State of Biobanks in India - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

State of Biobanks in India
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
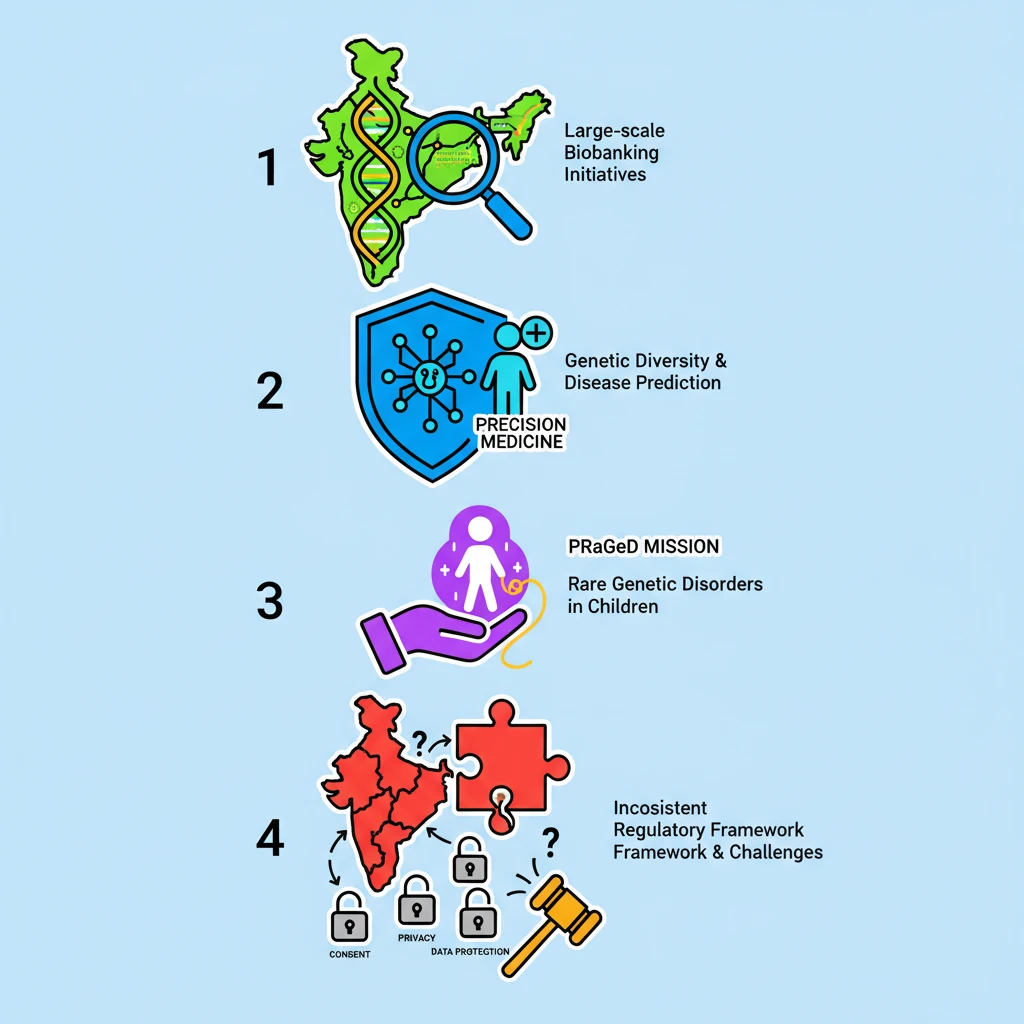
<h4>Introduction to Biobanks in India</h4><p><strong>Biobanks</strong> are crucial repositories that store biological samples (like blood, tissue, DNA) and associated health information. They are vital for medical research, especially in understanding diseases, developing new diagnostics, and advancing <strong>precision medicine</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>In India, the development of biobanking infrastructure and research initiatives is progressing, aiming to leverage the country's diverse genetic landscape for healthcare advancements.</p></div><h4>Key Initiatives in Indian Biobanking</h4><p>India has launched several significant programs to bolster its biobanking capabilities and genetic research. These initiatives focus on different aspects of human health and genetic diversity.</p><h4>Genome India Programme</h4><p>The <strong>Genome India Programme</strong> is a flagship initiative focused on sequencing the genomes of a large and diverse Indian population. It aims to create a comprehensive map of genetic variations.</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li><strong>Scope:</strong> Completed sequencing of <strong>10,000 genomes</strong>.</li><li><strong>Diversity:</strong> Samples collected from <strong>99 distinct ethnic groups</strong> across India.</li><li><strong>Primary Goal:</strong> To identify genetic markers for rare genetic diseases and develop targeted treatments.</li></ul></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>This program is crucial for understanding India's unique genetic diversity and its implications for personalized medicine, a key topic for <strong>UPSC Mains GS-III Science & Technology</strong>.</p></div><h4>Phenome India Project</h4><p>Complementing genomic studies, the <strong>Phenome India Project</strong> focuses on collecting phenotypic data, which includes observable characteristics and health information of individuals.</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li><strong>Scope:</strong> Gathered <strong>10,000 samples</strong> across India.</li><li><strong>Objective:</strong> To enhance prediction models for complex diseases, particularly <strong>cardio-metabolic diseases</strong>.</li><li><strong>Significance:</strong> Links genetic information with lifestyle and environmental factors to provide a holistic view of disease risk.</li></ul></div><h4>Paediatric Rare Genetic Disorders (PRaGeD) Mission</h4><p>The <strong>PRaGeD Mission</strong> is specifically designed to address the challenges posed by rare genetic disorders affecting children in India. It focuses on early identification and therapeutic development.