What is Machine Learning? - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What is Machine Learning?
Medium⏱️ 10 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
<h4>Understanding Machine Learning: Core Concepts</h4><p><strong>Machine Learning (ML)</strong> is a significant branch of <strong>Artificial Intelligence (AI)</strong>. It empowers computers to learn from experience by analyzing data and algorithms.</p><p>This learning process allows systems to progressively enhance their accuracy and performance over time, without explicit programming for every task.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Definition:</strong> <strong>Machine Learning</strong> is a subset of <strong>AI</strong> that enables systems to learn from data, identify patterns, and make decisions with minimal human intervention.</p></div><h4>Operating Mechanism of Machine Learning</h4><p>The functioning of a <strong>Machine Learning model</strong> involves a cyclical process of prediction, evaluation, and optimization. This iterative approach refines the model's capabilities.</p><p>It continuously adjusts its internal parameters based on feedback, striving for higher accuracy in its predictions.</p><h5>1. Decision Process</h5><p>In the initial stage, <strong>algorithms</strong> within the ML model analyze input data. Based on this analysis, they either predict an outcome or classify the data into predefined categories.</p><p>The input data can be either <strong>labelled</strong>, meaning it comes with associated target outputs, or <strong>unlabelled</strong>, requiring the model to find inherent structures.</p><h5>2. Error Function (Loss Function)</h5><p>Following a prediction, an <strong>error function</strong>, also known as a <strong>loss function</strong>, comes into play. Its purpose is to quantify the discrepancy between the model's prediction and the actual, known outcome.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The <strong>error function</strong> is crucial as it provides a measure of how 'wrong' the model's current predictions are, guiding subsequent adjustments.</p></div><h5>3. Model Optimization Process</h5><p>The final step in the cycle is <strong>model optimization</strong>. Here, the model iteratively adjusts its internal parameters, often called <strong>weights</strong>, to minimize the error identified by the error function.</p><p>This process continues until the model achieves an acceptable level of accuracy, meaning its predictions are consistently close to the actual outcomes.</p><h4>ML vs. Deep Learning vs. Neural Networks</h4><p>Understanding the hierarchical relationship between these terms is vital for grasping the landscape of AI. They represent progressively specialized areas within the broader field.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>UPSC often tests conceptual clarity on these distinctions. A clear understanding of the hierarchy is key for both Prelims and Mains.