What are the Key Features of MACE? - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What are the Key Features of MACE?
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
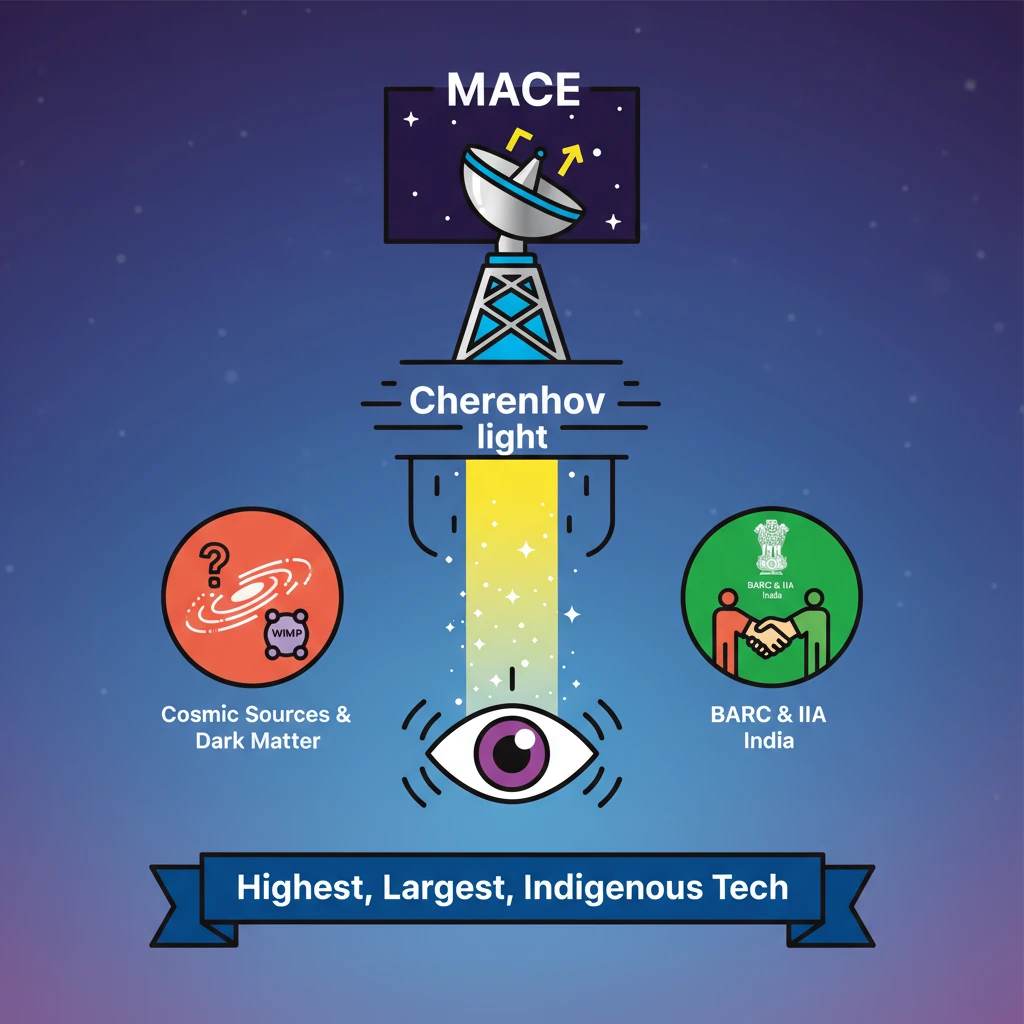
<h4>Introduction to MACE</h4><p>The <strong>Major Atmospheric Cherenkov Experiment (MACE)</strong> is a cutting-edge scientific instrument designed to observe the cosmos. It plays a crucial role in the field of <strong>gamma-ray astronomy</strong>, providing insights into some of the most energetic phenomena in the universe.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>MACE</strong> is an <strong>Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescope (IACT)</strong>. Its primary function is to indirectly detect <strong>high-energy gamma rays</strong> originating from various cosmic sources.</p></div><h4>Location and Scale</h4><p><strong>MACE</strong> is strategically located at an altitude of approximately <strong>4.3 kilometers</strong>. This elevated position provides a clearer view of the sky, minimizing atmospheric interference and enhancing observational capabilities.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Global Standing:</strong></p><ul><li>Highest imaging Cherenkov telescope globally.</li><li>Largest of its kind in Asia.</li><li>Second-largest worldwide.</li></ul></div><h4>Function and Detection Mechanism</h4><p>When <strong>high-energy gamma rays</strong> from cosmic sources enter Earth’s atmosphere, they interact with atmospheric particles. This interaction leads to the creation of <strong>electron-positron pairs</strong>, initiating a particle shower.</p><p>These rapidly moving charged particles (electrons and positrons) travel faster than the speed of light in the local medium (air). This phenomenon results in the emission of faint blue light, known as <strong>Cherenkov radiation</strong>.</p><p><strong>MACE</strong> is specifically designed to capture this ephemeral <strong>Cherenkov radiation</strong> using its highly sensitive equipment. By analyzing this light, scientists can deduce the properties and origins of the incoming <strong>gamma rays</strong>.</p><h4>Key Architectural Features</h4><p>The telescope's ability to collect faint light is significantly enhanced by its sophisticated light collector. This component is crucial for gathering the weak signals of <strong>Cherenkov radiation</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Light Collector Specifications:</strong></p><ul><li>Composed of <strong>356 mirror panels</strong>.</li><li>Arranged in a <strong>honeycomb structure</strong>.</li><li>Enhances both <strong>stability</strong> and the overall <strong>reflective area</strong>.</li></ul></div><h4>Research Objectives</h4><p>The fundamental goal of <strong>MACE</strong> is to conduct in-depth studies of <strong>high-energy gamma rays</strong> emitted from various cosmic sources. This research contributes significantly to our understanding of the extreme universe.