Last Universal Common Ancestor (LUCA) - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
Last Universal Common Ancestor (LUCA)
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
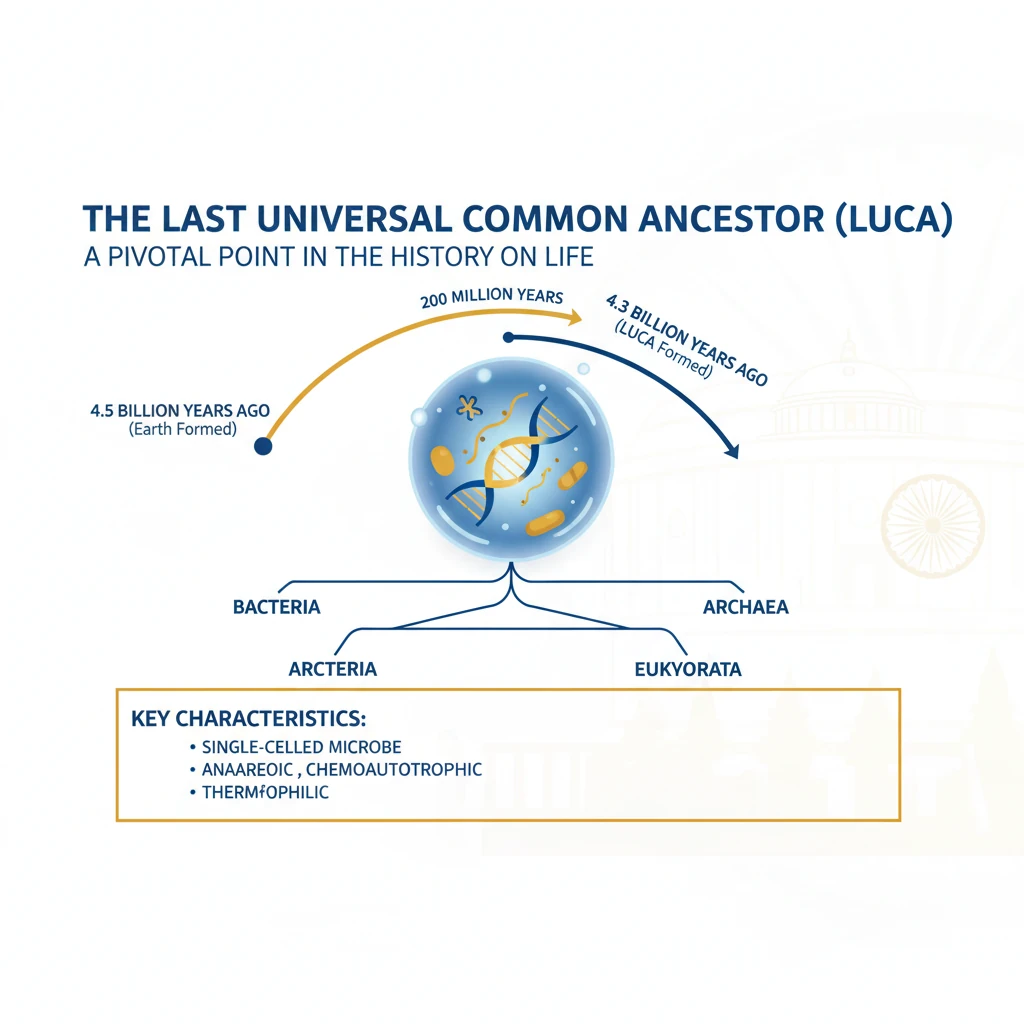
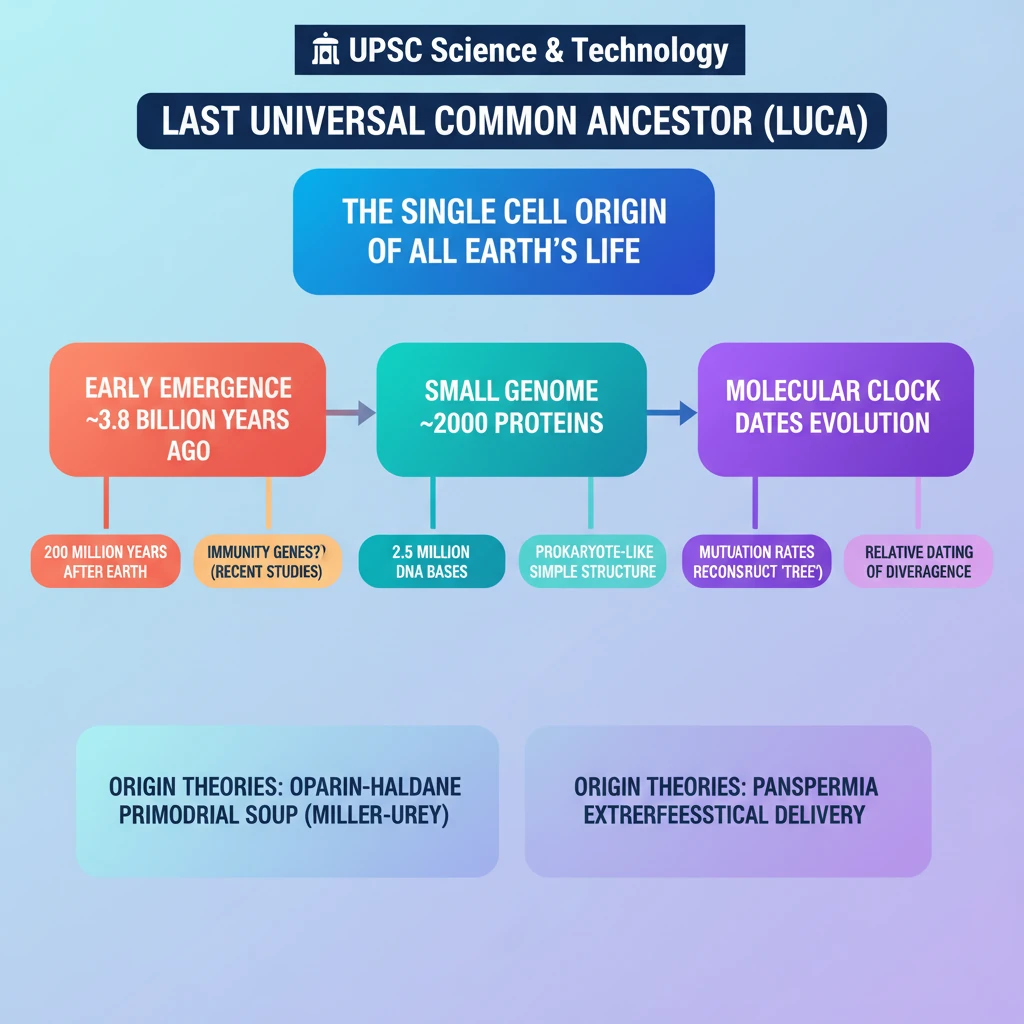
<h4>Introduction: The Last Universal Common Ancestor (LUCA)</h4><p>Recent scientific studies have reignited interest in the <strong>Last Universal Common Ancestor (LUCA)</strong>, suggesting its formation occurred just <strong>200 million years</strong> after Earth itself formed.</p><p><strong>LUCA</strong> represents a pivotal point in the history of life, believed to be the single cell from which all known life forms on Earth descended.</p><h4>Understanding LUCA's Nature</h4><div class='key-point-box'><p>Researchers hypothesize that <strong>LUCA</strong> was the common progenitor for all three major branches of life: <strong>Bacteria</strong>, <strong>Archaea</strong>, and <strong>Eukarya</strong>.</p></div><p>Despite the absence of direct <strong>fossil evidence</strong>, insights into <strong>LUCA's</strong> existence are derived from the shared features observed across modern genomes.</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li><strong>Genome Size:</strong> Estimated to have a small genome of approximately <strong>2.5 million bases</strong>.</li><li><strong>Proteins:</strong> Possessed around <strong>2,000 proteins</strong>, sufficient for survival in its primordial environment.</li><li><strong>Ecosystem Impact:</strong> Its metabolites might have fostered a secondary ecosystem, paving the way for other microbes.</li><li><strong>Immunity:</strong> Possibly contained <strong>immunity genes</strong> to defend against early viruses.</li></ul></div><h4>The Molecular Clock Theory and LUCA</h4><p>The concept of the <strong>molecular clock</strong> has been instrumental in reconstructing the <strong>'tree of life'</strong> and inferring the timing of evolutionary events.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Molecular Clock Theory:</strong> Posits that the rate at which <strong>mutations</strong> accumulate or are removed from a population's genome is relatively constant and proportional to the rate of acquiring new mutations.</p></div><p>While the mutation rate can vary between different species, this theory allows scientists to estimate the time elapsed between various <strong>evolutionary events</strong>.