What are Sugar and Sugar Substitutes? - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
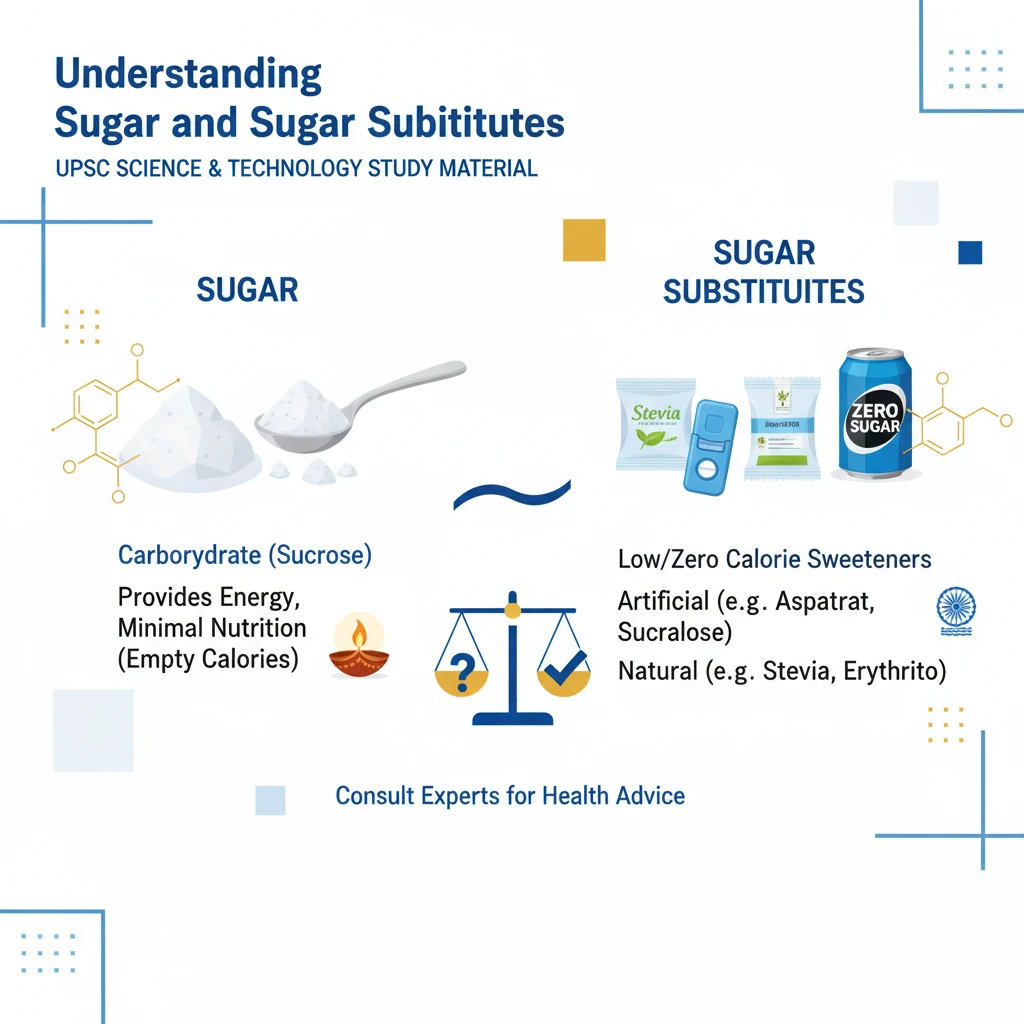
What are Sugar and Sugar Substitutes?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
<h4>Understanding Sugar and Sugar Substitutes</h4><p><strong>Sugar</strong> is a type of <strong>carbohydrate</strong>, alongside <strong>fibre</strong> and <strong>starch</strong>. While carbohydrates are vital for human health, sugar itself is not considered an essential nutrient for the body.</p><p>The most commonly used sweetener globally is <strong>white table sugar</strong>, scientifically known as <strong>sucrose</strong>. It provides energy but offers minimal nutritional value beyond calories.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Other Natural Sugars:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Fructose</strong> (found in fruits)</li><li><strong>Galactose</strong> (part of lactose)</li><li><strong>Glucose</strong> (primary energy source)</li><li><strong>Lactose</strong> (milk sugar)</li><li><strong>Maltose</strong> (malt sugar)</li></ul></div><h4>What are Sugar Substitutes?</h4><p><strong>Sugar substitutes</strong> are substances that provide a sweet taste similar to sugar but with significantly fewer or no calories. They are designed to help reduce overall calorie and sugar intake.</p><p>These substitutes are frequently found in food and beverage products marketed as <strong>“sugar-free”</strong>, <strong>“keto”</strong>, <strong>“low carb”</strong>, or <strong>“diet”</strong> options. Their primary appeal lies in their ability to deliver sweetness without the caloric load of traditional sugar.</p><h4>Types of Sugar Substitutes</h4><div class='key-point-box'><p>Sugar substitutes can be broadly categorized into three main types based on their origin and properties.</p></div><h5>Artificial Sweeteners (Non-Nutritive Sweeteners - NNS)</h5><p><strong>Artificial Sweeteners</strong>, also known as <strong>Non-Nutritive Sweeteners (NNS)</strong>, are primarily synthesized from chemicals in laboratories. Some can also be derived from natural herbs.</p><p>These sweeteners are remarkably potent, often being <strong>200 to 700 times sweeter</strong> than common table sugar (sucrose). They provide intense sweetness with virtually no calories.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Examples of Artificial Sweeteners:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Acesulfame Potassium (Ace-K)</strong></li><li><strong>Advantame</strong></li><li><strong>Aspartame</strong></li><li><strong>Neotame</strong></li><li><strong>Saccharin</strong></li><li><strong>Sucralose</strong></li></ul></div><h5>Sugar Alcohols</h5><p><strong>Sugar Alcohols</strong> are synthetically derived from sugars. They are commonly incorporated into many processed food products, offering both sweetness and texture.