What are Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)? - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
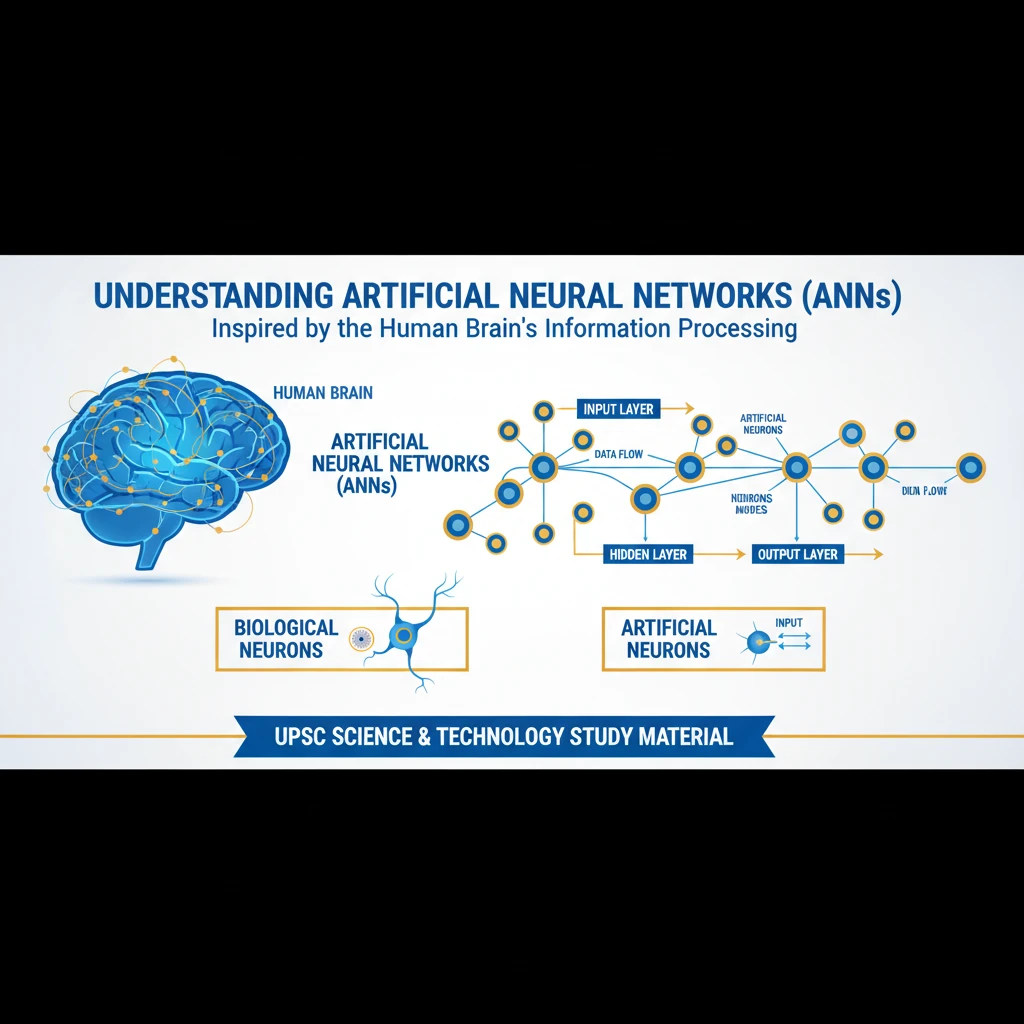
What are Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)?
