What is Parkinson’s Disease? - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
What is Parkinson’s Disease?
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
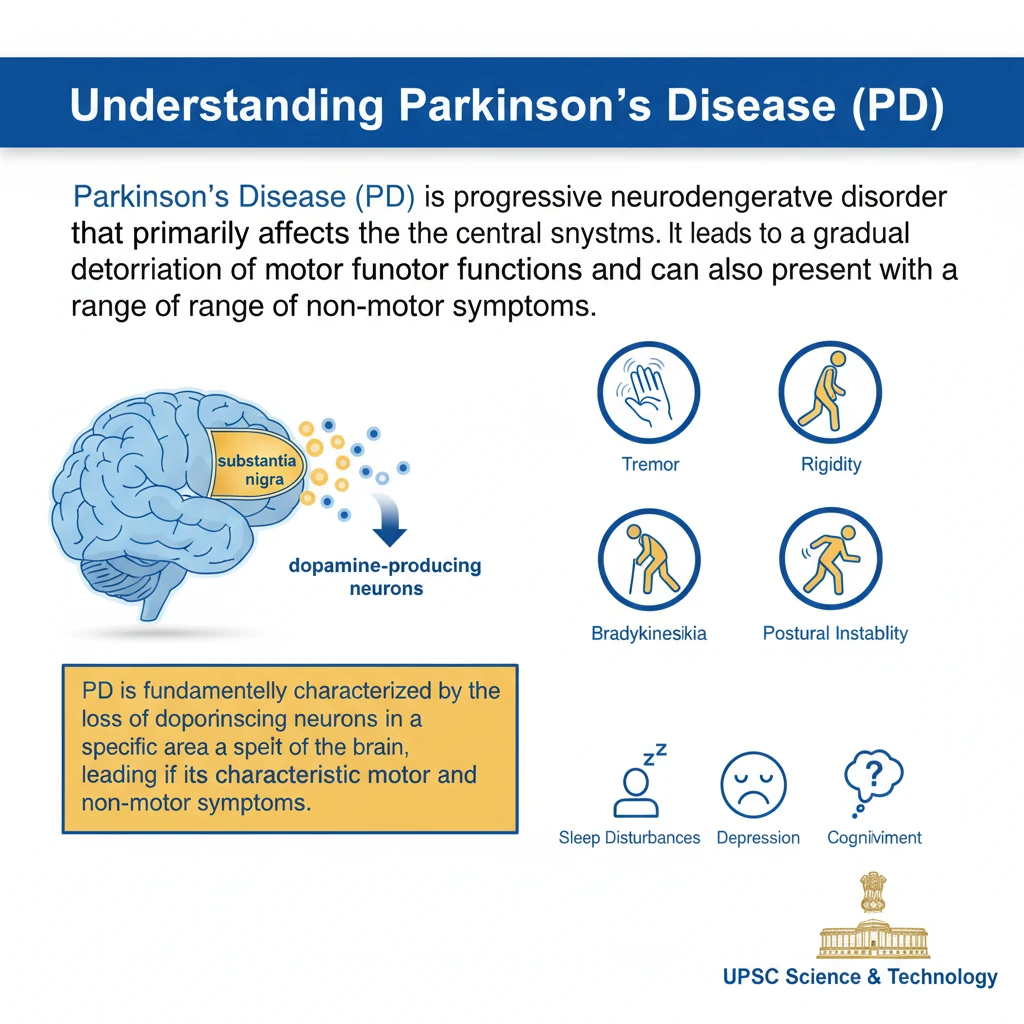
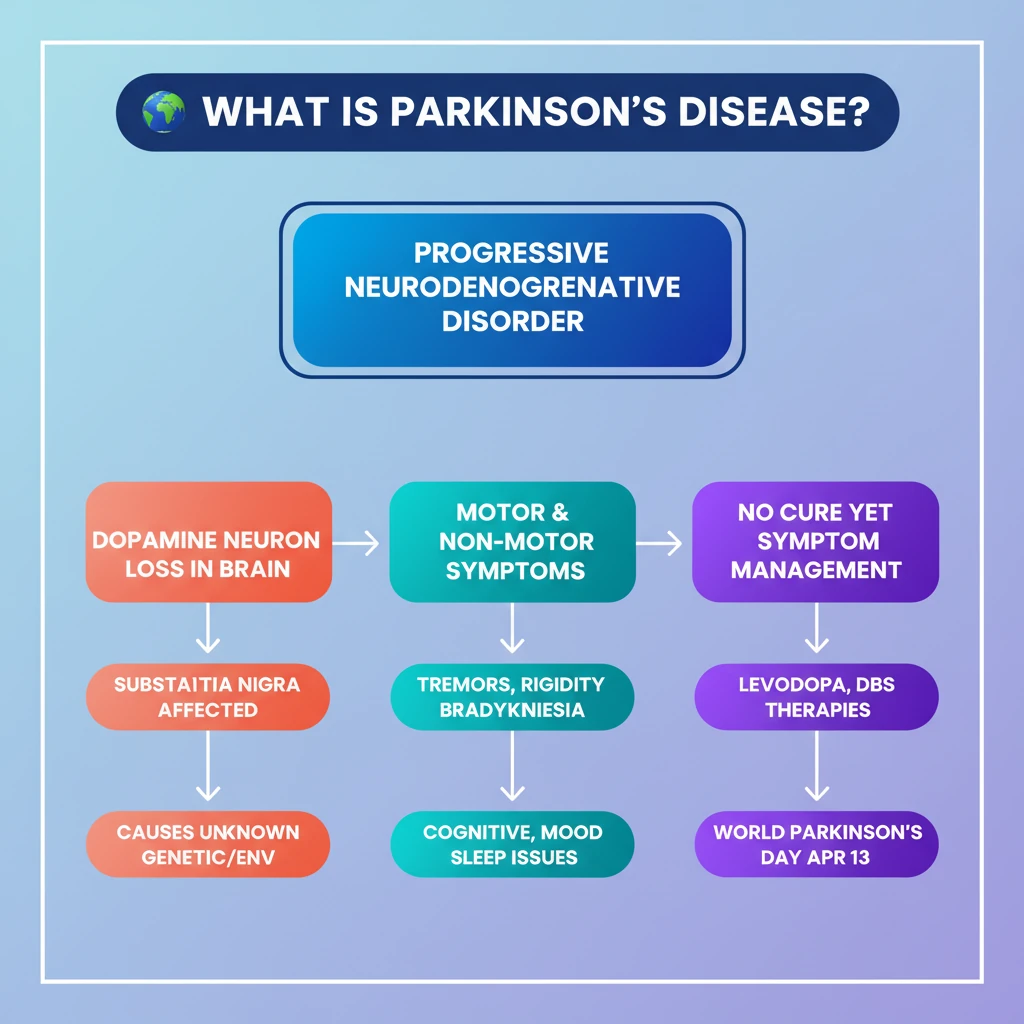
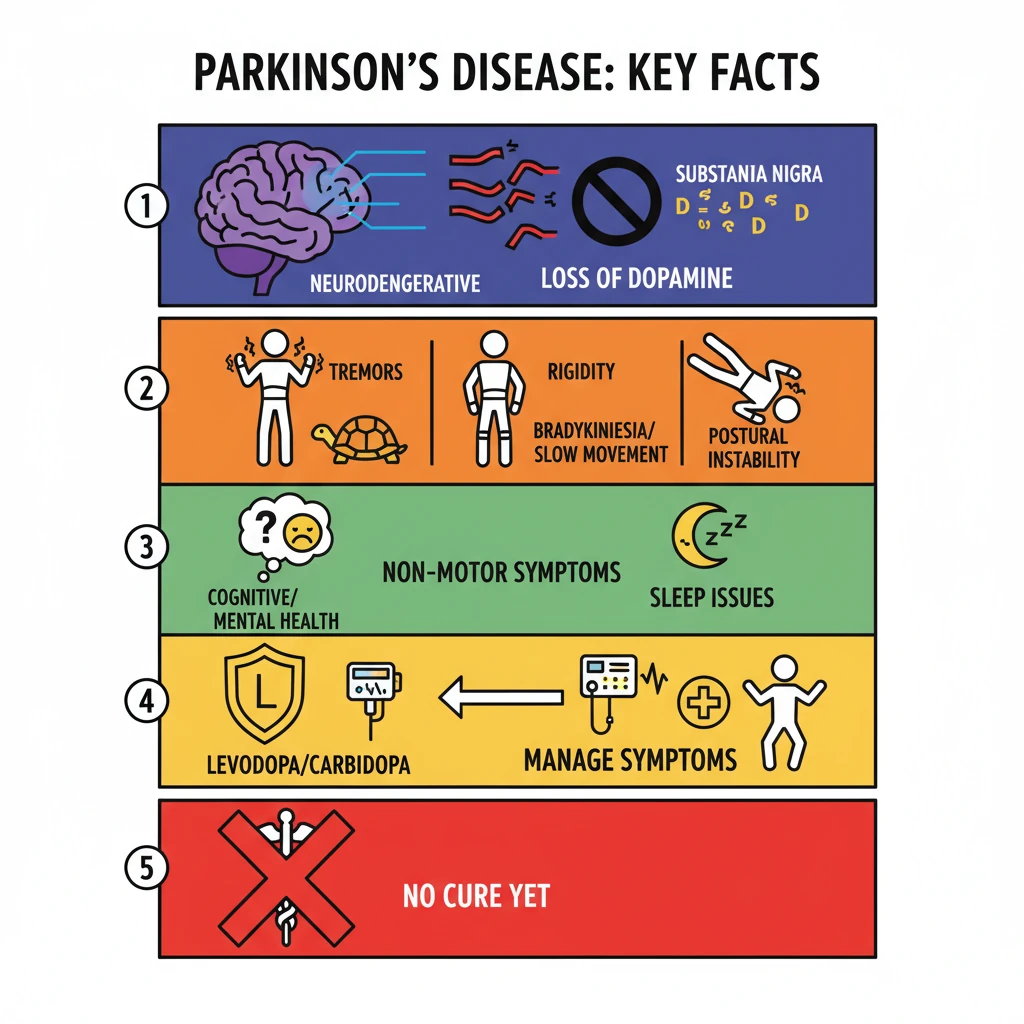
<h4>Understanding Parkinson's Disease (PD)</h4><p><strong>Parkinson's Disease (PD)</strong> is a <strong>progressive neurodegenerative disorder</strong> that primarily affects the central nervous system. It leads to a gradual deterioration of motor functions and can also present with a range of non-motor symptoms.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>PD is fundamentally characterized by the <strong>loss of dopamine-producing neurons</strong> in a specific area of the brain, leading to its characteristic symptoms.</p></div><h4>Key Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease</h4><p>Symptoms of PD are broadly categorized into <strong>motor</strong> and <strong>non-motor</strong> manifestations, impacting various aspects of daily life.</p><h5>Motor Symptoms:</h5><ul><li><strong>Tremors</strong>: Involuntary shaking, often starting in a limb, especially at rest.</li><li><strong>Rigidity</strong>: Stiffness of the limbs and trunk, which can cause pain and limit range of motion.</li><li><strong>Bradykinesia</strong>: Slowness of movement, making initiation and execution of voluntary movements difficult.</li><li><strong>Postural Instability</strong>: Impaired balance and coordination, significantly increasing the risk of falls.</li></ul><h5>Non-Motor Symptoms:</h5><p>These symptoms can often precede motor manifestations and significantly impact a patient's quality of life and overall well-being.</p><ul><li><strong>Cognitive Issues</strong>: Problems with memory, attention, and executive functions.</li><li><strong>Mental Health Disorders</strong>: Depression, anxiety, and apathy are common comorbidities.