NASA’s Mars Sample Return Program - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
NASA’s Mars Sample Return Program
Medium⏱️ 6 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
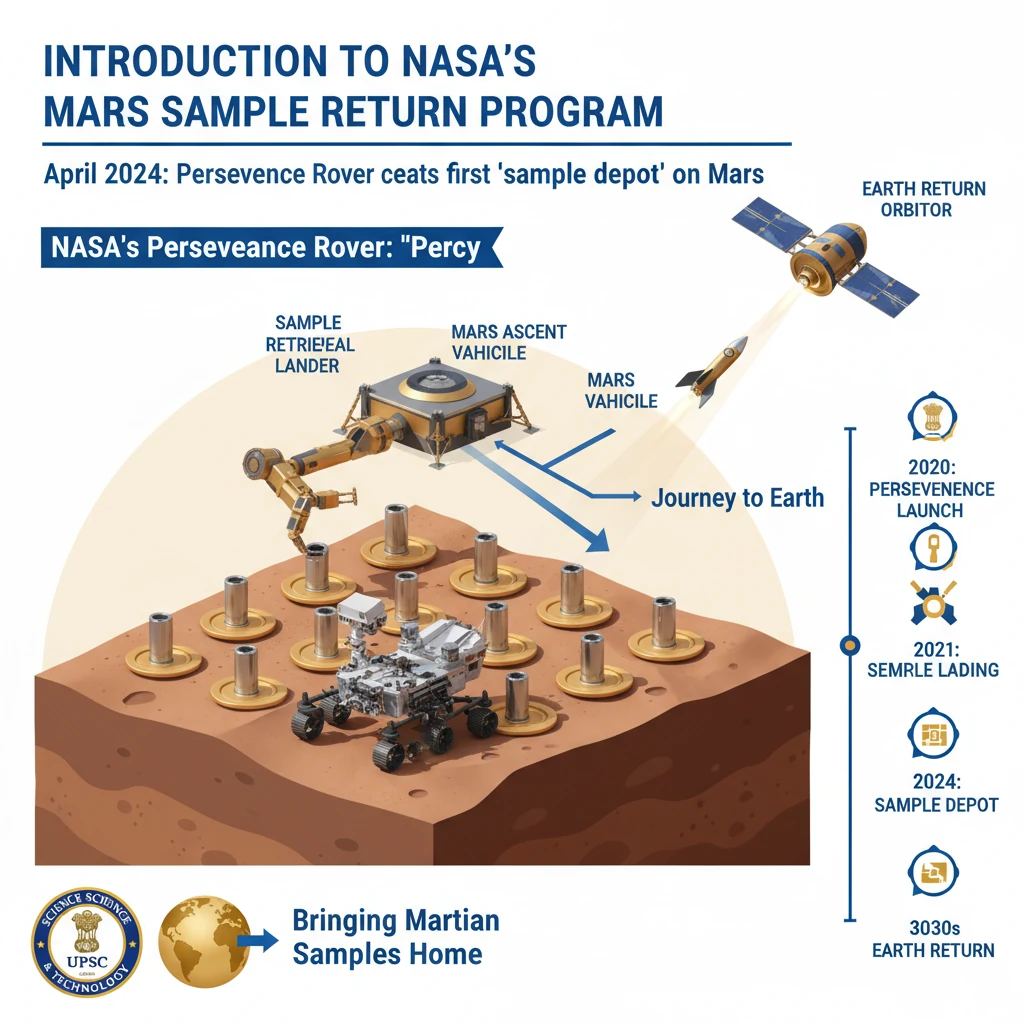
<h4>Introduction to NASA's Mars Sample Return Program</h4><p>In <strong>April 2024</strong>, <strong>NASA's Perseverance Rover</strong>, affectionately known as <strong>Percy</strong>, achieved a significant milestone by establishing the first-ever <strong>'sample depot on another world'</strong>. This involved carefully depositing ten rock sample tubes on the Martian surface.</p><p>These collected samples are intended to be retrieved and brought back to Earth as a crucial part of the ambitious <strong>Mars Sample Return (MSR) Campaign</strong>. The program aims to bring pristine Martian samples for detailed scientific analysis.</p><h4>Challenges and Timeline of the MSR Program</h4><p>The <strong>Mars Sample Return Program</strong> is a highly complex and resource-intensive endeavor. It is projected to be very expensive, with an estimated cost of <strong>$11 billion</strong>.</p><p>Furthermore, the mission has a long timeline. The full execution and return of samples to Earth are not anticipated until the year <strong>2040</strong>, highlighting the significant logistical and technological hurdles involved.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Relevance:</strong> Understand the dual nature of space missions – scientific advancement alongside financial and temporal challenges. This program exemplifies long-term international scientific collaboration.</p></div><h4>Understanding the Perseverance Rover</h4><p>The <strong>Perseverance Rover</strong> is a sophisticated robotic explorer that is an integral component of <strong>NASA's Mars 2020 mission</strong>. It represents the cutting edge of planetary exploration technology.</p><p>The rover was successfully launched in <strong>July 2020</strong>. After a journey through space, it made a precise landing on Mars's <strong>Jezero Crater</strong> in <strong>February 2021</strong>, a site believed to have once harbored ancient microbial life.