Medium⏱️ 9 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
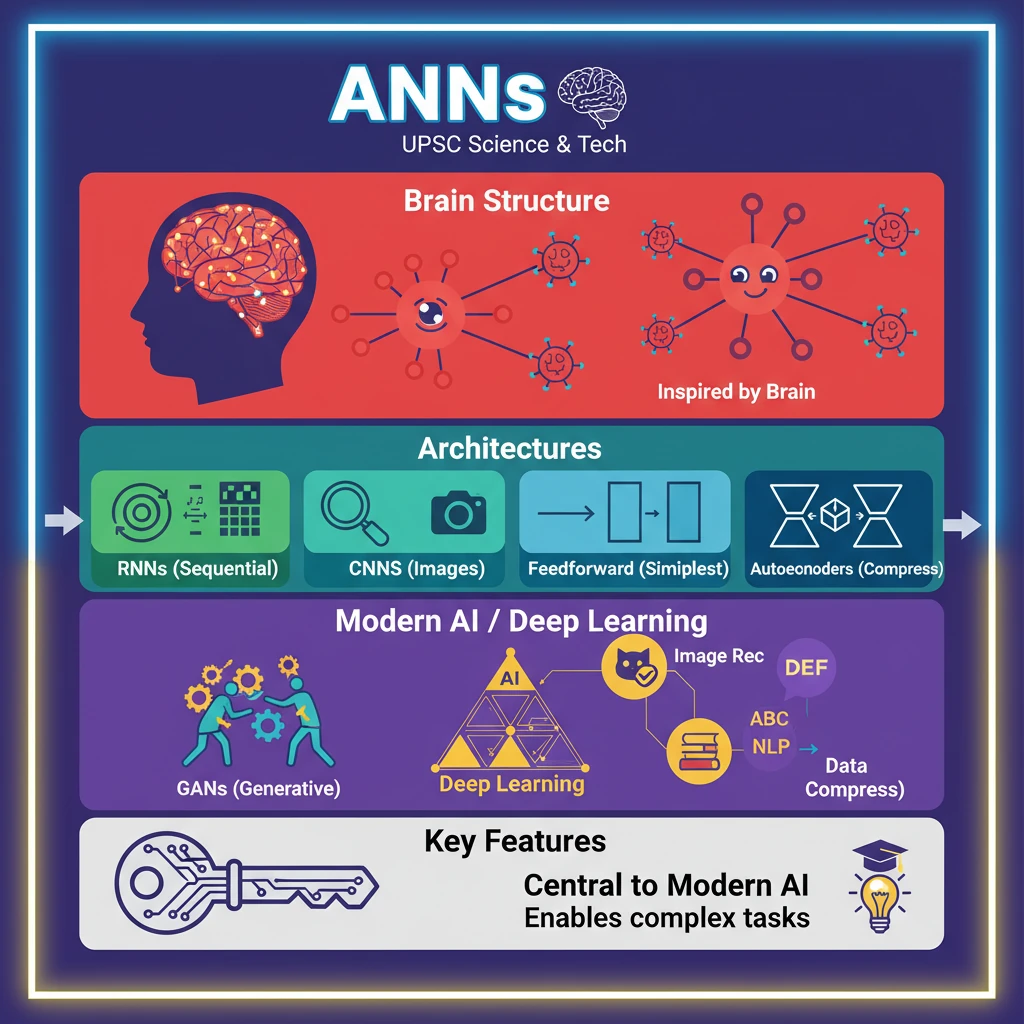
<h4>Understanding Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)</h4><p><strong>Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)</strong> are computational models directly inspired by the intricate structure and functioning of the <strong>human brain</strong>. They mimic how <strong>biological neurons</strong> are interconnected to process information and perform complex tasks.</p><p>In an ANN, fundamental units called <strong>artificial neurons</strong> or <strong>nodes</strong> work collectively. Data flows through these interconnected nodes, much like signals traverse through <strong>synapses</strong> in the brain, allowing the system to learn from data and make predictions or classifications.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Definition:</strong> <strong>Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)</strong> are a subset of <strong>machine learning</strong>, at the heart of <strong>deep learning</strong> algorithms, designed to simulate the way the human brain analyzes and processes information.</p></div><h4>Common Architectures of ANNs</h4><p>Different types of ANNs are designed for specific data types and tasks, each with a unique architectural approach.</p><div class='key-point-box'><h5>Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)</h5><p><strong>Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)</strong> are specifically engineered to handle <strong>sequential</strong> or <strong>time series data</strong>. They possess an internal memory that allows them to process sequences of inputs, making them suitable for tasks requiring context from previous data points.</p><p>RNNs are trained to create <strong>machine learning (ML) models</strong> that can generate <strong>sequential predictions</strong> or conclusions. This capability is crucial for applications like natural language processing and speech recognition.</p></div><div class='key-point-box'><h5>Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)</h5><p><strong>Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)</strong> are primarily designed for processing <strong>grid-like data</strong>, with images being the most common example. They excel at identifying patterns and features within visual information.</p><p>CNNs utilize <strong>three-dimensional data</strong> processing, making them highly effective for tasks such as <strong>image classification</strong>, where they categorize images, and <strong>object recognition</strong>, where they locate and identify objects within images.