What are Key Facts About Proteins? - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
What are Key Facts About Proteins?
Easy⏱️ 8 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
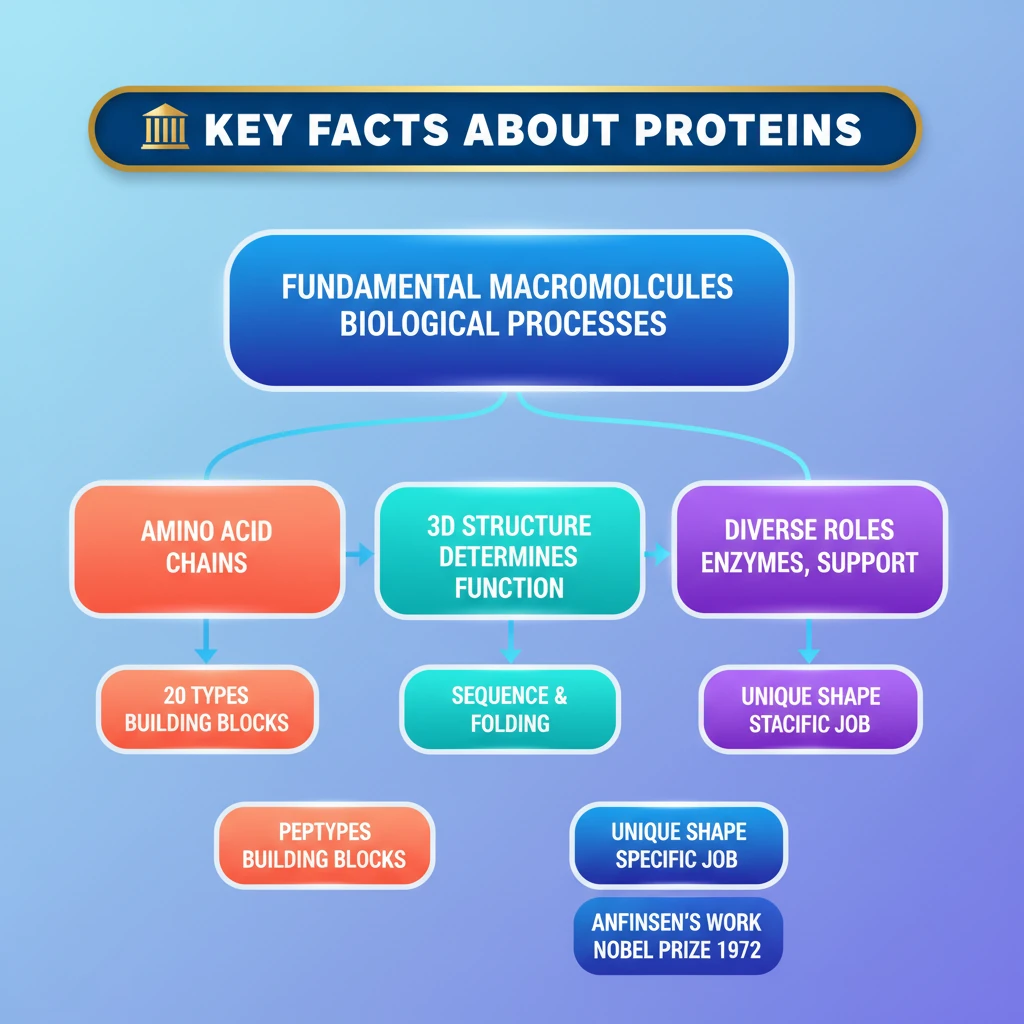
<h4>What are Proteins?</h4><p><strong>Proteins</strong> are fundamental <strong>macromolecules</strong> essential for virtually every biological process in living organisms. They are complex organic compounds that play a crucial role in the structure, function, and regulation of the body's tissues and organs.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Fact:</strong> Proteins are often referred to as the 'workhorses' of the cell due to their diverse and indispensable functions.</p></div><h4>Amino Acids: The Building Blocks of Proteins</h4><p><strong>Proteins</strong> are constructed from smaller units called <strong>amino acids</strong>. These are <strong>organic molecules</strong> containing specific elements: <strong>carbon</strong>, <strong>hydrogen</strong>, <strong>nitrogen</strong>, <strong>oxygen</strong>, and sometimes <strong>sulphur</strong>.</p><p>There are <strong>20 different types of amino acids</strong> that serve as the basic building blocks. The unique sequence and combination of these amino acids determine the specific protein formed.</p><h4>Protein Structure and Function</h4><p>The sequence of <strong>amino acids</strong> in a protein dictates how it folds into a precise <strong>three-dimensional structure</strong>. This intricate 3D shape is absolutely critical, as it directly determines the protein's specific <strong>function</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Important Concept:</strong> A change in a protein's <strong>amino acid sequence</strong> or its <strong>three-dimensional structure</strong> can lead to a loss of function, often with significant biological consequences.</p></div><h4>Nobel Prize in Protein Research</h4><p>The profound connection between a protein's <strong>amino acid sequence</strong> and its <strong>three-dimensional structure</strong> was a groundbreaking discovery. In <strong>1972</strong>, the <strong>Nobel Prize in Chemistry</strong> was awarded to <strong>Christian Anfinsen</strong> for his pioneering work.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Christian Anfinsen's</strong> research, particularly on the enzyme <strong>ribonuclease</strong>, demonstrated that the information required for a protein to fold into its correct 3D structure is inherent in its <strong>amino acid sequence</strong>.</p></div><h4>Diverse Roles of Proteins in Biology</h4><p><strong>Proteins</strong> perform a wide array of vital functions necessary for life. Their versatility enables them to participate in almost every cellular process.</p><ul><li><strong>Speeding up Biochemical Reactions:</strong> Many proteins act as <strong>enzymes</strong>, catalyzing (speeding up) essential biochemical reactions in the body, such as digestion and metabolism.</li><li><strong>Providing Structural Support:</strong> Proteins like <strong>collagen</strong> and <strong>keratin</strong> provide structural integrity to cells, tissues, and organs, forming components of skin, hair, and connective tissues.</li><li><strong>Aiding in Immune Responses:</strong> <strong>Antibodies</strong>, which are proteins, play a crucial role in the body's immune system, identifying and neutralizing foreign invaders like bacteria and viruses.</li><li><strong>Storing Nutrients:</strong> Some proteins are involved in the storage and transport of essential nutrients. For example, <strong>ferritin</strong> stores iron in the body.</li><li><strong>Transporting Molecules:</strong> Proteins like <strong>hemoglobin</strong> transport oxygen in the blood, while others facilitate the movement of substances across cell membranes.</li></ul><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding the diverse functions of <strong>proteins</strong> is crucial for topics related to human physiology, nutrition, biotechnology, and disease mechanisms in <strong>GS Paper III (Science and Technology)</strong> and <strong>GS Paper II (Health)</strong>.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Proteins are fundamental macromolecules, essential for nearly all biological processes.
- •They are long chains of 20 different types of amino acids, their basic building blocks.
- •A protein's unique three-dimensional structure is determined by its amino acid sequence and dictates its specific function.
- •Proteins perform diverse roles: enzymes (catalysis), structural support (collagen), immune response (antibodies), and nutrient storage/transport.
- •Christian Anfinsen's 1972 Nobel Prize-winning work established the crucial link between amino acid sequence and protein folding/function.
🧠 Memory Techniques
98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•NCERT Biology Textbooks (Class XI & XII)
•Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
•National Institutes of Health (NIH) - General information on proteins