Gravity Energy Storage - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Gravity Energy Storage
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
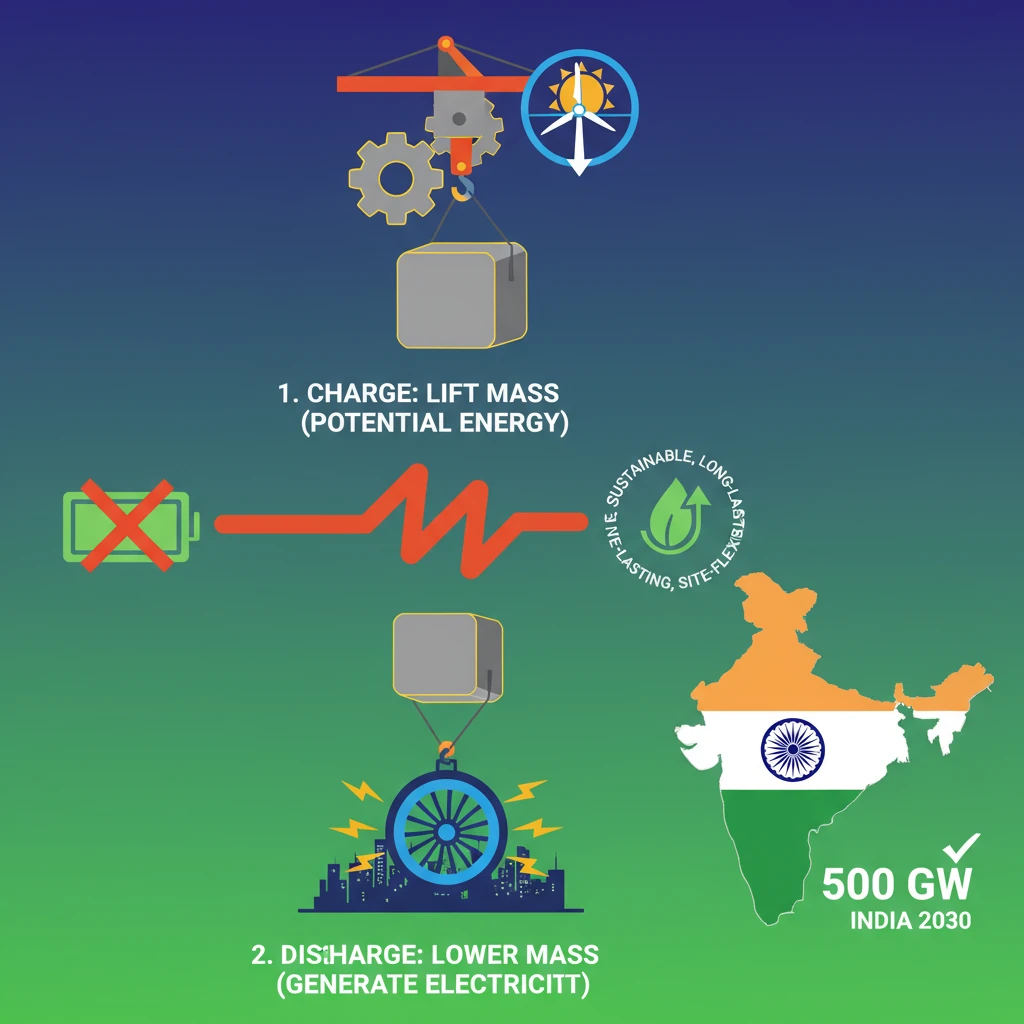
<h4>Introduction to Gravity Energy Storage</h4><p><strong>Gravity Energy Storage (GES)</strong> is emerging as an innovative and cost-effective solution. It directly addresses a key challenge faced by <strong>renewable energy sources</strong> like solar and wind.</p><p>This technology also serves as a promising alternative to traditional <strong>battery energy storage systems</strong>, which often involve chemical components.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>GES</strong> offers a sustainable and long-lasting method to store energy, crucial for stabilizing modern electricity grids.</p></div><h4>Defining Gravity Energy Storage</h4><p><strong>Gravity Energy Storage</strong> is an innovative technology designed to store energy by leveraging the fundamental force of <strong>gravity</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Definition</strong>: It is a system that stores energy by lifting a heavy mass and releases it by allowing the mass to descend, converting potential energy into usable electricity.</p></div><h4>Mechanism of Operation</h4><p>The core principle of <strong>Gravity Energy Storage</strong> lies in the concept of <strong>potential energy</strong>. It involves lifting <strong>heavy masses</strong> during periods when there is an excess of energy generation.</p><p>When electricity is needed, these heavy masses are released. Their descending motion is then converted into electrical energy.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Energy Conversion</strong>: A <strong>turbine</strong> or <strong>generator</strong> is used to convert the kinetic energy from the descending motion of the mass into electricity.</p></div><p>A common design involves a <strong>fluid-filled cylinder</strong> equipped with a <strong>heavy piston</strong>.