</p><p>By using known mutation rates and benchmarking against events like the evolution of the first mammal or the age of fossils, researchers can map out the timeline of life's origins.</p><h4>Early Life Forms and Geological Evidence</h4><p>Earlier findings from the <strong>Pilbara Craton</strong> in <strong>Australia</strong> indicated that the earliest known life forms date back approximately <strong>3.4 billion years ago</strong>.</p><p>These geological benchmarks are crucial for calibrating the molecular clock and understanding the deep history of life on Earth.</p><h4>Significance of LUCA Research</h4><p>Understanding <strong>LUCA</strong> is fundamental to comprehending the initial stages of life's emergence and subsequent evolution on Earth.</p><p>The insights gained are vital for the search for extraterrestrial life and for developing advanced <strong>synthetic organisms</strong>.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Relevance:</strong> Knowledge of <strong>LUCA</strong> and theories of life's origin is essential for questions on <strong>Evolution</strong>, <strong>Biotechnology</strong>, and <strong>Astrobiology</strong> in <strong>GS Paper III</strong>.</p></div><h4>Recent Discovery: Obelisks</h4><p>Separately, scientists at <strong>Stanford University</strong> recently identified a novel, remarkably simple form of life termed <strong>"obelisks."</strong></p><p>This discovery highlights the ongoing exploration and expansion of our understanding of biological diversity and fundamental life forms.</p>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •LUCA is the Last Universal Common Ancestor, the single cell from which all life on Earth diverged.
- •Recent studies suggest LUCA formed about 200 million years after Earth, earlier than previously thought.
- •LUCA had a small genome (2.5M bases, 2000 proteins) and possibly immunity genes.
- •The Molecular Clock theory uses mutation rates to reconstruct the 'tree of life' and date evolutionary events.
- •Competing theories for life's origin include Oparin-Haldane (primordial soup, supported by Miller-Urey experiment) and Panspermia (extraterrestrial origin).
- •Research on LUCA is crucial for astrobiology, synthetic biology, and understanding Earth's evolutionary history.
- •Recent discovery of "obelisks" highlights ongoing exploration of fundamental life forms.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•General scientific consensus on evolutionary biology and astrobiology