Natural and artificial neurons - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
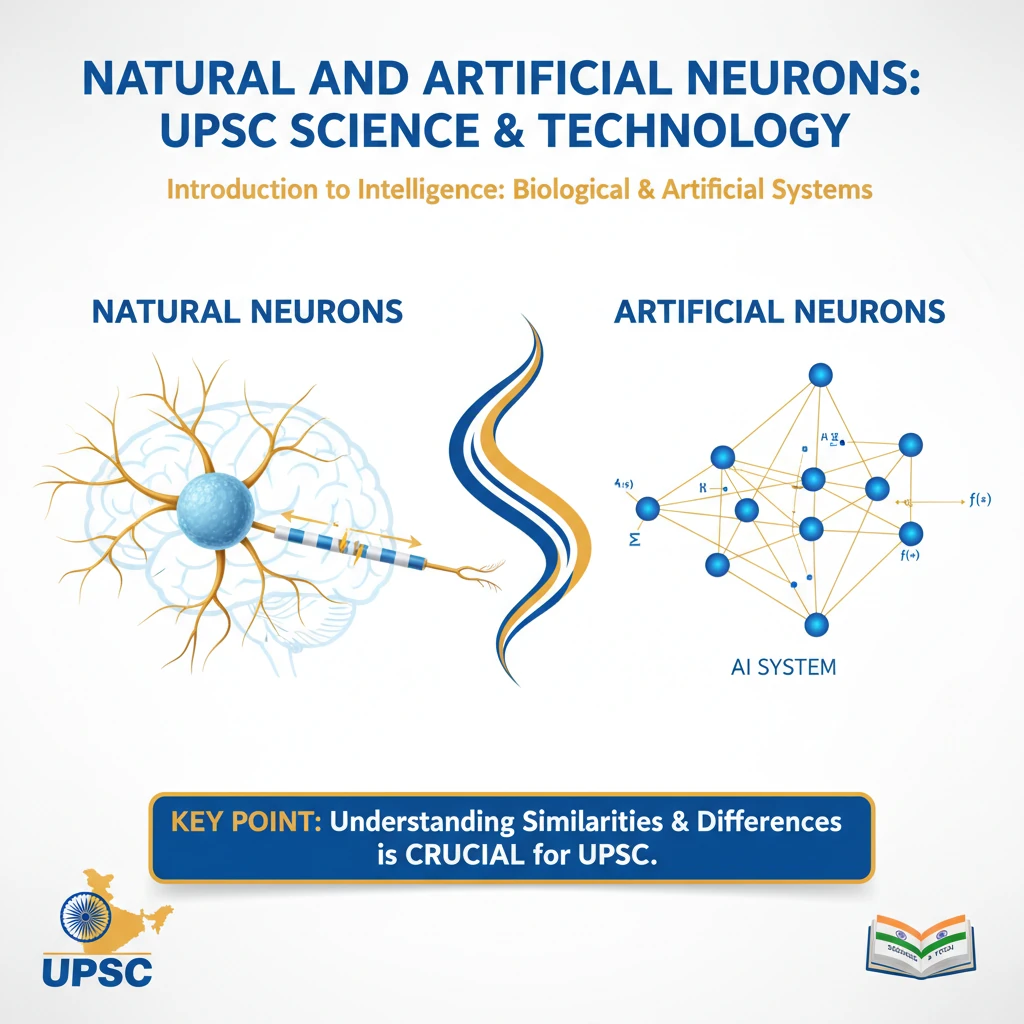
Natural and artificial neurons
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
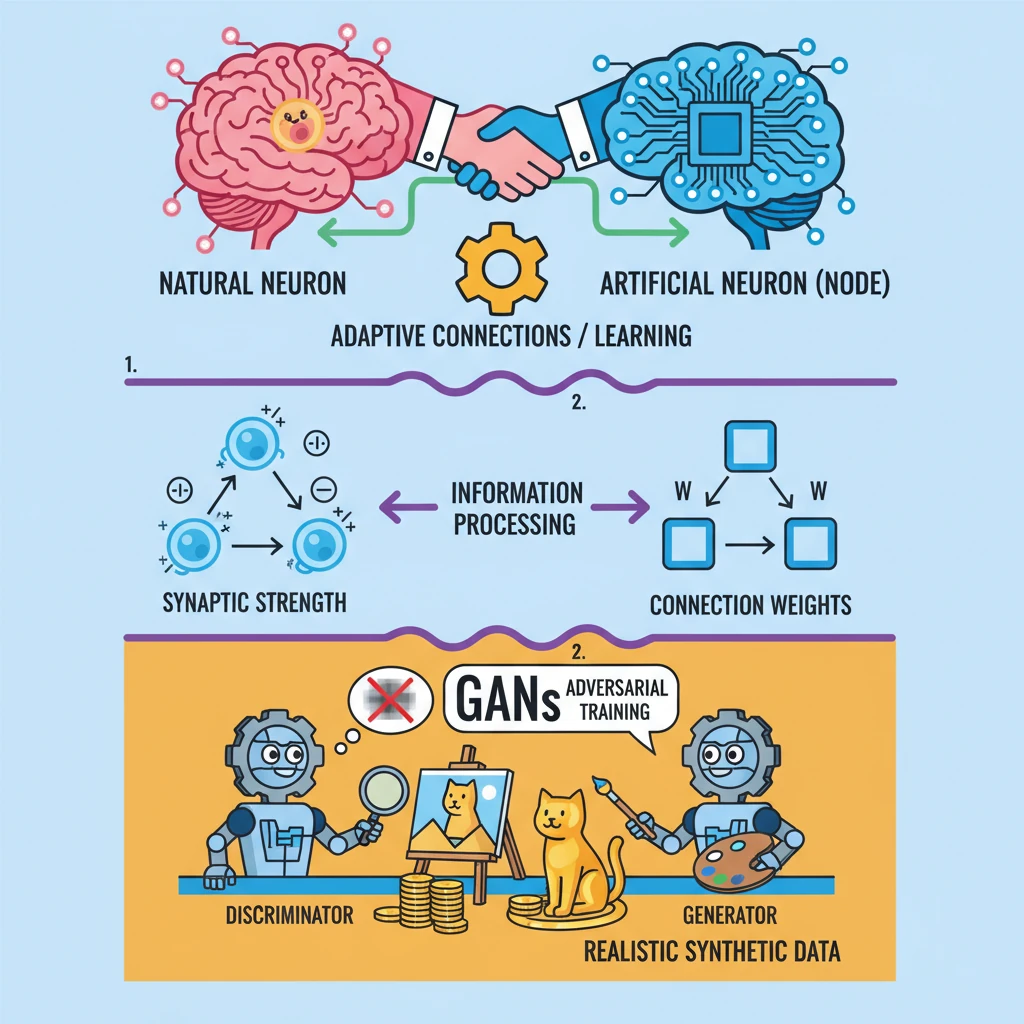
<h4>Introduction to Neurons: Natural and Artificial</h4><p>The concept of <strong>neurons</strong> is fundamental to understanding intelligence, both biological and artificial. While <strong>natural neurons</strong> form the basis of living brains, <strong>artificial neurons</strong> are the building blocks of modern <strong>Artificial Intelligence (AI)</strong> systems.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>Understanding the similarities and differences between these two types of neurons is crucial for comprehending the advancements in <strong>Machine Learning</strong> and <strong>Deep Learning</strong>.</p></div><h4>Natural Neurons: The Brain's Living Cells</h4><p>The brain's <strong>neural network</strong> is intricately constructed from billions of <strong>living cells</strong> known as <strong>neurons</strong>. These cells possess advanced internal machinery that enables complex biological computations.</p><p><strong>Natural neurons</strong> communicate with each other by sending signals across specialized junctions called <strong>synapses</strong>. This electrochemical signaling forms the basis of all brain activity, including thought, emotion, and learning.</p><div class='info-box'><p>When we <strong>learn</strong> new information or skills, the <strong>connections</strong> between certain <strong>natural neurons</strong> in the brain become <strong>stronger</strong>. Conversely, connections that are less frequently used or are irrelevant may become <strong>weaker</strong>.