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Perseverance Rover Specifications:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Size:</strong> Approximately the size of a car.</li><li><strong>Weight:</strong> About <strong>1,025 kilograms</strong>, including all its scientific instruments.</li><li><strong>Primary Function:</strong> To collect and cache rock and soil samples from the Martian surface.</li><li><strong>Sample Collection:</strong> Encasing collected samples in sealed tubes for future return to Earth.</li></ul></div><h4>Perseverance Rover's Power Source</h4><p>The <strong>Perseverance Rover</strong> is powered by a robust and reliable system known as a <strong>Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG)</strong>. This technology is vital for long-duration missions in harsh environments.</p><p>The <strong>MMRTG</strong> generates electricity by converting heat. This heat is produced from the natural radioactive decay of <strong>plutonium-238</strong>, ensuring a consistent power supply for the rover's operations and scientific instruments.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Key Concept:</strong> <strong>Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generators (RTGs)</strong> are crucial for deep space and long-duration planetary missions where solar power is insufficient or unavailable. They provide continuous power irrespective of sunlight.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
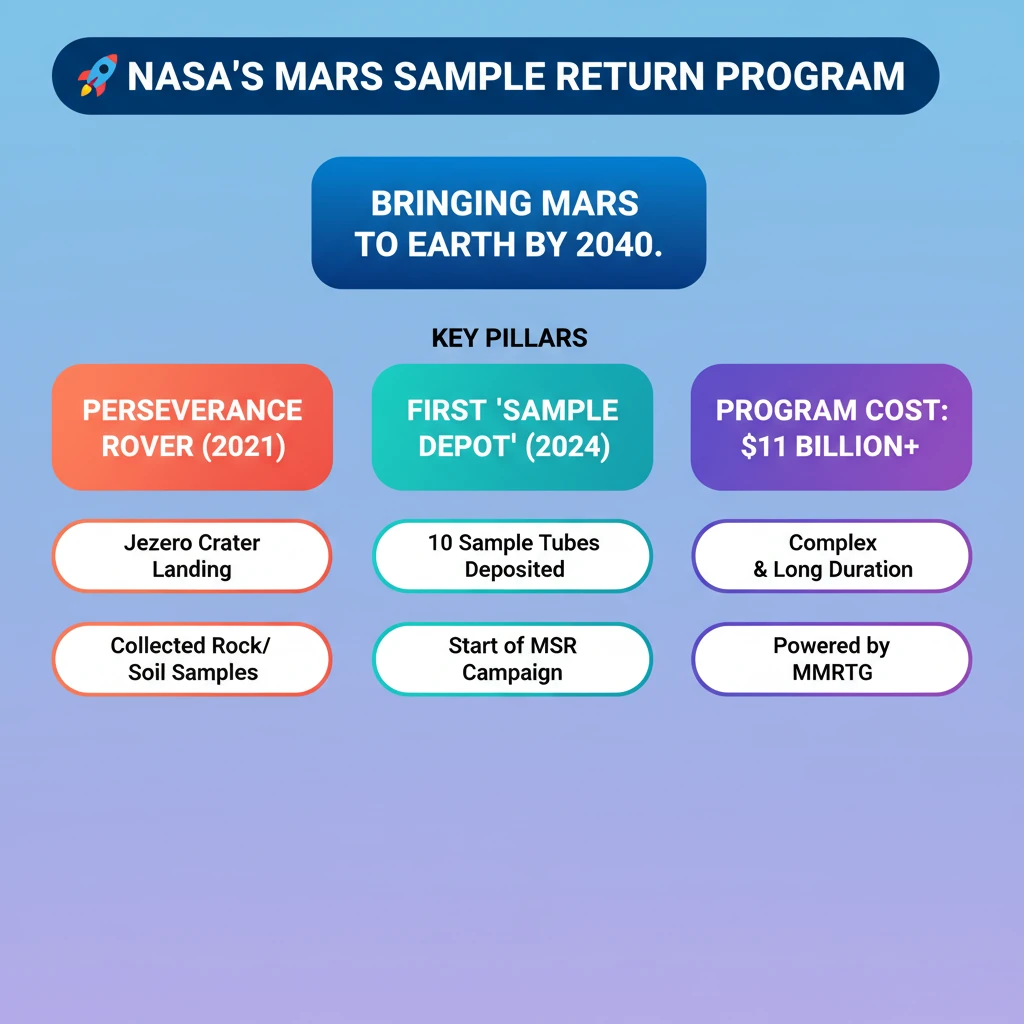
- •NASA's Perseverance Rover created the first 'sample depot' on Mars in April 2024, depositing 10 rock sample tubes.
- •These samples are part of the Mars Sample Return (MSR) Campaign, aiming to bring Martian samples to Earth by 2040.
- •The MSR program is highly expensive, estimated at $11 billion, reflecting its complexity and long timeline.
- •Perseverance Rover (part of Mars 2020 mission) landed in Jezero Crater in Feb 2021, collecting rock/soil samples.
- •The rover is powered by a Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG) using plutonium decay for electricity.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•NASA Official Website (for program details and rover specifications)
•European Space Agency (ESA) Official Website (for MSR collaboration details)