One Nation One Time - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

One Nation One Time
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
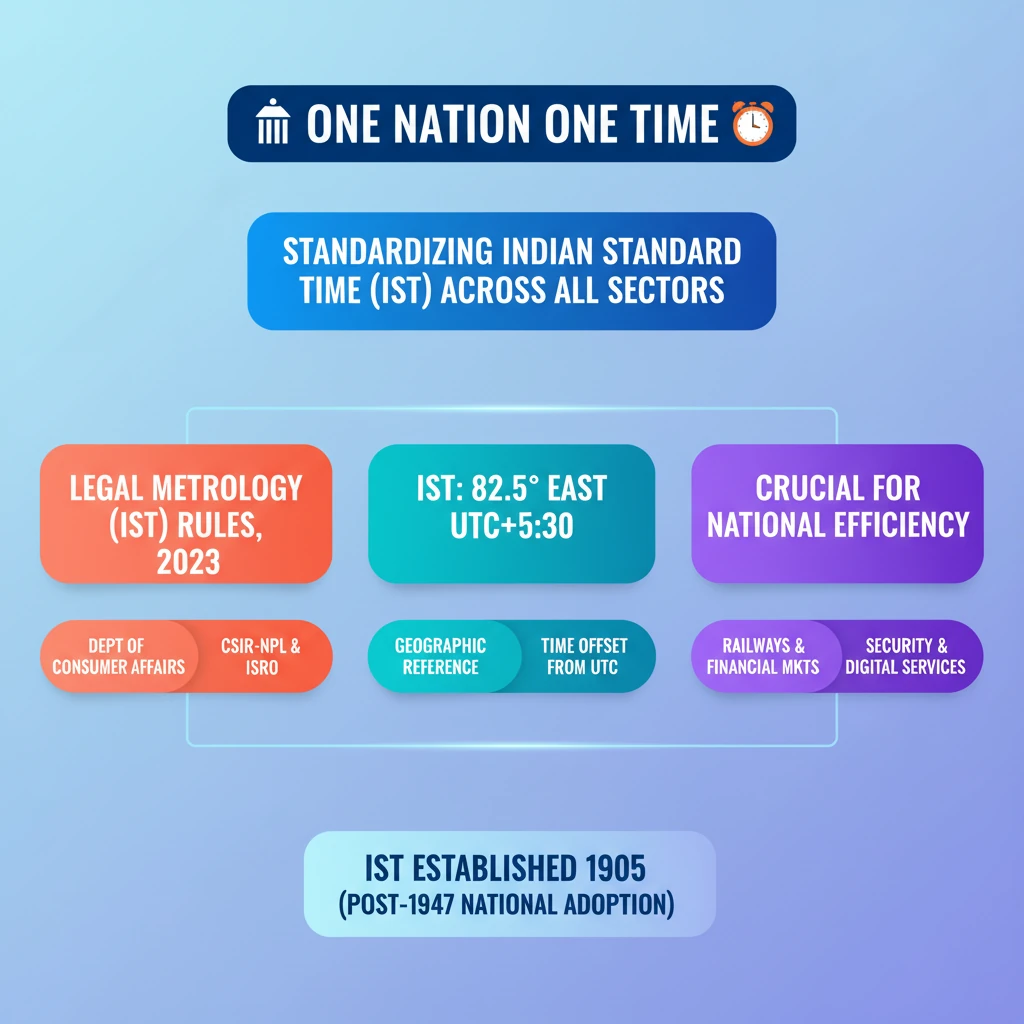
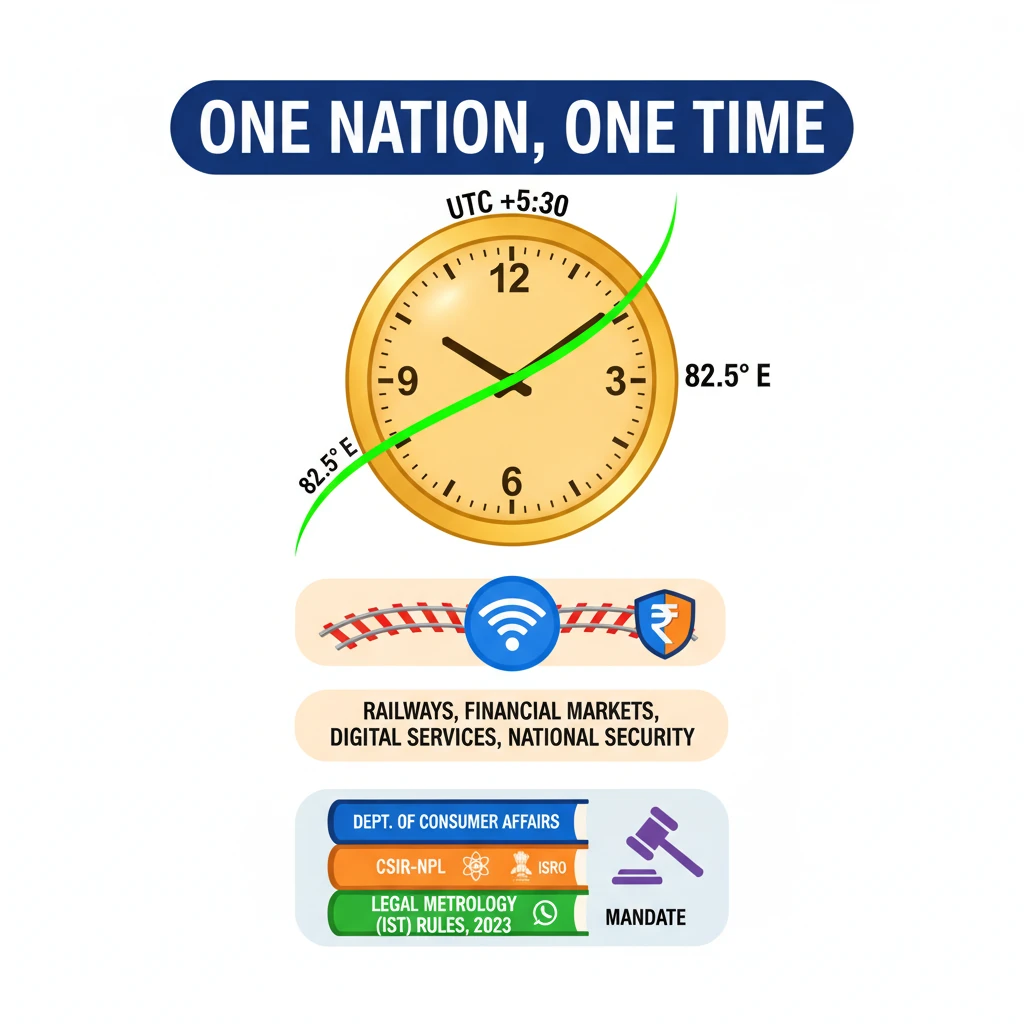
<h4>Context and Introduction</h4><p>The <strong>Department of Consumer Affairs</strong>, in collaboration with the <strong>Council of Scientific & Industrial Research - National Physical Laboratory (CSIR-NPL)</strong> and the <strong>Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)</strong>, has drafted the <strong>Legal Metrology (Indian Standard Time (IST)) Rules, 2023</strong>.</p><p>These rules aim to standardize and mandate the adoption of <strong>Indian Standard Time (IST)</strong> across all sectors, reinforcing the national vision of <strong>“One Nation, One Time”</strong>.</p><h4>Key Features of the Legal Metrology (IST) Rules, 2023</h4><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Mandatory Adoption of IST:</strong> <strong>IST</strong>, as maintained by the <strong>CSIR-NPL</strong>, will be the only legally recognized time standard in India. This move solidifies the <strong>“One Nation, One Time”</strong> initiative.</p></div><ul><li>The use of <strong>foreign time references</strong>, such as <strong>Global Positioning System (GPS) time</strong>, will be prohibited unless specifically approved by the government.</li><li><strong>Synchronization of Critical Sectors:</strong> All government institutions, financial entities, telecom service providers, power grids, and digital infrastructure must synchronize their systems with <strong>IST</strong>.</li><li><strong>Regulatory Framework & Compliance:</strong> Compliance with these rules will be monitored through periodic audits. Penalties will be imposed for any non-adherence.