</p><ul><li>During surplus electricity generation, the <strong>piston is lifted</strong>, effectively storing energy as potential energy.</li><li>When energy is required, the <strong>piston descends</strong>, driving water or another fluid through a <strong>turbine</strong> to produce power.</li></ul><h4>Environmental Sustainability</h4><p>Unlike traditional <strong>battery storage</strong>, <strong>gravity energy systems</strong> avoid reliance on <strong>chemical-based energy storage</strong> methods.</p><p>This characteristic makes them inherently more <strong>environmentally sustainable</strong> and ensures a significantly <strong>longer operational lifespan</strong>.</p><h4>Key Advantages of Gravity Energy Storage</h4><ul><li><strong>Site Flexibility</strong>: Unlike <strong>pumped-hydro systems</strong> which require specific geographical features, <strong>gravity energy systems</strong> can be implemented in diverse locations.</li><li><strong>Scalability</strong>: These systems can be easily adapted to different energy capacities, making them ideal for both small-scale and large-scale <strong>grid-scale storage</strong> applications.</li><li><strong>Longevity</strong>: With minimal mechanical degradation, <strong>GES</strong> systems are designed to operate for decades, requiring relatively low maintenance.</li></ul><h4>Addressing Renewable Energy Challenges in India</h4><p><strong>Gravity Energy Storage</strong> can effectively address the significant <strong>intermittency issue</strong> of renewable energy sources in India. Solar and wind energy are not constant; they depend heavily on weather conditions and time of day.</p><p>With initiatives like the <strong>National Solar Mission</strong> and expanding <strong>wind power capacities</strong>, <strong>GES</strong> can help stabilize the grid by providing reliable storage.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Reliable energy storage</strong> is essential to balance electricity supply and demand, particularly during periods of <strong>peak usage</strong> or when renewable energy production is low.