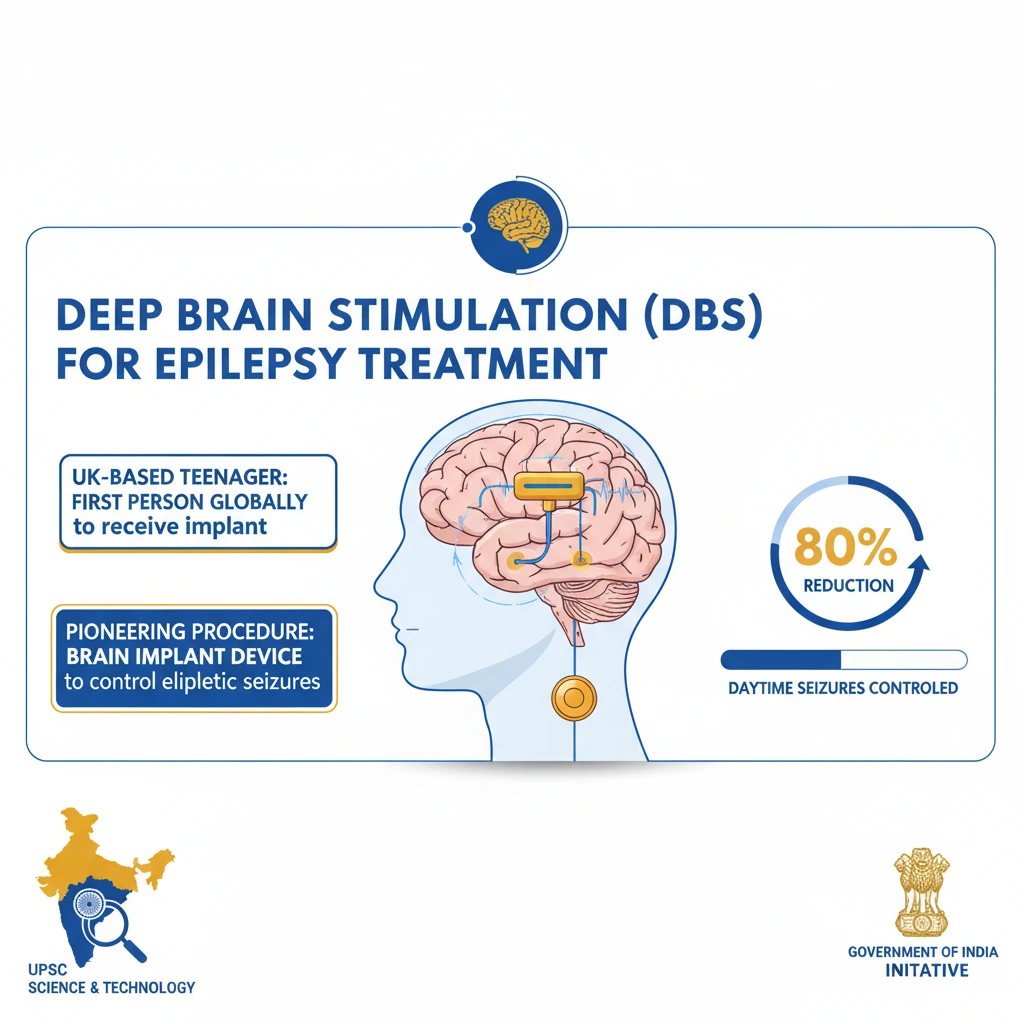
DBS Brain Implant Surgery for Epilepsy Treatment
Medium⏱️ 10 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) for Epilepsy</h4><p>Recently, a <strong>UK-based teenager</strong> made headlines as the <strong>first person globally</strong> to receive a <strong>brain implant device</strong> designed to control epileptic seizures. This pioneering procedure involved the insertion of a <strong>Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) device</strong> into his skull.</p><p>The successful implantation led to a remarkable <strong>80% reduction</strong> in his daytime seizures, offering significant hope for individuals suffering from drug-resistant epilepsy.</p><h4>Understanding Epilepsy Disorder</h4><p><strong>Epilepsy</strong> is a <strong>central nervous system (neurological) disorder</strong> characterized by abnormal brain activity. This abnormality leads to recurrent seizures, which can manifest as periods of unusual behavior, sensations, or sometimes a loss of awareness.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Definition:</strong> Epilepsy is a neurological disorder where brain activity becomes abnormal, causing seizures or periods of unusual behavior, sensations, and sometimes loss of awareness.</p></div><p>The primary cause of epilepsy is <strong>abnormal electrical activity</strong> in the brain. However, in nearly <strong>50% of cases</strong>, no identifiable cause can be determined.</p><p>Known risk factors include <strong>head trauma</strong>, <strong>brain tumours</strong>, certain <strong>infections</strong> like meningitis, and even <strong>genetics</strong>.</p><p>Epilepsy is observed more frequently in <strong>young children</strong> and <strong>older adults</strong>. Statistically, it occurs slightly more often in males than in females.</p><h4>Traditional Surgical Approaches to Epilepsy</h4><p>For patients whose seizures cannot be controlled by medication, surgical interventions are considered. These procedures aim to either remove the seizure-originating area or prevent the spread of abnormal electrical signals.