Earth's Magnetic and Geographic Poles: Location, Compass Use, and Protection - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
Earth's Magnetic and Geographic Poles: Location, Compass Use, and Protection
Medium⏱️ 6 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
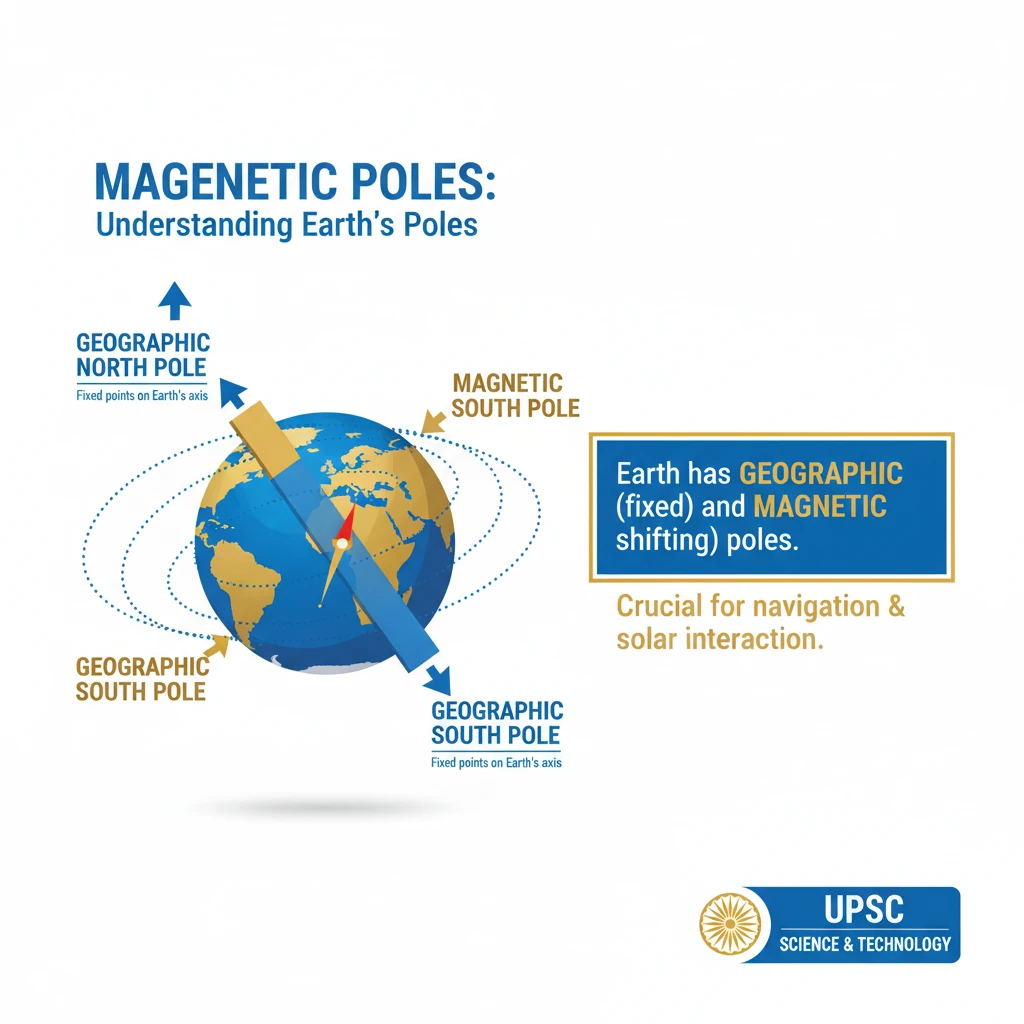
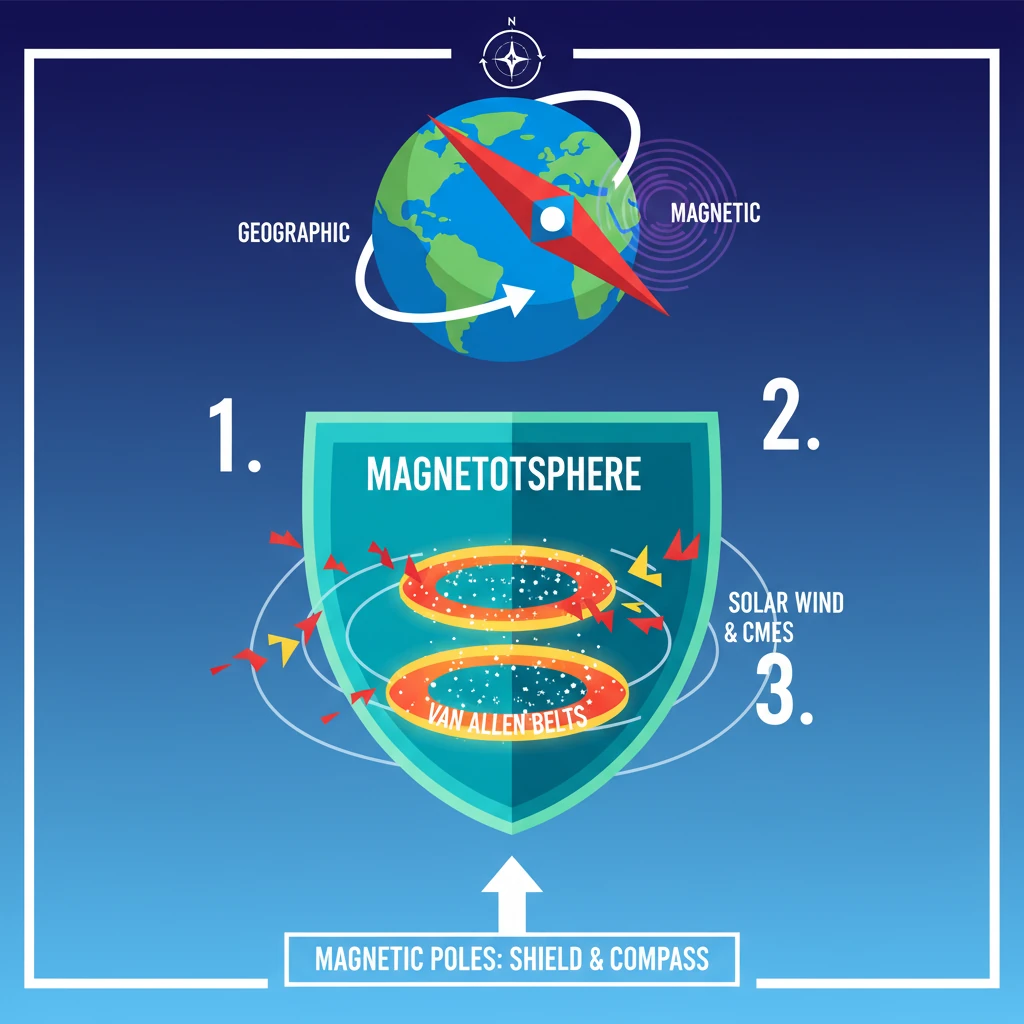
<h4>Understanding Earth's Poles</h4><p>The Earth possesses two distinct sets of poles: <strong>geographic poles</strong> and <strong>magnetic poles</strong>.</p><p>These poles are crucial for understanding Earth's orientation in space and its interaction with the solar environment.</p><h4>Geographic Poles Explained</h4><p>The <strong>geographic North</strong> and <strong>South poles</strong> are fixed points on Earth's surface.</p><div class='info-box'><p>They represent the locations where all lines of <strong>longitude converge</strong>.</p></div><ul><li>The <strong>Geographic North Pole</strong> is located in the middle of the <strong>Arctic Ocean</strong>.</li><li>The <strong>Geographic South Pole</strong> is found in <strong>Antarctica</strong>.</li></ul><h4>Magnetic Poles Explained</h4><p>In contrast, the <strong>magnetic poles</strong> are dynamic locations where the Earth's <strong>magnetic field lines</strong> interact with the surface.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>Magnetic North Pole</strong> (also known as the <strong>North Dip Pole</strong>) is where magnetic field lines <strong>enter</strong> the Earth's surface.</p></div><p>Conversely, the <strong>Magnetic South Pole</strong> is where magnetic field lines <strong>exit</strong> the Earth's surface.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>It is important to note that the <strong>Magnetic North Pole</strong> is geographically located near the <strong>Geographic South Pole</strong>, and vice-versa, due to the Earth's internal dynamo.</p></div><h4>Current Location of Magnetic North Pole</h4><p>The <strong>Magnetic North Pole</strong> is not stationary; it constantly drifts over time.</p><div class='info-box'><p>It is currently found on <strong>Ellesmere Island</strong> in <strong>northern Canada</strong>.</p></div><h4>Compass Navigation and Magnetic Poles</h4><p>When a <strong>compass</strong> points "north," it is not aligning with the <strong>true Geographic North Pole</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>Instead, a compass aligns itself with the Earth's <strong>magnetic field</strong> and points towards the <strong>Magnetic North Pole</strong>.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Understanding this distinction is crucial for navigation and for explaining phenomena like <strong>magnetic declination</strong> in UPSC Geography questions.