Dementia: Definition, Symptoms, and Cognitive Impact - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
Dementia: Definition, Symptoms, and Cognitive Impact
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
<h4>Understanding Dementia: A Syndrome of Cognitive Decline</h4><p><strong>Dementia</strong> is not a single disease but a <strong>syndrome</strong>. It typically presents as a <strong>chronic</strong> or <strong>progressive</strong> condition, meaning its effects tend to worsen over time rather than improve.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Definition:</strong> <strong>Dementia</strong> is a syndrome characterized by a deterioration in <strong>cognitive function</strong> – the ability to process thought – beyond what is considered normal for typical biological aging.</p></div><p>This deterioration significantly impacts an individual's daily life, affecting various mental capacities essential for independent functioning.</p><h4>Key Cognitive Functions Affected by Dementia</h4><p>Dementia affects a broad spectrum of cognitive abilities, leading to noticeable changes in a person's mental faculties. These impairments are often progressive and can severely hinder daily activities.</p><ul><li><strong>Memory:</strong> Difficulty recalling recent events, names, or conversations.</li><li><strong>Thinking:</strong> Challenges with problem-solving, abstract thought, and reasoning.</li><li><strong>Orientation:</strong> Confusion about time, place, or personal identity.</li><li><strong>Comprehension:</strong> Struggling to understand spoken or written language.</li><li><strong>Calculation:</strong> Impairment in basic arithmetic and financial management.</li><li><strong>Learning Capacity:</strong> Reduced ability to acquire new information or skills.</li><li><strong>Language:</strong> Difficulties with finding words, speaking, or understanding communication.</li><li><strong>Judgment:</strong> Poor decision-making and impaired ability to assess situations.</li></ul><h4>Unaffected Aspect: Consciousness</h4><div class='key-point-box'><p>An important distinction in <strong>dementia</strong> is that, despite severe cognitive decline, the individual's <strong>consciousness</strong> is generally not affected. This means they remain awake and aware of their surroundings, even if their ability to interact meaningfully is compromised.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>For <strong>UPSC Mains GS Paper 2 (Social Justice)</strong> and <strong>GS Paper 3 (Science & Technology)</strong>, understanding <strong>dementia</strong> is crucial. It relates to public health challenges, elderly care, and advancements in neurological sciences. Differentiate it from normal aging and other neurological conditions.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
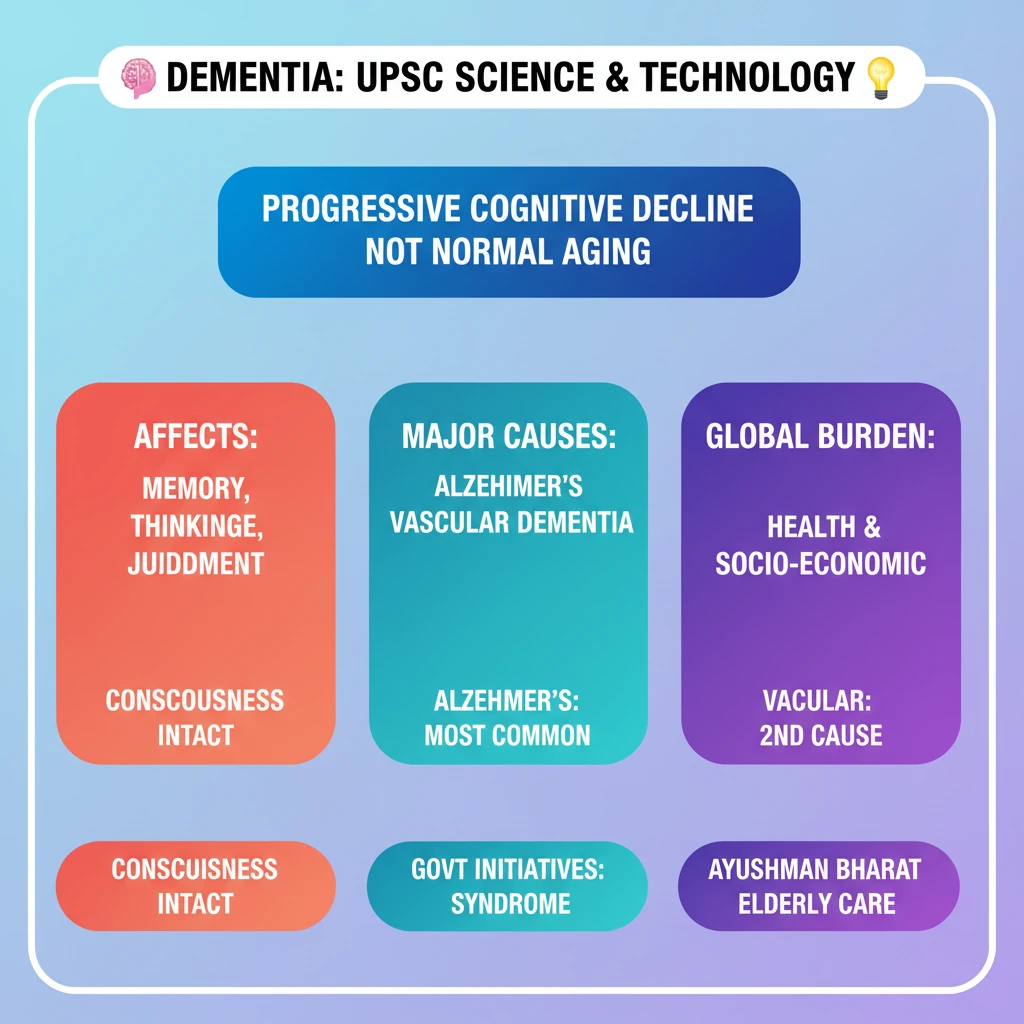
- •Dementia is a syndrome of progressive cognitive decline, not a normal part of aging.
- •It affects memory, thinking, language, judgment, and other cognitive functions, but consciousness remains intact.
- •Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause, followed by vascular dementia.
- •Dementia poses a significant global health and socio-economic burden.
- •Government programs like NPHCE and Ayushman Bharat indirectly address aspects of elderly care relevant to dementia.
- •Early diagnosis, caregiver support, and continued research are crucial for managing dementia.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) - Dementia Information Page
•Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India - National Programme for Health Care of the Elderly (NPHCE) documents
•Alzheimer's Association - About Alzheimer's and Dementia