</li><li><strong>Special Provisions:</strong> Certain applications like <strong>scientific research</strong>, <strong>astronomy</strong>, and <strong>navigational applications</strong> may use alternative time references, but only with prior government approval.</li><li>The rules also provide necessary flexibility for <strong>strategic and national security applications</strong>.</li></ul><h4>Understanding Indian Standard Time (IST)</h4><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>Indian Standard Time (IST)</strong> is based on a specific <strong>longitude of 82.5° East</strong>.</p></div><p>This reference longitude passes through <strong>Mirzapur, Uttar Pradesh</strong>, serving as the central meridian for India's time zone.</p><p><strong>IST</strong> is precisely <strong>5 hours and 30 minutes ahead</strong> of <strong>Greenwich Mean Time (GMT)</strong>, which is now universally known as <strong>Universal Coordinated Time (UTC)</strong>.</p>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •The Legal Metrology (IST) Rules, 2023, mandate the adoption of Indian Standard Time (IST) across all sectors.
- •IST is maintained by CSIR-NPL and is 5 hours 30 minutes ahead of Universal Coordinated Time (UTC).
- •The rules prohibit the general use of foreign time references like GPS time, reinforcing national time sovereignty.
- •Critical sectors including government, finance, telecom, and power grids must synchronize their systems with IST.
- •IST was established in 1906, replacing multiple regional time zones from the British era.
- •The initiative aligns with the vision of "One Nation, One Time" for enhanced national coordination and efficiency.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Legal Metrology Act, 2009 (contextual for Legal Metrology Rules)
•CSIR-National Physical Laboratory (NPL) official website (for IST maintenance role)
•Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) official website (for general contributions to national infrastructure and timing)