What are the Key Facts About DRDO? - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What are the Key Facts About DRDO?
Medium⏱️ 12 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
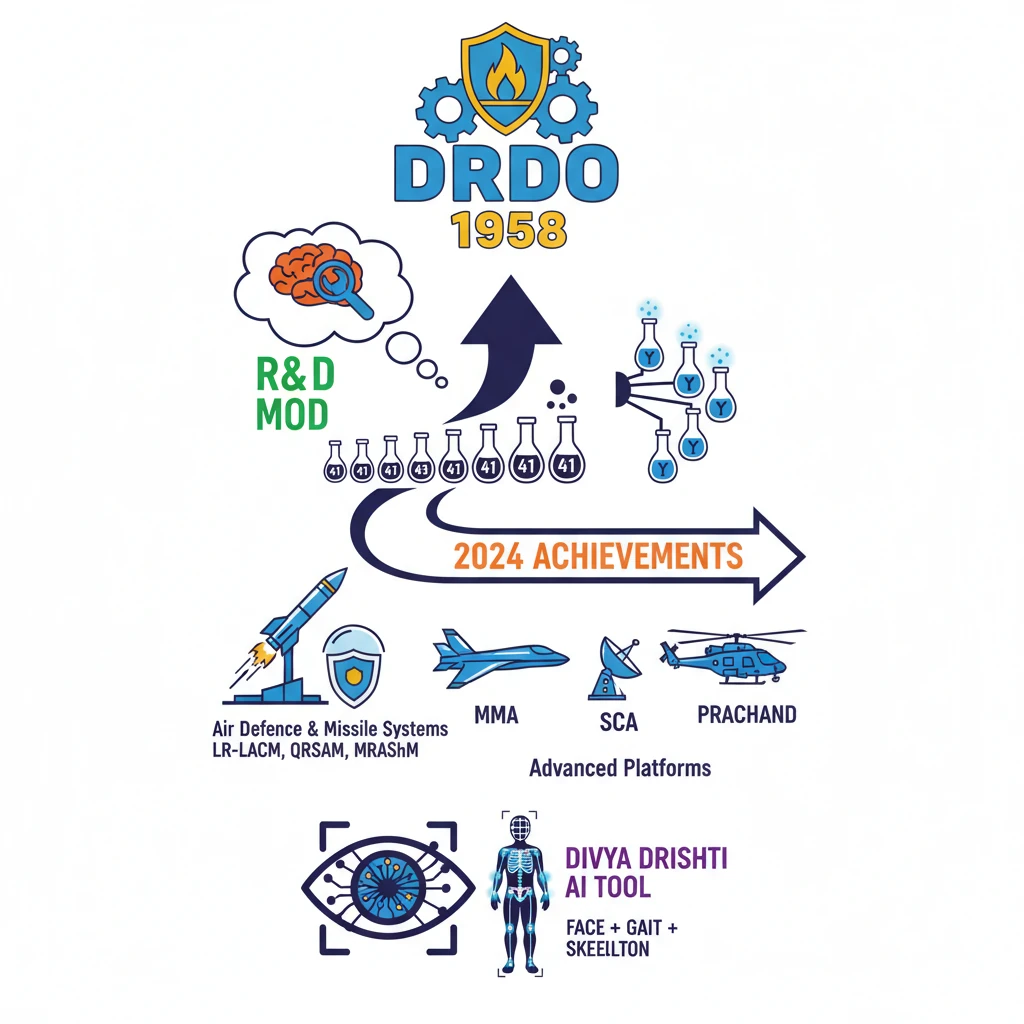
<h4>Introduction to DRDO</h4><p>The <strong>Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO)</strong> is the premier <strong>Research & Development (R&D) wing</strong> of the <strong>Ministry of Defence, Government of India</strong>. Its primary mandate is to empower India with cutting-edge defence technologies and achieve self-reliance in critical military capabilities.</p><div class='info-box'> <p><strong>Establishment:</strong> DRDO was founded in <strong>1958</strong> through the merger of three key defence entities:</p> <ul> <li>The <strong>Technical Development Establishment (TDEs)</strong> of the Indian Army.</li> <li>The <strong>Directorate of Technical Development and Production (DTDP)</strong>.</li> <li>The <strong>Defence Science Organisation (DSO)</strong>.</li> </ul></div><p>Starting with a modest <strong>10 laboratories</strong> at its inception, DRDO has significantly expanded its footprint. It currently operates a vast network of <strong>41 laboratories</strong> and <strong>5 DRDO Young Scientist Laboratories (DYSLs)</strong> across the nation, focusing on diverse areas of defence technology.</p><h4>Key Achievements and Contributions of DRDO</h4><p>Over the decades, DRDO has been instrumental in developing a wide array of defence systems, platforms, and technologies. These contributions have bolstered India's national security and reduced its dependence on foreign imports.</p><div class='key-point-box'> <p>DRDO's work spans various domains, including <strong>missile technology</strong>, <strong>aeronautics</strong>, <strong>electronics</strong>, <strong>armaments</strong>, <strong>combat engineering</strong>, and <strong>life sciences</strong>, among others. Its efforts are central to India's strategic autonomy.</p></div><h4>DRDO's Notable Achievements in 2024</h4><p>The year <strong>2024</strong> witnessed significant milestones for DRDO, marked by the handover of advanced systems and the sanctioning of crucial flagship programs.</p><h5>System Handover: Strengthening India's Defence Capabilities</h5><p>DRDO successfully handed over multiple advanced systems to the Indian armed forces, enhancing their operational readiness and strategic advantage. These systems represent years of indigenous research and development.</p><div class='info-box'> <p><strong>Notable Systems Handed Over:</strong></p> <ul> <li><strong>Air Defence Systems:</strong> <ul> <li><strong>Air Defence Tactical Control Radar (ADTCR)</strong></li> <li><strong>Air Defence Fire Control Radar (ADFCR)</strong></li> </ul> </li> <li><strong>Missile Systems:</strong> <ul> <li><strong>Long Range Land Attack Cruise Missile (LR-LACM)</strong></li> <li><strong>Quick Reaction Surface to Air Missile (QRSAM)</strong></li> <li><strong>Medium Range Anti-Ship Missile (MRAShM)</strong></li> </ul> </li> <li><strong>Advanced Platforms & Munitions:</strong> <ul> <li><strong>Multi-Mission Maritime Aircraft (MMA)</strong></li> <li><strong>SCA (Signal Intelligence and COMJAM Aircraft)</strong></li> <li><strong>Anti-Tank Influence Mine PRACHAND</strong></li> </ul> </li> </ul></div><h5>AI Tools Development: 'Divya Drishti'</h5><p>In a significant stride towards integrating artificial intelligence into defence, DRDO developed an innovative AI tool named <strong>'Divya Drishti'</strong>. This tool showcases advanced capabilities in surveillance and identification.</p><div class='info-box'> <p><strong>About 'Divya Drishti':</strong></p> <ul> <li>An <strong>AI tool</strong> that integrates <strong>face recognition</strong> technology.</li> <li>Combines face recognition with <strong>immutable physiological traits</strong> such as <strong>gait (pattern of walking)</strong> and <strong>skeleton analysis</strong> for enhanced accuracy and identification.