AR Gene Transfer Mechanisms: PBNPs, HGT, and OMVs - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
AR Gene Transfer Mechanisms: PBNPs, HGT, and OMVs
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
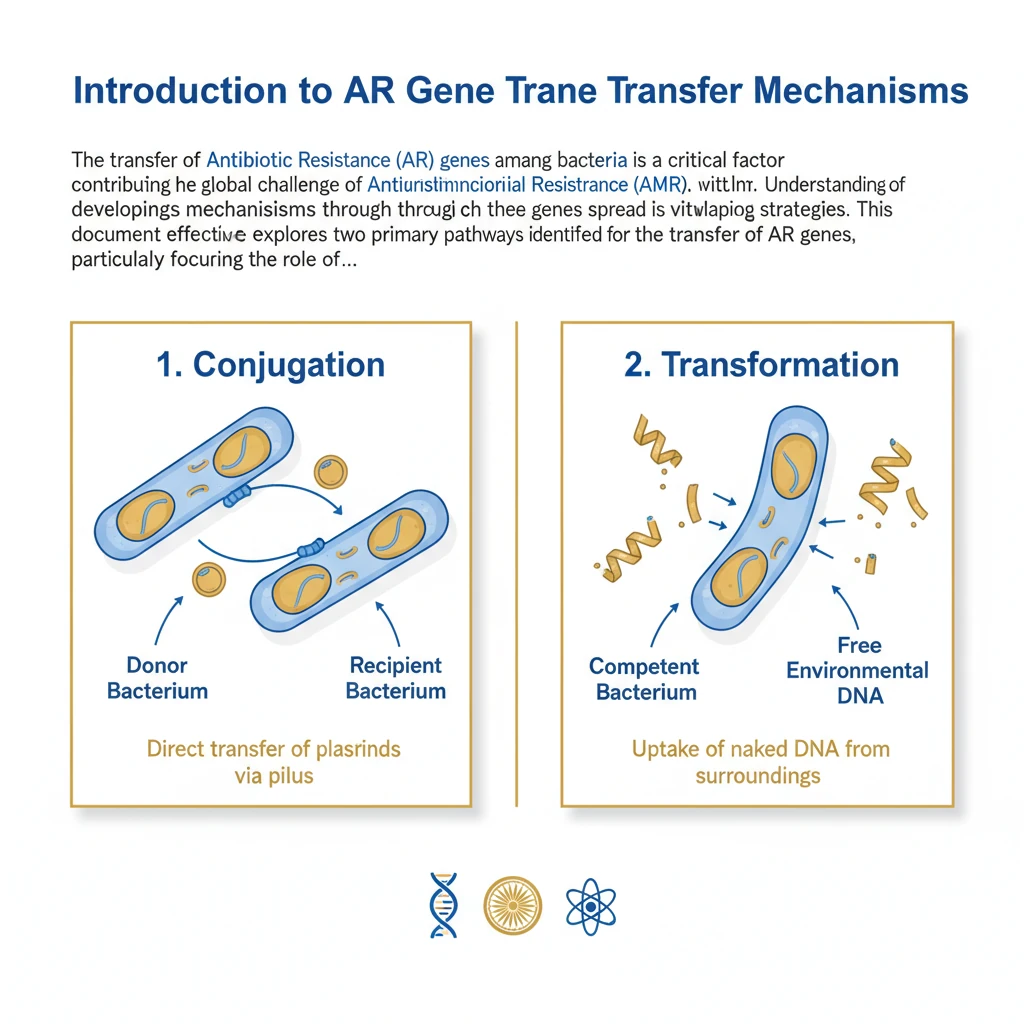
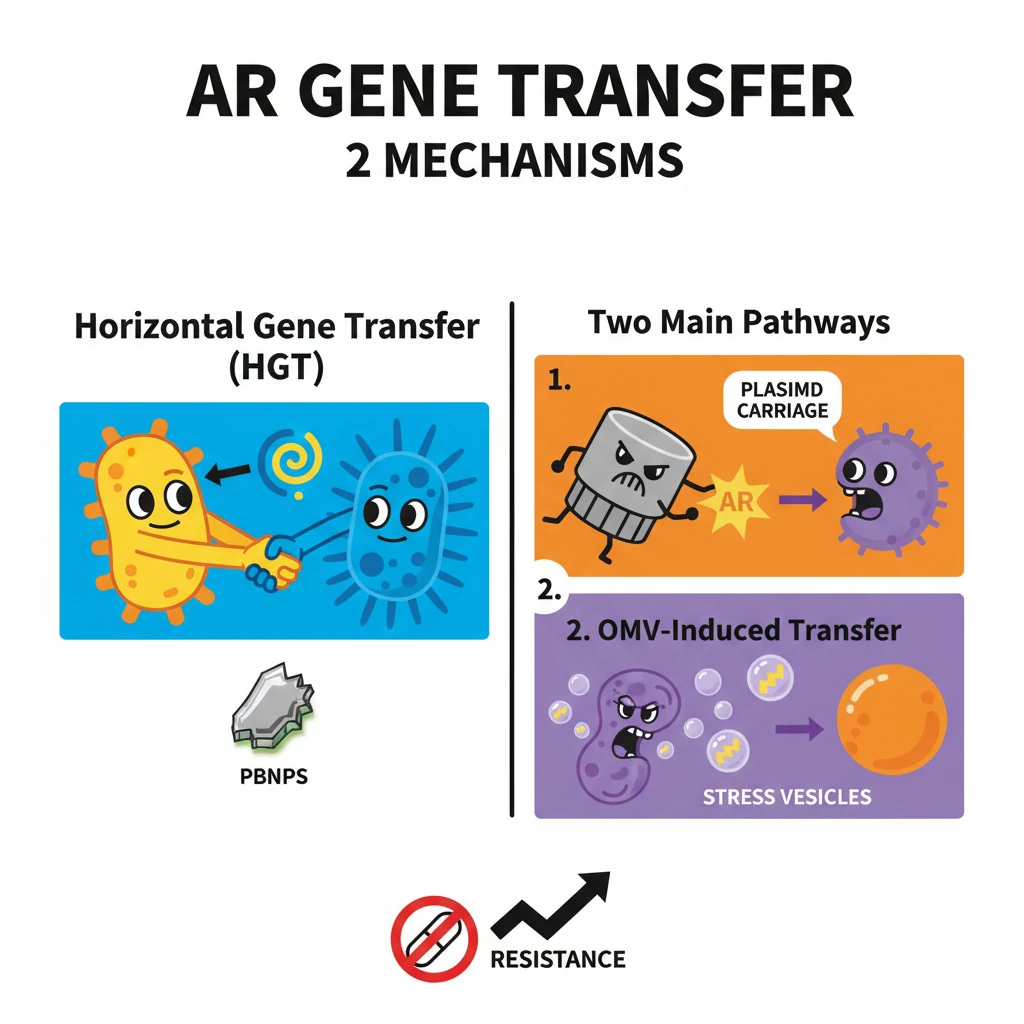
<h4>Introduction to AR Gene Transfer Mechanisms</h4><p>The transfer of <strong>Antibiotic Resistance (AR) genes</strong> among bacteria is a critical factor contributing to the global challenge of <strong>Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)</strong>. Understanding the mechanisms through which these genes spread is vital for developing effective mitigation strategies.</p><p>This document explores two primary pathways identified for the transfer of AR genes, particularly focusing on the role of <strong>nanoplastics</strong> as facilitators in this process.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Key Concept:</strong> The rapid spread of <strong>AR genes</strong> through various mechanisms poses a significant threat to public health and the efficacy of existing antibiotics.</p></div><h4>Horizontal Gene Transfer (HGT)</h4><p><strong>Horizontal Gene Transfer (HGT)</strong> is a fundamental mechanism by which bacteria acquire new genetic material. Unlike vertical gene transfer (from parent to offspring), HGT involves the direct transfer of genetic information between organisms, even across different species.</p><div class='info-box'><p>In the context of AR, <strong>Polyethylene terephthalate bottle-derived nanoplastics (PBNPs)</strong> have been shown to significantly facilitate the transfer of <strong>AR genes</strong>. This occurs specifically from bacteria like <strong><em>E. coli</em></strong> to other species such as <strong><em>Lactobacillus acidophilus</em></strong> via HGT.