</p><p>A major objective is to investigate the elusive nature of <strong>dark matter</strong>. <strong>MACE</strong> aims to detect <strong>gamma rays</strong> that might be produced from the annihilation events of <strong>Weakly Interacting Massive Particles (WIMPs)</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>Understanding <strong>WIMPs</strong> is critical, as these hypothetical particles are believed to constitute a substantial portion of the universe's total mass, yet they do not interact with ordinary matter via electromagnetic or strong nuclear forces.</p></div><h4>Institutions Involved</h4><p>The development and operation of <strong>MACE</strong> involve significant collaboration between leading Indian scientific institutions. These collaborations are vital for advancing India's capabilities in high-energy astrophysics.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Primary Institutions:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC)</strong></li><li><strong>Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA)</strong></li></ul></div><h4>Technological Innovations</h4><p><strong>MACE</strong> incorporates several advanced technological features to ensure its observational prowess. These innovations are key to its ability to detect extremely faint and short-lived signals.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>High-Resolution Camera:</strong></p><ul><li>Equipped with <strong>1,088 photomultiplier tubes</strong>.</li><li>Designed to detect and significantly amplify faint signals from <strong>Cherenkov radiation</strong>.</li></ul></div><p>The telescope's elevated location provides a distinct advantage. Positioned high above the majority of atmospheric disturbances, it offers a clearer and more stable view of the celestial sphere, optimizing its observational capabilities.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>For <strong>UPSC GS Paper 3 (Science and Technology)</strong>, understanding instruments like <strong>MACE</strong> is crucial. Focus on its purpose (gamma-ray detection, dark matter), location, and the underlying scientific principle (Cherenkov radiation).</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
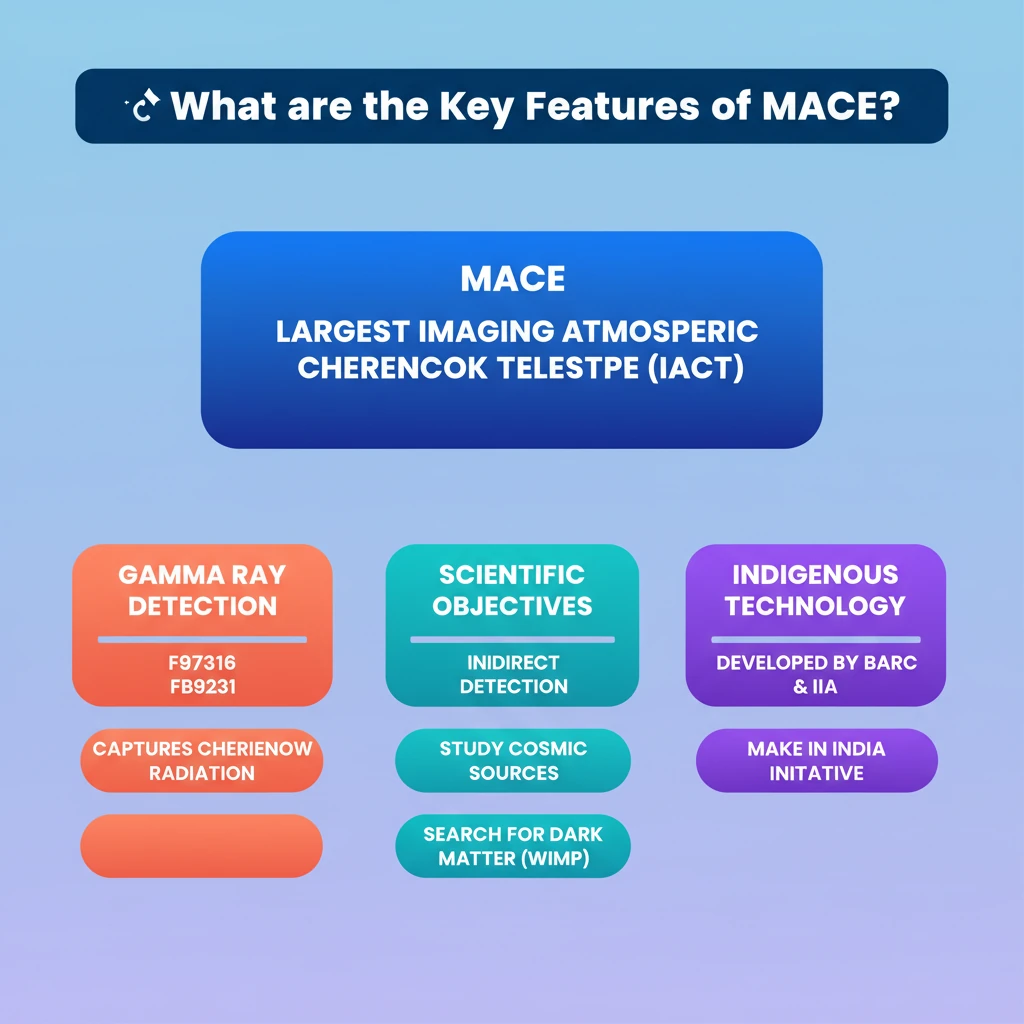
- •MACE is the highest and one of the largest Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescopes (IACTs) globally.
- •It indirectly detects high-energy gamma rays by capturing Cherenkov radiation produced in the atmosphere.
- •Key objectives include studying cosmic gamma-ray sources and searching for dark matter (WIMP annihilation).
- •Developed by BARC and IIA, it represents a significant indigenous technological achievement for India.
- •Its high-altitude location and advanced camera system are crucial for its observational capabilities.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) official publications
•Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) research outlines
•General astrophysics and particle physics literature on Cherenkov telescopes