</p></div><h4>Artificial Neurons: Computational Nodes</h4><p><strong>Artificial neural networks (ANNs)</strong> are computational models inspired by the structure and function of biological brains. They are built from interconnected processing units called <strong>nodes</strong>, which are the artificial counterparts of natural neurons.</p><p>Each <strong>node</strong> in an <strong>ANN</strong> is typically scaled with a numerical <strong>value</strong>, representing the strength of the signal. These nodes are connected to each other, forming layers within the network.</p><div class='info-box'><p>During the <strong>training</strong> phase of an <strong>artificial neural network</strong>, the <strong>connections</strong> (or <strong>weights</strong>) between nodes that are frequently active together become <strong>stronger</strong>. Connections between less active or unhelpful nodes become <strong>weaker</strong>, mimicking the learning process in biological brains.</p></div><h4>Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Their Versatility</h4><p>The source content briefly mentions <strong>Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)</strong>, a powerful class of <strong>AI tools</strong>. GANs utilize a unique <strong>adversarial training</strong> technique involving two competing neural networks: a <strong>generator</strong> and a <strong>discriminator</strong>.</p><p>This adversarial process allows GANs to produce highly realistic and high-quality synthetic data, such as images, text, or audio. They have revolutionized the field of <strong>generative modeling</strong>.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>While <strong>GANs</strong> are an advanced application of <strong>artificial neural networks</strong>, understanding their core principle of learning and adaptation is essential for <strong>UPSC Mains GS Paper 3</strong>, particularly in the context of emerging technologies and their impact.