Carbon Footprint of Artificial Intelligence - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
Carbon Footprint of Artificial Intelligence
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
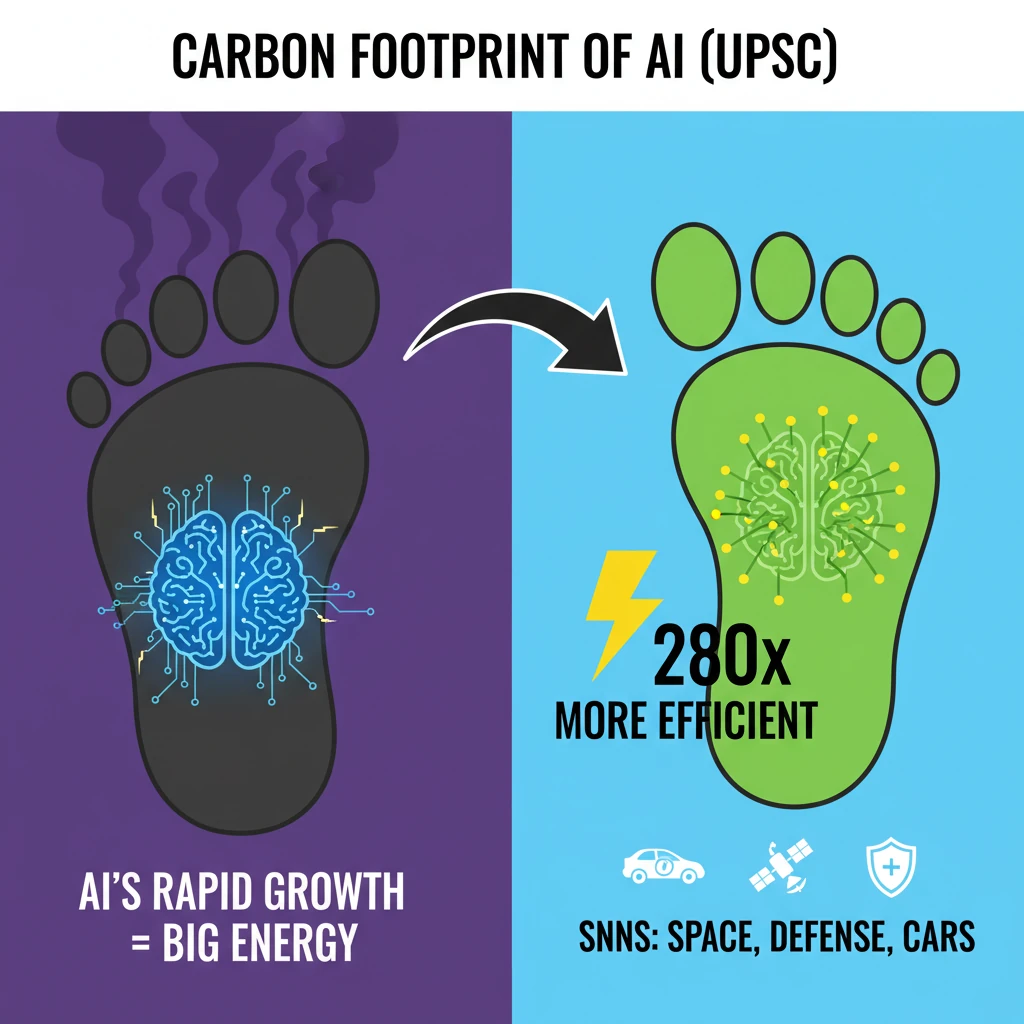
<h4>Introduction to AI's Carbon Footprint</h4><p>The rapid advancement of <strong>Artificial Intelligence (AI)</strong> technology has brought about significant innovations across various sectors. However, its increasingly <strong>energy-intensive operations</strong> are raising substantial <strong>environmental concerns</strong>.</p><p>Training and deploying complex AI models, especially large language models and deep neural networks, consume vast amounts of electricity, contributing to a growing <strong>carbon footprint</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Key Challenge:</strong> Balancing AI's immense potential for societal benefit with its escalating environmental impact due to high energy consumption.</p></div><h4>Promising Avenues for Reduction</h4><p>Despite these challenges, ongoing research and technological advancements offer promising solutions to mitigate AI's carbon footprint. Innovations like <strong>Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs)</strong> and the concept of <strong>lifelong learning</strong> are crucial in this endeavor.</p><p>These approaches aim to make AI more energy-efficient, allowing us to leverage its capabilities, including its potential to address <strong>climate change</strong>, in a sustainable manner.</p><h4>Understanding Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs)</h4><p><strong>Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs)</strong> represent a novel type of <strong>artificial neural network (ANN)</strong>. Their design is directly inspired by the intricate and efficient neural structure of the <strong>human brain</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>SNNs vs. ANNs:</strong> Unlike traditional ANNs, which process data using continuous numerical values, SNNs operate based on discrete, event-driven <strong>spikes or pulses of activity</strong>.</p></div><p>This fundamental difference in operation mimics how biological neurons communicate. Neurons in the brain transmit information through electrical impulses, known as spikes.</p><p>Consider <strong>Morse code</strong>, which uses specific sequences of dots and dashes to convey messages. Similarly, SNNs utilize patterns or timings of these spikes to process and transmit information efficiently.