</p></div><h4>Earth's Magnetosphere: A Protective Shield</h4><p>The Earth's <strong>magnetosphere</strong> is an invisible shield extending into space, generated by the planet's internal dynamo.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>Its primary function is to <strong>shield the planet</strong> from harmful <strong>space weather</strong>.</p></div><p>This includes dangerous phenomena such as <strong>solar wind</strong>, <strong>coronal mass ejections (CMEs)</strong>, and high-energy <strong>cosmic rays</strong>.</p><h4>Van Allen Radiation Belts</h4><p>The magnetosphere effectively <strong>repels harmful energy</strong> away from Earth.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Some of this trapped energy is concentrated in specific regions known as the <strong>Van Allen radiation belts</strong>.</p></div><p>These belts are toroidal regions of energetic charged particles, held in place by Earth's magnetic field.</p><h4>Geomagnetic Storms and Their Impacts</h4><p>During intense <strong>space weather events</strong>, the Earth's magnetic field can be significantly disturbed.</p><p>These disturbances lead to phenomena called <strong>geomagnetic storms</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Geomagnetic storms</strong> can have severe consequences, including widespread <strong>power blackouts</strong> and disruptions to <strong>communication systems</strong>.</p></div><h4>The Spectacle of Auroras</h4><p>Disturbances in Earth's magnetic field also play a role in creating beautiful natural light displays.</p><div class='info-box'><p>These disturbances <strong>funnel charged ions</strong> towards the <strong>polar regions</strong>.</p></div><p>When these ions collide with atmospheric gases, they create the spectacular light shows known as <strong>auroras</strong>.</p><ul><li>The <strong>Northern Lights</strong> are called <strong>Aurora Borealis</strong>.</li><li>The <strong>Southern Lights</strong> are called <strong>Aurora Australis</strong>.</li></ul>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Earth has distinct geographic (fixed) and magnetic (dynamic) poles.
- •Magnetic poles are where field lines enter/exit; compasses point to magnetic north.
- •The magnetosphere shields Earth from harmful solar wind and CMEs.
- •Van Allen belts trap energetic particles within the magnetosphere.
- •Geomagnetic storms can cause power blackouts and communication disruptions.
- •Auroras are spectacular light shows caused by charged particles funneled to polar regions.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content