</li> </ul></div><h5>Flagship Programs Sanctioned by CCS</h5><p>The <strong>Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS)</strong> sanctioned two pivotal flagship programs, underscoring India's commitment to advanced defence manufacturing and testing infrastructure.</p><div class='key-point-box'> <p><strong>Sanctioned Programs:</strong></p> <ol> <li><strong>Full Scale Engineering Development (FSED) of Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA):</strong> This program aims to develop India's next-generation <strong>stealth fighter aircraft</strong>, a critical step in aerospace self-reliance.</li> <li><strong>New Missile Test Range in Andhra Pradesh:</strong> Establishment of a dedicated facility to further enhance India's capabilities in <strong>missile testing and evaluation</strong>.</li> </ol></div><h4>Overview of Major Missile Systems Developed by DRDO</h4><p>DRDO has been a pioneer in developing a comprehensive range of missile systems, categorized by their launch platforms and targets. These systems form the backbone of India's strategic deterrence.</p><div class='info-box'> <table class='info-table'> <tr> <th>Missile Type</th> <th>Examples</th> </tr> <tr> <td><strong>Air-to-Air Missile</strong></td> <td><strong>MICA</strong>, <strong>Astra Missile</strong></td> </tr> <tr> <td><strong>Surface-to-Air Missiles</strong></td> <td><strong>Trishul</strong>, <strong>Akash</strong>, <strong>Barak 8</strong></td> </tr> <tr> <td><strong>Surface-to-Surface Missiles</strong></td> <td><strong>Agni</strong> (series), <strong>Prithvi</strong> (series), <strong>Dhanush</strong>, <strong>Shaurya</strong></td> </tr> <tr> <td><strong>Cruise Missiles</strong></td> <td><strong>BrahMos</strong>, <strong>Nirbhay</strong></td> </tr> </table></div><h4>DRDO's Contribution to Combat Aircraft</h4><p>Beyond missile technology, DRDO has made significant strides in indigenous aircraft development, notably with the Light Combat Aircraft program.</p><div class='info-box'> <p><strong>Indigenous Fighter Jet:</strong></p> <ul> <li><strong>Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas:</strong> A multi-role light fighter developed by <strong>Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA)</strong> and produced by <strong>Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL)</strong>, with DRDO playing a crucial R&D role.</li> </ul></div><div class='exam-tip-box'> <p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Questions on DRDO often appear in <strong>GS-III Science & Technology</strong> and <strong>Internal Security</strong>. Focus on its role in <strong>self-reliance</strong>, specific <strong>flagship programs</strong>, and the <strong>strategic implications</strong> of its developments.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •DRDO was established in <strong>1958</strong> by merging three defence entities, serving as the <strong>R&D wing of the Ministry of Defence</strong>.
- •It has grown from <strong>10 to 41 laboratories</strong>, plus <strong>5 DRDO Young Scientist Laboratories (DYSLs)</strong>.
- •Key <strong>2024 achievements</strong> include handover of <strong>Air Defence</strong>, <strong>Missile Systems (LR-LACM, QRSAM, MRAShM)</strong>, <strong>Advanced Platforms (MMA, SCA, PRACHAND)</strong>.
- •Developed <strong>'Divya Drishti'</strong>, an <strong>AI tool</strong> for face recognition integrated with gait and skeleton analysis.
- •<strong>CCS sanctioned flagship programs</strong>: <strong>Full Scale Engineering Development (FSED) of AMCA</strong> and a <strong>new Missile Test Range in Andhra Pradesh</strong>.
- •DRDO has developed a wide range of <strong>missile systems</strong> (Air-to-Air, Surface-to-Air, Surface-to-Surface, Cruise) and contributed to <strong>LCA Tejas</strong>.
- •Its work is crucial for <strong>'Atmanirbhar Bharat'</strong> in defence, promoting indigenous capabilities and strategic autonomy.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Official DRDO Website (General information and mission statement)
•Ministry of Defence Press Releases (for 2024 achievements and flagship programs)