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Brain Surgery:</strong> Doctors can perform surgery to remove a specific portion of the brain where the seizures are known to originate. This is a resective procedure.</p></div><p>Another specialized surgical technique is <strong>Corpus Callosotomy</strong>. This procedure involves surgically removing the <strong>corpus callosum</strong>, which is the part of the brain that connects the two hemispheres.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Corpus Callosotomy:</strong> This surgical procedure involves removing the <strong>corpus callosum</strong> to prevent abnormal electrical signals from traveling between the two halves of the brain, thereby stopping the spread of seizures.</p></div><h4>Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) Technology</h4><p><strong>Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)</strong> represents an advanced neuromodulation therapy for epilepsy. It involves the precise implantation of a medical device within the brain.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>DBS Mechanism:</strong> DBS involves implanting a medical device with <strong>electrodes</strong> that deliver mild, continuous electrical currents to specific brain regions. These targeted regions are typically linked to the generation or spread of seizures.</p></div><p>The DBS system typically comprises several components: the <strong>DBS device (neurostimulator)</strong>, <strong>electrode leads</strong> that are inserted into the brain, and <strong>lead anchors</strong> or <strong>skull anchors</strong> to secure the leads. A <strong>guide tube</strong> and <strong>electrode contacts</strong> facilitate the precise placement and function of the system.</p><h4>Current Treatments for Epilepsy</h4><p>The initial and most common approach to managing epilepsy involves pharmacological interventions.</p><ul><li><strong>Anti-Seizure Medications:</strong> These are the <strong>first line of treatment</strong> for epilepsy. Their primary goal is to control the frequency and severity of seizures.