</p><p>These are generally <strong>less sweet</strong> than artificial sweeteners. They are often used in items like <strong>chewing gum</strong> and <strong>hard candies</strong> to add bulk, texture, and a mild sweet taste.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Examples of Sugar Alcohols:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Erythritol</strong></li><li><strong>Isomalt</strong></li><li><strong>Lactitol</strong></li><li><strong>Maltitol</strong></li><li><strong>Sorbitol</strong></li><li><strong>Xylitol</strong></li></ul></div><h5>Novel Sweeteners</h5><p><strong>Novel Sweeteners</strong> are derived from natural sources, offering a blend of benefits found in both artificial and natural sweeteners. They are a newer class of sugar alternatives.</p><p>They are characterized by being <strong>low in calories</strong> and sugar, which helps in preventing weight gain and managing blood sugar spikes. These are typically <strong>less processed</strong> and closely resemble their natural origins.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Examples of Novel Sweeteners:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Allulose</strong></li><li><strong>Monk fruit</strong></li><li><strong>Stevia</strong></li><li><strong>Tagatose</strong></li></ul></div><h4>Sucralose Study Findings and Significance for India</h4><p>Recent studies have shown that participants using <strong>sucralose</strong> experienced slight improvements in key health indicators. These included a reduction in <strong>body weight</strong>, <strong>waist circumference</strong>, and <strong>Body Mass Index (BMI)</strong>.</p><p>The judicious and informed use of sucralose can play a significant role in reducing an individual's overall <strong>calorie and sugar intake</strong>. This aspect is particularly crucial for the effective management of conditions like <strong>diabetes</strong>.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>These findings hold substantial significance for <strong>India</strong>, a country where the adoption of artificial sweeteners is currently less common. The study suggests that sucralose could potentially enhance <strong>dietary compliance</strong> and support <strong>weight management</strong> efforts for diabetic patients across the nation. This has implications for public health policies.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Sugar is a carbohydrate, not essential, with sucrose being the most common.
- •Sugar substitutes offer sweetness with fewer/no calories, aiding in calorie reduction and diabetes management.
- •Three main types: Artificial Sweeteners (e.g., sucralose), Sugar Alcohols (e.g., xylitol), and Novel Sweeteners (e.g., stevia).
- •Sucralose has shown potential in improving body weight and BMI, crucial for India's diabetic population.
- •Judicious use of sugar substitutes is key, as part of an overall healthy diet and lifestyle.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content