</p></div><p>These systems offer <strong>high energy capacity</strong>, capable of storing large amounts of energy. This bridges the gap during periods of low renewable production.</p><p><strong>GES</strong> also boasts a <strong>low environmental impact</strong>. It reduces harmful chemical reactions and minimizes disposal issues, thereby supporting India's transition to a greener planet.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight</strong>: India aims to achieve <strong>500 GW of non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030</strong> under its renewable energy initiatives. <strong>Gravity Energy Storage</strong> can complement these efforts by providing reliable and cost-effective storage for the large-scale solar and wind projects being deployed across the country, a crucial point for <strong>GS Paper 3</strong>.</p></div>
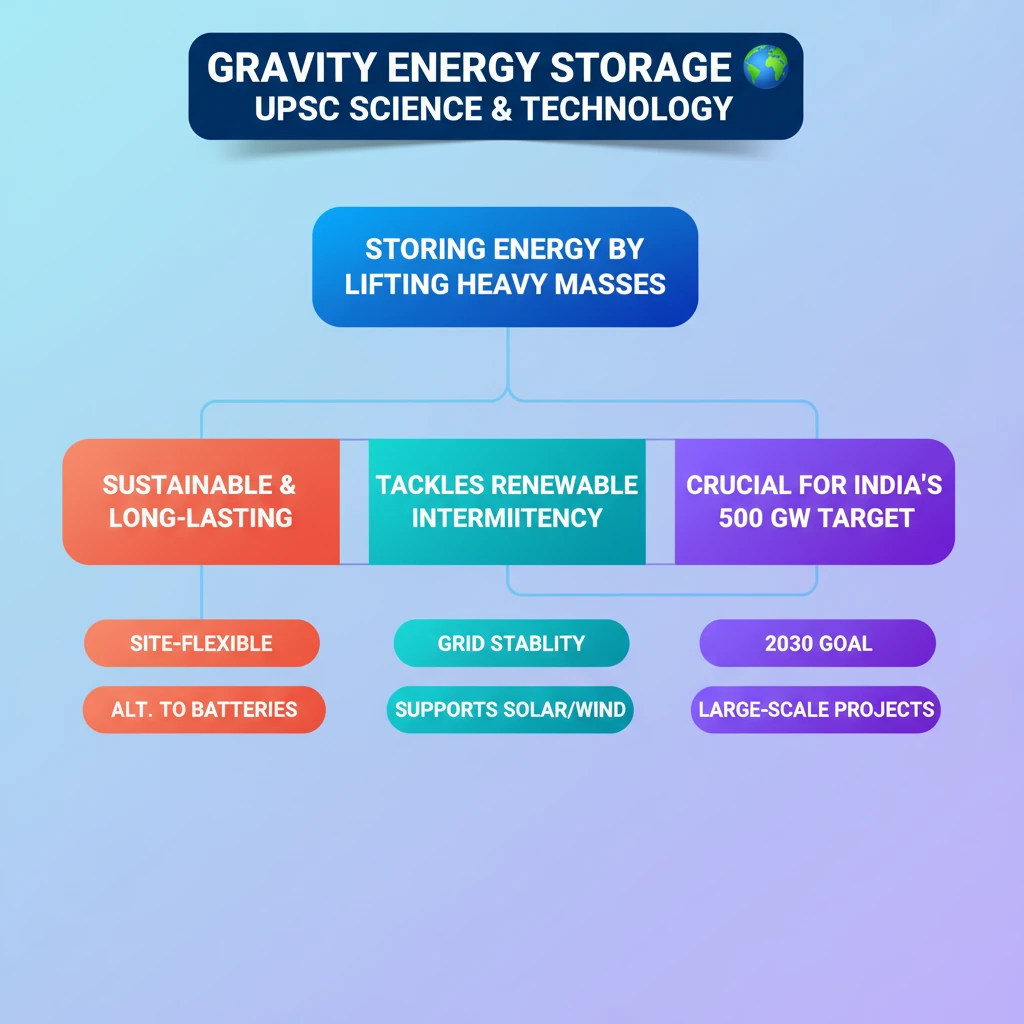
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Gravity Energy Storage (GES) stores energy by lifting heavy masses (potential energy) and releases it by lowering them to generate electricity.
- •GES is a sustainable, long-lasting, and site-flexible alternative to traditional chemical batteries.
- •It effectively addresses the intermittency of renewable energy sources like solar and wind, crucial for grid stability.
- •GES is vital for India's target of 500 GW non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030, supporting large-scale renewable projects.
- •Common designs include fluid-piston systems or stacked block/weight systems, converting kinetic energy into electricity via turbines.
- •Offers high energy capacity and low environmental impact compared to chemical storage.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Energy Vault official website (for example details)
•Gravitricity official website (for example details)
•General knowledge on renewable energy storage technologies and physics principles