</p></div><p><strong>GANs</strong> are incredibly versatile and find wide application in various fields. They are extensively used in <strong>image synthesis</strong>, creating new images from scratch, and <strong>style transfer</strong>, applying the artistic style of one image to another.</p><p>Furthermore, <strong>GANs</strong> are crucial in <strong>text-to-image synthesis</strong>, where textual descriptions are transformed into visual representations. This highlights the transformative potential of advanced AI architectures built upon artificial neurons.</p>
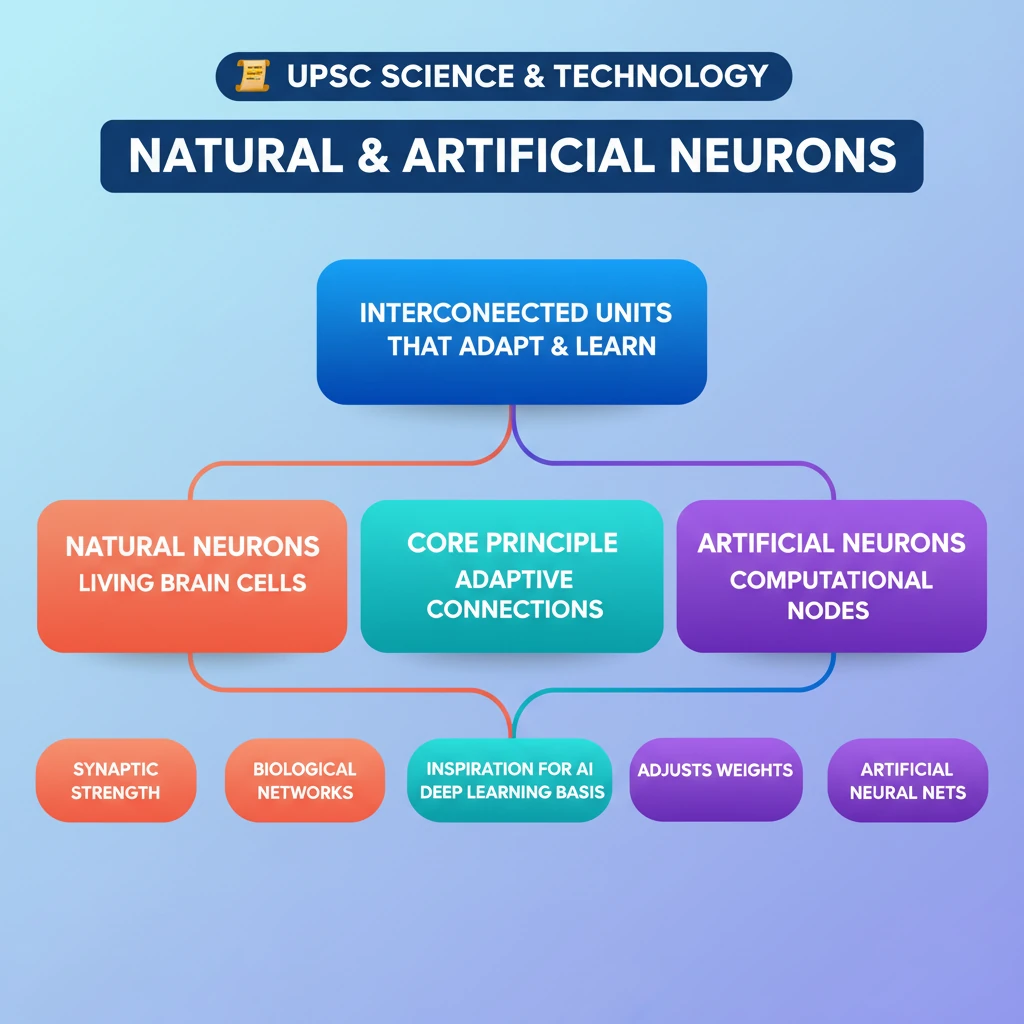
💡 Key Takeaways
- •<strong>Natural neurons</strong> are living cells in the brain, forming neural networks that learn by strengthening/weakening synaptic connections.
- •<strong>Artificial neurons (nodes)</strong> are computational units in ANNs, learning by adjusting connection strengths (weights) based on activity.
- •Both systems fundamentally rely on interconnected units that adapt their connections to process information and learn.
- •<strong>Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)</strong> are advanced ANNs that use adversarial training to produce realistic synthetic data.
- •The inspiration for AI and ANNs comes from the biological brain, with a history spanning from early theoretical models to modern Deep Learning.
- •AI, powered by artificial neurons, has vast contemporary relevance in healthcare, autonomous systems, NLP, and economic transformation.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., & Courville, A. (2016). Deep Learning. MIT Press.
•Principles of Neural Science (Kandel, Schwartz, Jessell, Siegelbaum, Hudspeth)
•MIT Technology Review articles on AI and GANs
•Wikipedia entries for Artificial Neural Networks, Perceptron, GANs