</li></ul><p>For some patients, particularly children with medication-resistant epilepsy, dietary changes can be remarkably effective.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Ketogenic Diet:</strong> This is a <strong>high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet</strong> that can be particularly effective in managing seizures, especially in children who do not respond well to anti-seizure medications.</p></div><h4>Global and Indian Context of Epilepsy</h4><p>Epilepsy is a globally recognized health challenge, impacting millions worldwide.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>World Health Organisation (WHO)</strong> has officially recognized epilepsy as a significant <strong>neurological disorder</strong>, highlighting its public health importance.</p></div><p>In India, the prevalence of epilepsy presents a considerable health burden. According to a <strong>2022 Lancet study</strong>, the prevalence of epilepsy in India ranges from <strong>3 to 11.9 cases per 1,000 people</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>Despite the availability of various anti-seizure medications, approximately <strong>30% of patients</strong> with epilepsy remain <strong>resistant to treatment</strong>, underscoring the need for advanced therapies like DBS.</p></div>
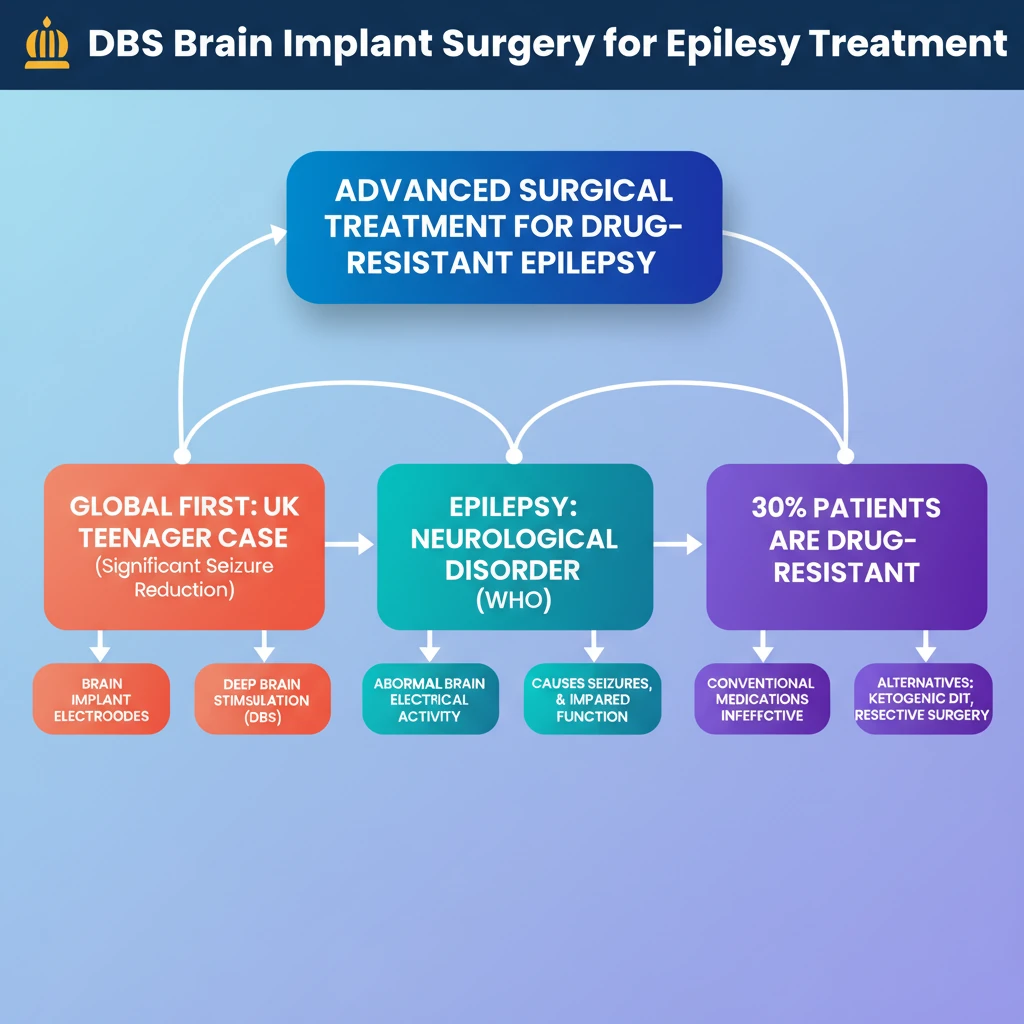
💡 Key Takeaways
- •DBS is an advanced surgical treatment for drug-resistant epilepsy, involving brain implant electrodes.
- •The UK teenager case marks a global first for DBS application in epilepsy, showing significant seizure reduction.
- •Epilepsy is a neurological disorder caused by abnormal brain electrical activity, recognized by WHO.
- •Around 30% of epilepsy patients are resistant to conventional anti-seizure medications.
- •Traditional treatments include anti-seizure medications, ketogenic diet, and resective surgeries like Corpus Callosotomy.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•World Health Organisation (WHO) publications on neurological disorders
•Lancet study (2022) on epilepsy prevalence in India