</li><li><strong>Sleep Disturbances</strong>: Insomnia, vivid dreams, and REM sleep behavior disorder.</li><li><strong>Pain and Sensory Problems</strong>: Numbness, tingling, and generalized pain are frequently reported.</li></ul><h4>Defining Bradykinesia</h4><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Bradykinesia</strong> specifically refers to the <strong>slowness of movement</strong> and a reduction in the speed of voluntary movements. It can also manifest as progressive hesitations or halts as movements are continued, making routine tasks challenging.</p></div><h4>Etiology: Causes of Parkinson's Disease</h4><p>The precise <strong>cause of Parkinson's Disease</strong> is not yet fully known. However, it is widely believed to result from a complex interplay of both <strong>genetic and environmental factors</strong>.</p><p>The primary pathological feature is the degeneration of <strong>dopamine-producing neurons</strong> in the <strong>substantia nigra</strong> region of the brain. This critical loss of dopamine leads to the impaired motor control observed in patients.</p><h4>Global Prevalence and Awareness</h4><p>The global burden of Parkinson's Disease has seen a significant and concerning increase over recent decades, reflecting a growing public health challenge.</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li>The <strong>global prevalence of PD has doubled in the past 25 years</strong>, indicating a substantial rise in affected individuals.</li><li>In <strong>2019</strong>, global estimates indicated <strong>over 8.5 million individuals</strong> living with PD worldwide.</li></ul></div><p>To raise awareness, foster understanding, and support those affected by the condition, <strong>World Parkinson's Day</strong> is observed annually on <strong>April 13th</strong>.