</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li><strong>Focus:</strong> Identifies new genes or genetic variants associated with paediatric rare genetic disorders.</li><li><strong>Aim:</strong> To develop <strong>targeted therapies</strong> and improve outcomes for affected children.</li></ul></div><h4>Regulatory Challenges in Indian Biobanking</h4><p>Despite significant research initiatives, India faces substantial hurdles in establishing a robust and consistent regulatory framework for biobanks. This inconsistency impedes the full realization of <strong>precision medicine's potential</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The absence of comprehensive regulations creates ambiguities concerning critical aspects of biobanking operations.</p></div><h4>Inconsistent Regulatory Framework</h4><p>India's regulatory landscape for biobanking is characterized by its fragmented and inconsistent nature. This contrasts sharply with many developed nations.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Key areas lacking comprehensive regulation in India include:</p><ul><li><strong>Informed Consent:</strong> Clear guidelines for obtaining and managing consent for sample collection and future use.</li><li><strong>Privacy:</strong> Robust measures to protect the personal and genetic information of donors.</li><li><strong>Data Protection:</strong> Legal frameworks to safeguard sensitive genetic data from misuse or breaches.</li></ul></div><h4>Global Comparison</h4><p>Many countries have established advanced and comprehensive regulatory frameworks for biobanking. These frameworks provide clarity and build public trust.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Countries with comprehensive biobanking regulations include:</p><ul><li><strong>United Kingdom (UK)</strong></li><li><strong>United States (US)</strong></li><li><strong>Japan</strong></li><li>Many <strong>European nations</strong></li></ul><p>These nations address issues like informed consent, privacy, and data protection through dedicated laws and guidelines.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Understanding these regulatory gaps is vital for policy-related questions in <strong>UPSC Mains GS-II Governance</strong> and <strong>GS-III Science & Technology</strong>, especially concerning ethical implications of emerging technologies.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •India is actively pursuing large-scale biobanking initiatives like Genome India and Phenome India.
- •These programs aim to map genetic diversity and understand disease predictors for precision medicine.
- •The PRaGeD Mission specifically targets rare genetic disorders in children.
- •A major challenge is India's inconsistent regulatory framework for biobanks, lacking comprehensive rules for consent, privacy, and data protection.
- •Robust regulations are crucial for realizing biobanking's full potential and ensuring ethical practices.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content