</p><h4>Energy Efficiency of SNNs</h4><p>The inherent <strong>binary, all-or-nothing characteristic</strong> of spikes is what makes SNNs remarkably energy-efficient. Energy is consumed only when a spike occurs, indicating activity.</p><p>In contrast, artificial neurons in conventional ANNs are often continuously active, leading to constant energy consumption. This makes ANNs significantly more power-hungry.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Core Principle:</strong> SNNs exhibit exceptionally low energy consumption when there are no spikes, directly contributing to their superior energy efficiency.</p></div><p>Studies have indicated that SNNs possess the potential to be up to <strong>280 times more energy-efficient</strong> than traditional ANNs. This efficiency stems from their <strong>sparsity in activity</strong> and <strong>event-driven processing</strong>.</p><h4>Applications and Future of SNNs</h4><p>The energy-efficient properties of SNNs make them highly suitable for applications where power resources are limited or computational efficiency is paramount. This includes critical domains such as <strong>space exploration</strong>, advanced <strong>defence systems</strong>, and sophisticated <strong>self-driving cars</strong>.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Questions on emerging technologies often focus on their benefits, challenges, and applications. Understanding SNNs' energy efficiency is crucial for topics like <strong>sustainable technology</strong> and <strong>climate change mitigation</strong> in <strong>GS3</strong>.</p></div><p>Ongoing research is actively focused on further optimizing SNNs and developing advanced learning algorithms. The goal is to fully harness their energy efficiency for a wide spectrum of practical and impactful applications, paving the way for more sustainable AI.</p>
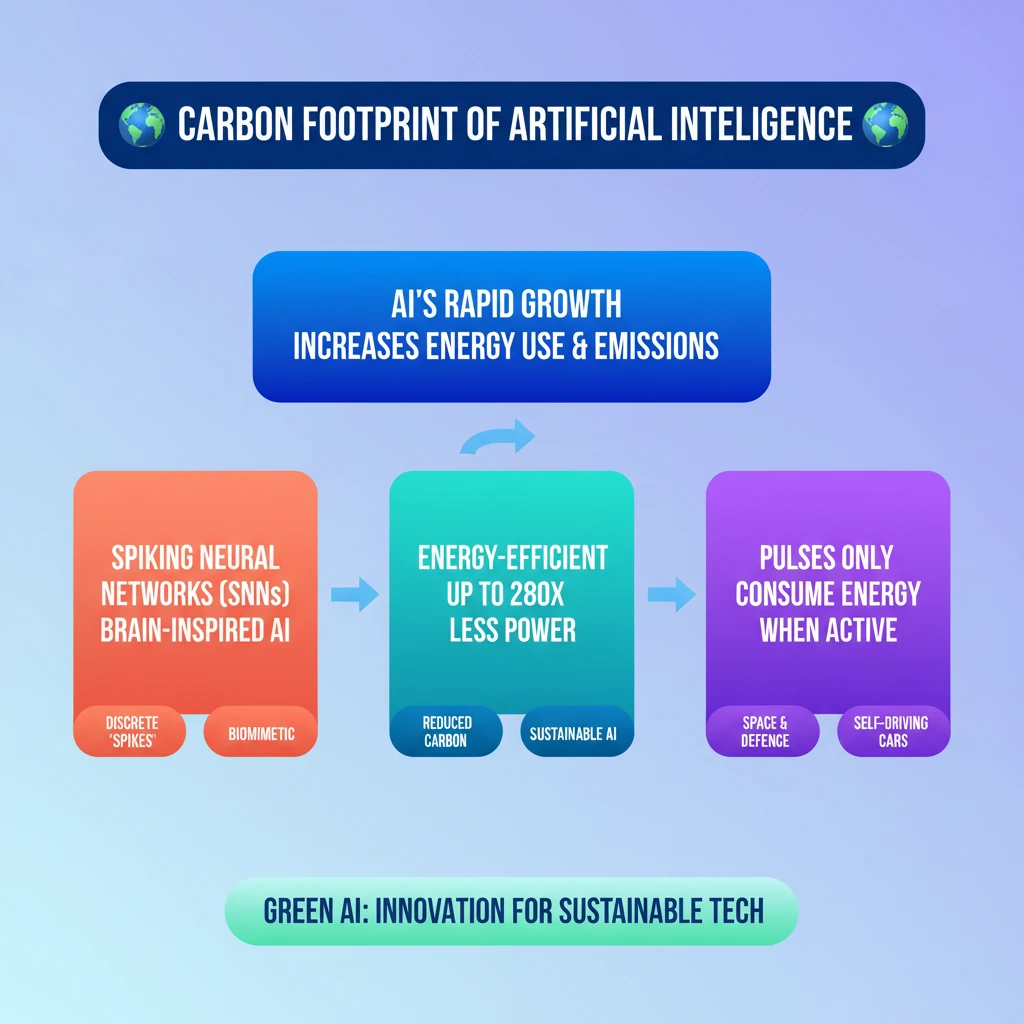
💡 Key Takeaways
- •AI's rapid growth leads to significant energy consumption and a rising carbon footprint.
- •Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) are brain-inspired AI models that use discrete 'spikes' for communication.
- •SNNs are highly energy-efficient, potentially 280 times more so than traditional ANNs, as they only consume energy when active.
- •This efficiency makes SNNs ideal for power-constrained applications like space exploration, defence, and self-driving cars.
- •Developing 'Green AI' through innovations like SNNs and lifelong learning is crucial for sustainable technological progress.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•General knowledge on Artificial Intelligence and Spiking Neural Networks