</p><h4>Treatment Approaches for Parkinson's Disease</h4><p>Currently, there is <strong>no known cure</strong> for Parkinson's Disease. However, various therapies are available to effectively manage and reduce the severity of symptoms, significantly improving patients' quality of life.</p><p>Treatment strategies typically involve a combination of approaches:</p><ul><li><strong>Medications</strong>: Pharmacological interventions are used to alleviate symptoms and improve motor function.</li><li><strong>Surgery</strong>: For advanced cases, procedures such as Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) may be considered.</li><li><strong>Rehabilitation Therapies</strong>: Including physical, occupational, and speech therapy, crucial for maintaining function and independence.</li></ul><div class='info-box'><p>The most common medication used is <strong>Levodopa/carbidopa</strong>. This combination medicine works by increasing the amount of <strong>dopamine</strong> in the brain, thereby compensating for the loss of natural dopamine production and reducing symptoms.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Parkinson's Disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder affecting the central nervous system.
- •It is primarily caused by the loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain's substantia nigra.
- •Symptoms include both motor (tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia, postural instability) and non-motor (cognitive, mental health, sleep) issues.
- •There is currently no cure, but treatments like Levodopa/carbidopa and DBS effectively manage symptoms.
- •Global prevalence has doubled in 25 years, making it a significant public health concern, highlighted by World Parkinson's Day on April 13th.
🧠 Memory Techniques
98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•World Health Organization (WHO) reports on Neurological Disorders
•National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) publications