</p></div><p>This process allows bacteria to rapidly adapt to new environments and acquire resistance traits from other bacteria, accelerating the evolution of antibiotic-resistant strains.</p><h4>Direct Transformation Pathway</h4><p>One of the ways <strong>PBNPs</strong> facilitate HGT is through a <strong>Direct Transformation Pathway</strong>. In this mechanism, the nanoplastics act as physical carriers for genetic material.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Specifically, <strong>PBNPs</strong> transport <strong>AR plasmids</strong> directly across bacterial membranes. These plasmids are small, circular DNA molecules that often carry genes for antibiotic resistance.</p></div><p>By physically assisting the passage of these plasmids, PBNPs effectively promote the direct transfer of <strong>AR genes</strong> into recipient bacterial cells, enabling them to acquire resistance.</p><h4>OMV-Induced Transfer Pathway</h4><p>Another significant pathway facilitated by <strong>PBNPs</strong> is the <strong>OMV-Induced Transfer Pathway</strong>. This mechanism involves the bacterial response to environmental stressors.</p><p>Exposure to <strong>PBNPs</strong> induces <strong>oxidative stress</strong> within bacterial cells. This stress, in turn, triggers an increased secretion of <strong>Outer Membrane Vesicles (OMVs)</strong> from the bacteria.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>OMVs</strong> are small, spherical structures released by bacteria, which can encapsulate various cellular contents, including <strong>AR genes</strong>. These vesicles then act as vehicles for gene transfer.</p></div><p>The <strong>OMVs</strong>, carrying the <strong>AR genes</strong>, facilitate their transfer between different bacterial species. This includes transfers between both <strong>beneficial bacteria</strong> and <strong>pathogenic bacteria</strong>, further disseminating resistance.