</p></div><div class='key-point-box'><h5>Feedforward Neural Networks</h5><p>The <strong>Feedforward Neural Network</strong> represents the simplest and most fundamental architecture among ANNs. In this model, information flows in a single, unidirectional path.</p><p>Data moves strictly from the <strong>input layer</strong>, through one or more hidden layers, to the <strong>output layer</strong>. These networks typically feature <strong>fully connected layers</strong>, where every neuron in one layer is connected to every neuron in the next.</p></div><div class='key-point-box'><h5>Autoencoders</h5><p><strong>Autoencoders</strong> are a type of neural network primarily used for <strong>unsupervised learning</strong>. Their main purpose is to learn efficient data codings in an unsupervised manner.</p><p>They function by taking <strong>input data</strong>, compressing it into a lower-dimensional representation (keeping only the most important parts), and then attempting to <strong>rebuild the original data</strong> from this compressed version. This makes them useful for dimensionality reduction and feature learning.</p></div><div class='key-point-box'><h5>Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)</h5><p><strong>Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)</strong> are a powerful and advanced type of neural network also employed for <strong>unsupervised learning</strong>. They consist of two competing neural networks working in tandem.</p><p>A <strong>generator network</strong> is tasked with creating <strong>fake data</strong> (e.g., images, text) that resembles real data. Simultaneously, a <strong>discriminator network</strong> attempts to distinguish between the <strong>real and fake data</strong>. This adversarial process drives both networks to improve, resulting in highly realistic generated content.</p></div>
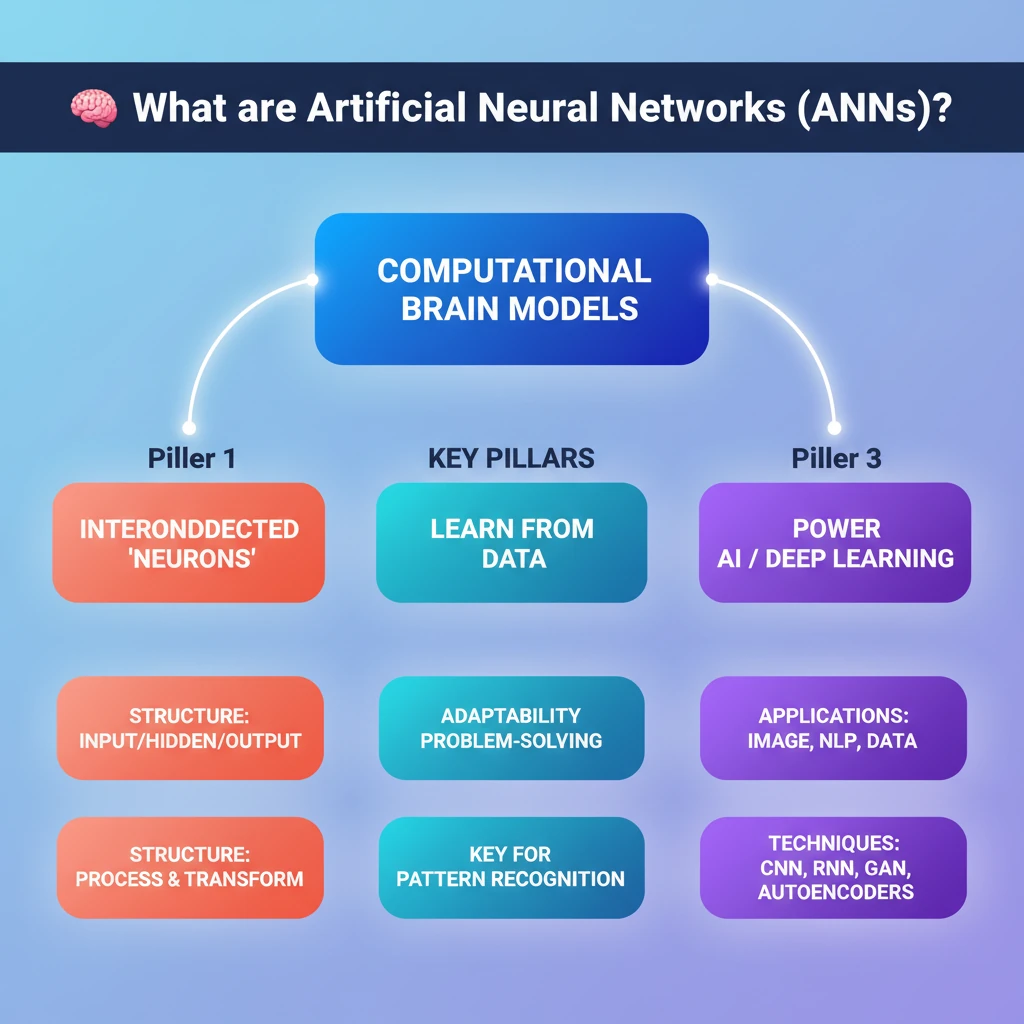
💡 Key Takeaways
- •ANNs are computational models inspired by the human brain's structure and function.
- •They consist of interconnected 'artificial neurons' that process information collectively.
- •Key architectures include RNNs (sequential data), CNNs (grid-like data/images), Feedforward (simplest, unidirectional flow), Autoencoders (unsupervised, compression), and GANs (unsupervised, generative).
- •ANNs are central to modern AI and deep learning, enabling tasks like image recognition, NLP, and data compression.
- •Their ability to learn from data makes them highly adaptable and powerful for complex problem-solving.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content