</p></div><h5>Hierarchy of AI Technologies</h5><ul><li><strong>Artificial Intelligence (AI)</strong>: The broadest field, aiming to create intelligent machines that can reason, learn, and act.</li><li><strong>Machine Learning (ML)</strong>: A subset of <strong>AI</strong>, focusing on enabling systems to learn from data without explicit programming.</li><li><strong>Deep Learning (DL)</strong>: A specialized subset of <strong>ML</strong>, characterized by the use of multi-layered <strong>neural networks</strong>.</li><li><strong>Neural Networks (NN)</strong>: The underlying architecture that <strong>Deep Learning</strong> models rely upon.</li></ul><h5>Deep Learning Explained</h5><p><strong>Deep Learning</strong> is a powerful subset of <strong>Machine Learning</strong>. It distinguishes itself by employing <strong>neural networks</strong> that have a large number of layers, often referred to as <strong>deep neural networks</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Feature:</strong> <strong>Deep Learning</strong> can effectively process <strong>unstructured data</strong>, such as images, audio, and text, often without the need for extensive <strong>labelled datasets</strong> in its initial stages.</p></div><h5>Neural Networks Explained</h5><p><strong>Neural Networks</strong> are a specific type of <strong>Machine Learning model</strong> inspired by the structure and function of the human brain. They consist of interconnected layers of nodes.</p><p>These layers typically include an <strong>input layer</strong>, one or more <strong>hidden layers</strong>, and an <strong>output layer</strong>, allowing for complex pattern recognition.</p><h5>Complexity and Specialization</h5><p>As one moves from the general concept of <strong>AI</strong> towards <strong>Neural Networks</strong>, the complexity and specificity of the tasks that can be addressed tend to increase.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Deep Learning</strong> and <strong>Neural Networks</strong> are highly specialized tools designed for intricate problems, operating within the larger framework of <strong>Artificial Intelligence</strong>.</p></div>
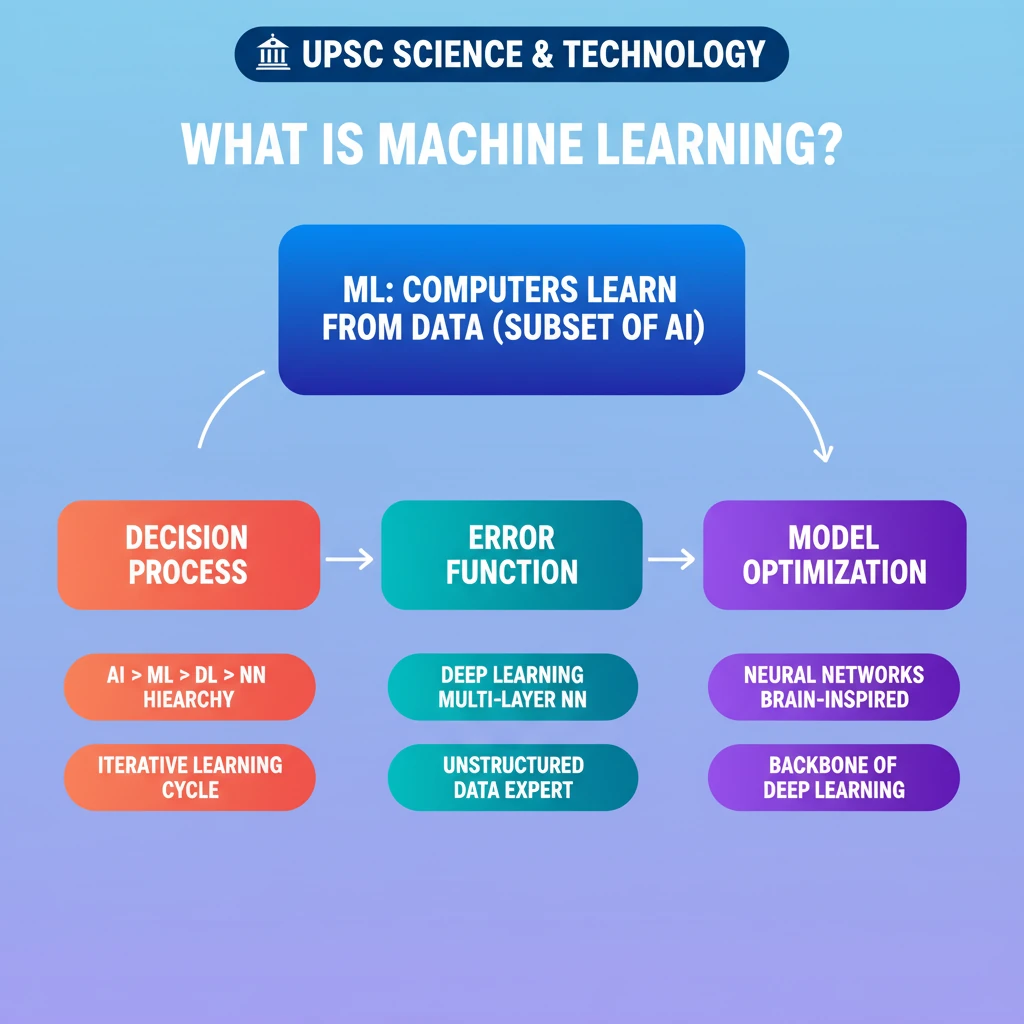
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI enabling computers to learn from data.
- •ML operates via a decision process, error function, and iterative model optimization.
- •AI > ML > Deep Learning > Neural Networks is the hierarchy of these technologies.
- •Deep Learning uses multi-layered neural networks and excels with unstructured data.
- •Neural Networks are brain-inspired models forming the backbone of Deep Learning.
- •ML is transforming sectors like healthcare, finance, and e-commerce globally.
- •India has initiatives like #AIforAll to leverage ML for national development.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•NITI Aayog's National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence
•IndiaAI Portal (indiaai.gov.in)
•General knowledge on AI/ML concepts and history