Large Language Models - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Large Language Models
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to Large Language Models (LLMs)</h4><p>The advent of <strong>advanced artificial intelligence (AI)</strong> has been significantly marked by the emergence of <strong>Large Language Models (LLMs)</strong>.</p><p>These models have fundamentally transformed how computers interact with humans and process complex language, opening new frontiers in <strong>AI technology</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>LLMs</strong> are revolutionizing fields from enhancing virtual conversations to powering creative content generation, showcasing their diverse capabilities.</p></div><h4>What are Large Language Models (LLMs)?</h4><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Definition:</strong> <strong>Large Language Models (LLMs)</strong> are <strong>general-purpose language models</strong> designed to solve common language problems.</p></div><p>These problems include <strong>text classification</strong>, <strong>question answering</strong>, and <strong>text generation</strong>, demonstrating their versatility.</p><p><strong>LLMs</strong> are trained on <strong>massive datasets</strong>, enabling them to comprehend intricate patterns, structures, and relationships inherent in <strong>human language</strong>.</p><h4>Types of Large Language Models (LLMs) Based on Architecture</h4><p><strong>LLMs</strong> can be categorized based on their underlying architectural designs, each with distinct mechanisms for language processing:</p><ul><li><strong>Autoregressive Models:</strong> These models predict the <strong>next word</strong> in a sequence by considering the <strong>previous words</strong>.</li><li>Example: <strong>GPT-3</strong> (Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3) is a prominent instance of an autoregressive LLM.</li><li><strong>Transformer-based Models:</strong> These models utilise a specific <strong>artificial neural network architecture</strong> known as the <strong>Transformer</strong> for efficient language processing.</li><li>Examples: <strong>LaMDA</strong> (Language Model for Dialogue Applications) and <strong>Gemini</strong> (formerly known as <strong>Bard</strong>) are notable transformer-based LLMs.</li><li><strong>Encoder-decoder Models:</strong> This architecture involves two main components: an <strong>encoder</strong> that converts input text into a numerical representation, and a <strong>decoder</strong> that then transforms this representation into another language or format.</li></ul>
💡 Key Takeaways
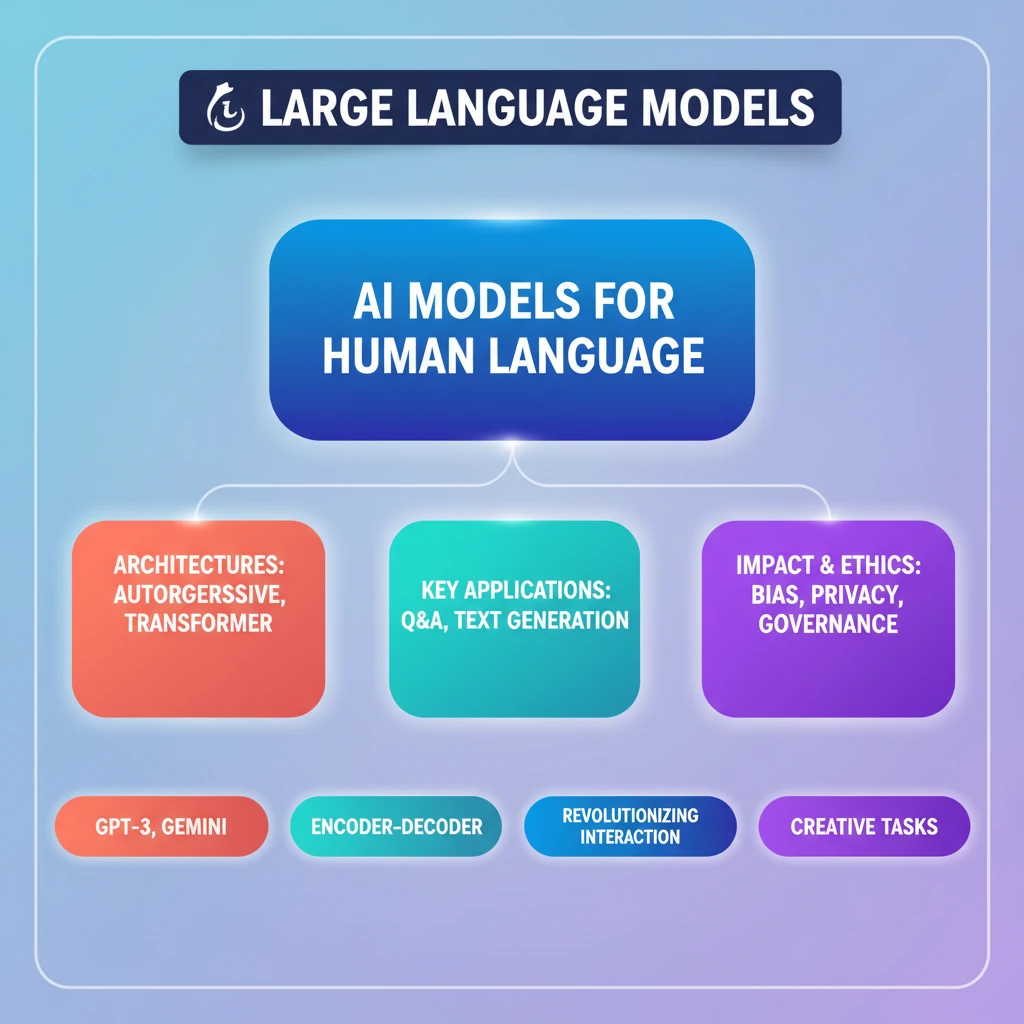
- •LLMs are AI models trained on vast datasets to understand and generate human language.
- •They solve common language problems like text classification, Q&A, and text generation.
- •Architectural types include Autoregressive (e.g., GPT-3), Transformer-based (e.g., Gemini), and Encoder-decoder models.
- •LLMs are revolutionizing human-computer interaction and creative tasks.
- •Their development raises important ethical and regulatory considerations regarding bias, privacy, and governance.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•OpenAI Documentation (GPT-3)
•Google AI Blog (LaMDA, Gemini/Bard)
•Academic papers on Transformer architecture and NLP history