💡 Key Takeaways
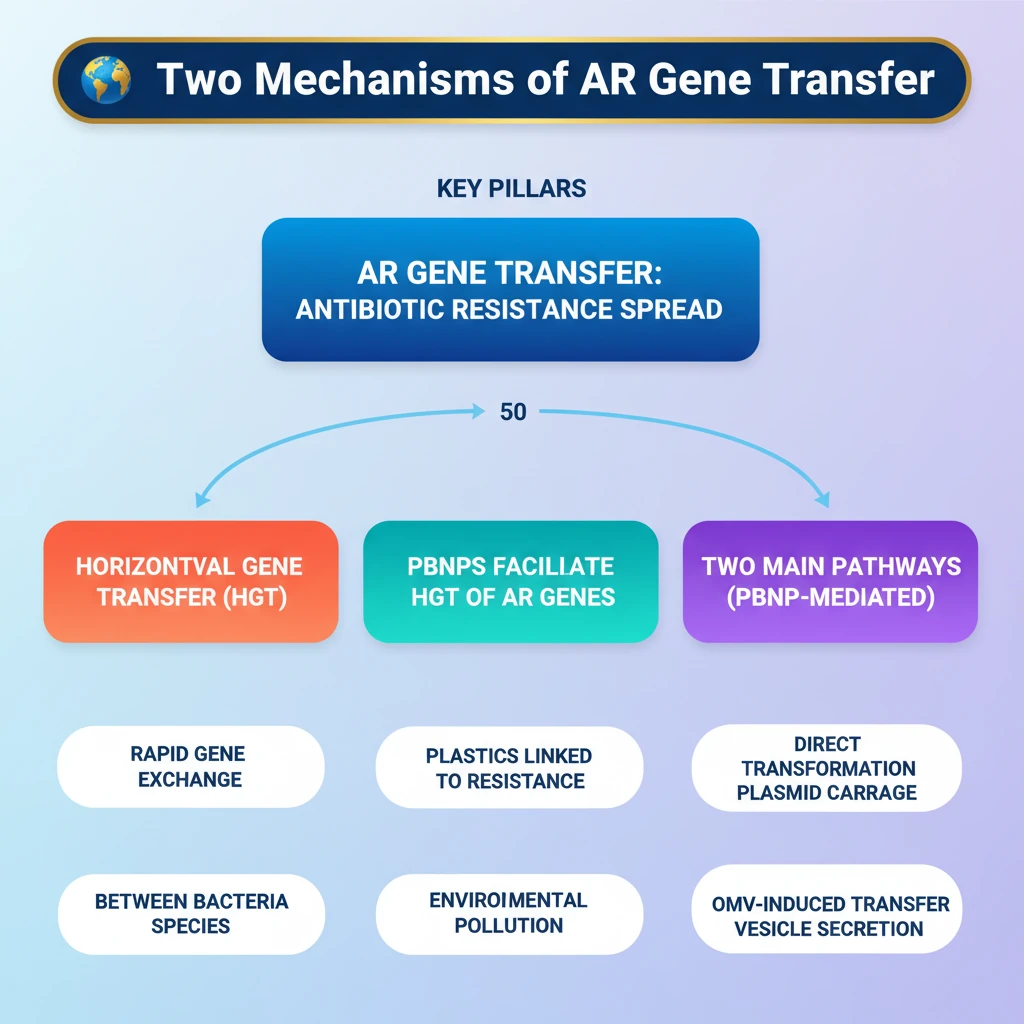
- •AR gene transfer is a critical factor in the spread of antibiotic resistance.
- •Horizontal Gene Transfer (HGT) allows rapid gene exchange between different bacterial species.
- •Polyethylene terephthalate bottle-derived nanoplastics (PBNPs) facilitate HGT of AR genes.
- •PBNPs act via two main pathways: Direct Transformation (physical carriage of plasmids) and OMV-Induced Transfer (stress-induced vesicle secretion).
- •Nanoplastics link environmental pollution directly to the acceleration of antibiotic resistance, posing a significant public health threat.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•General scientific literature on Horizontal Gene Transfer and Antibiotic Resistance
•Research papers on nanoplastics and microbial interactions