What are the Three stages of India’s Nuclear Energy Program? - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
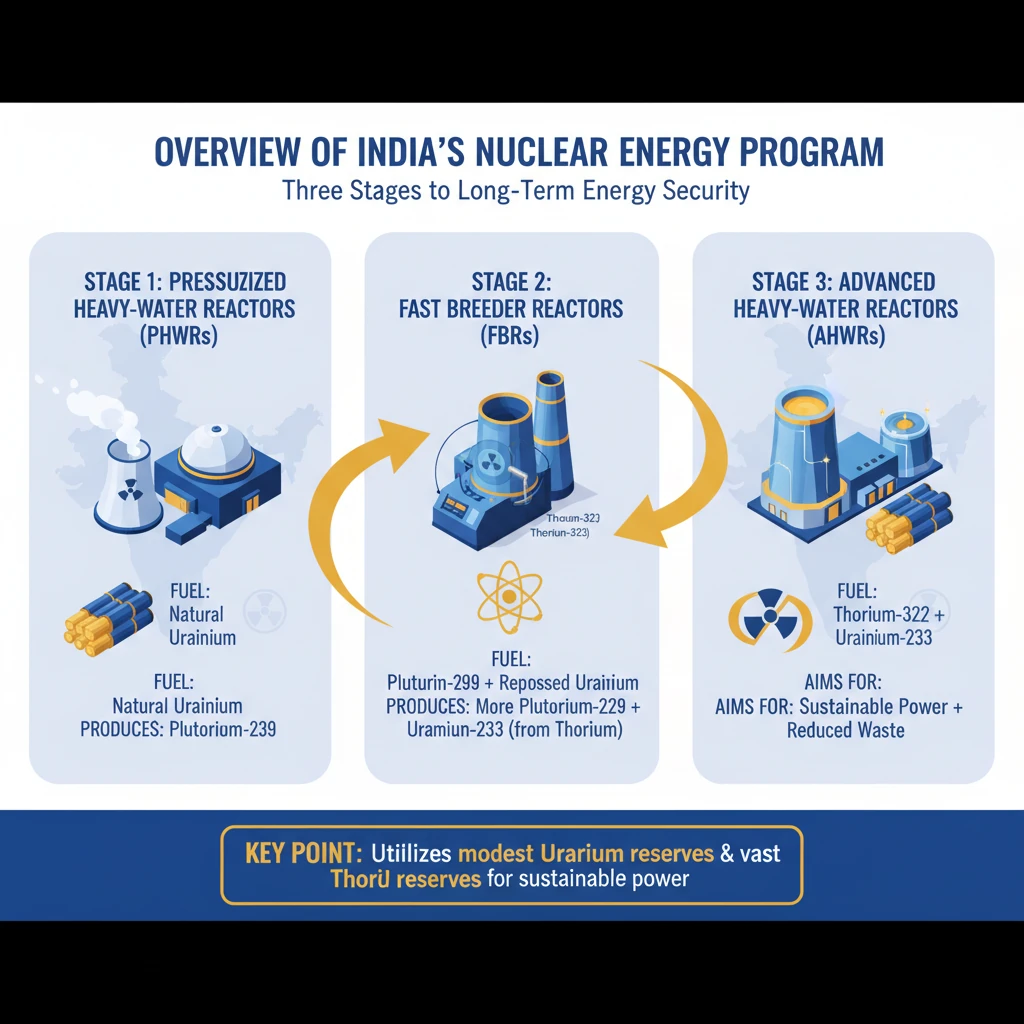
What are the Three stages of India’s Nuclear Energy Program?
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
<h4>Overview of India's Nuclear Energy Program</h4><p>India's <strong>Nuclear Energy Program</strong> is strategically designed in three stages to achieve long-term energy security. This comprehensive approach addresses the nation's specific resource availability and future energy demands.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>This multi-stage program aims to optimally utilize India's modest <strong>uranium</strong> reserves and vast <strong>thorium</strong> reserves for sustainable power generation.</p></div><h4>The First Stage: Pressurised Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs)</h4><p>The initial phase focuses on the deployment of <strong>Pressurised Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs)</strong>. These reactors form the backbone of India's current nuclear power generation capabilities.</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li><strong>Fuel:</strong> Natural Uranium</li><li><strong>Coolant & Moderator:</strong> Heavy Water</li><li><strong>Status:</strong> Currently operational and under expansion across the country.</li></ul></div><p><strong>PHWRs</strong> efficiently use <strong>natural uranium</strong> as fuel and produce <strong>plutonium-239</strong> as a byproduct, which is a crucial fissile material for the subsequent stages of the program.</p><h4>The Second Stage: Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs)</h4><p>The second stage involves the establishment of <strong>Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs)</strong>. These advanced reactors are designed to 'breed' more fissile material than they consume during operation.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The primary objective of <strong>FBRs</strong> is to <strong>multiply the inventory of fissile material</strong>, specifically <strong>Plutonium-239 (Pu-239)</strong>, which is extracted from the spent fuel of <strong>PHWRs</strong>.</p></div><p>This stage requires sophisticated infrastructure, including <strong>reprocessing plants</strong> and <strong>plutonium fabrication plants</strong>, to manage and prepare the nuclear fuel cycle efficiently.</p><p>The multiplication of fissile inventory is essential to create a sufficient power base. This base is vital for initiating the large-scale utilization of <strong>thorium</strong> in the program's third stage.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Progress in <strong>FBR technology</strong>, such as the <strong>Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor (PFBR)</strong> at Kalpakkam, is a critical enabler for India's energy independence. Questions on <strong>FBRs</strong> and their role often appear in <strong>UPSC Mains GS-III</strong>.</p></div><h4>The Third Stage: Thorium-Based Reactors (AHWRs)</h4><p>The final and most ambitious stage is centered on the <strong>Thorium and Uranium-233 (U-233) cycle</strong>. India possesses vast reserves of <strong>thorium</strong>, making this stage crucial for long-term energy security.</p><p><strong>Uranium-233 (U-233)</strong> is produced by irradiating <strong>thorium</strong> in existing <strong>PHWRs</strong> and future <strong>FBRs</strong>. This U-233 then becomes the fissile fuel for advanced reactors.</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li><strong>Key Reactor:</strong> Advanced Heavy Water Reactor (AHWR)</li><li><strong>Fuel Cycle:</strong> Thorium-Uranium-233 Cycle</li><li><strong>Goal:</strong> Sustainable, long-term energy generation using indigenous thorium resources.</li></ul></div><p>Commercial utilization of <strong>thorium</strong> on a significant scale is contingent upon the availability of abundant supplies of either <strong>Uranium-233 (U-233)</strong> or <strong>Plutonium-239 (Pu-239)</strong> to initiate and sustain the cycle.</p><p>The successful progression of <strong>FBRs</strong> in the second stage is a prerequisite, making the transition to this thorium-based third phase viable and achievable for India's energy future.</p>
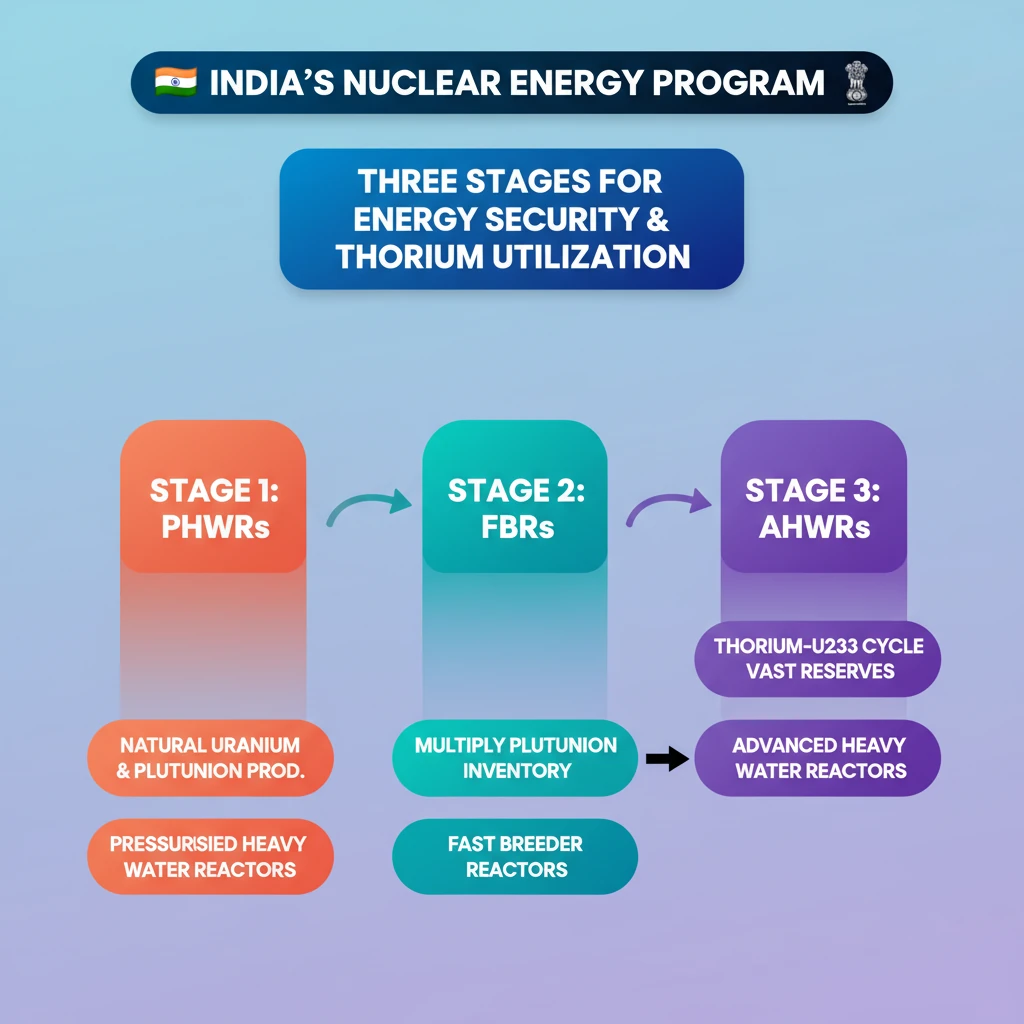
💡 Key Takeaways
- •India's nuclear program is a three-stage plan for long-term energy security, leveraging indigenous resources.
- •Stage 1 uses Pressurised Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) with natural uranium, producing plutonium as a byproduct.
- •Stage 2 employs Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs) to multiply plutonium inventory, crucial for future thorium utilization.
- •Stage 3 aims for the thorium-Uranium-233 (U-233) cycle via Advanced Heavy Water Reactors (AHWRs), utilizing India's vast thorium reserves.
- •Successful FBR development in Stage 2 is a prerequisite for the commercial viability of the thorium-based Stage 3.
- •The program ensures energy independence, reduces carbon footprint, and showcases India's technological prowess in nuclear science.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) official website
•Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) annual reports and publications
•Press Information Bureau (PIB) releases related to nuclear energy