Discoveries in Biology Using C. elegans - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Discoveries in Biology Using C. elegans
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
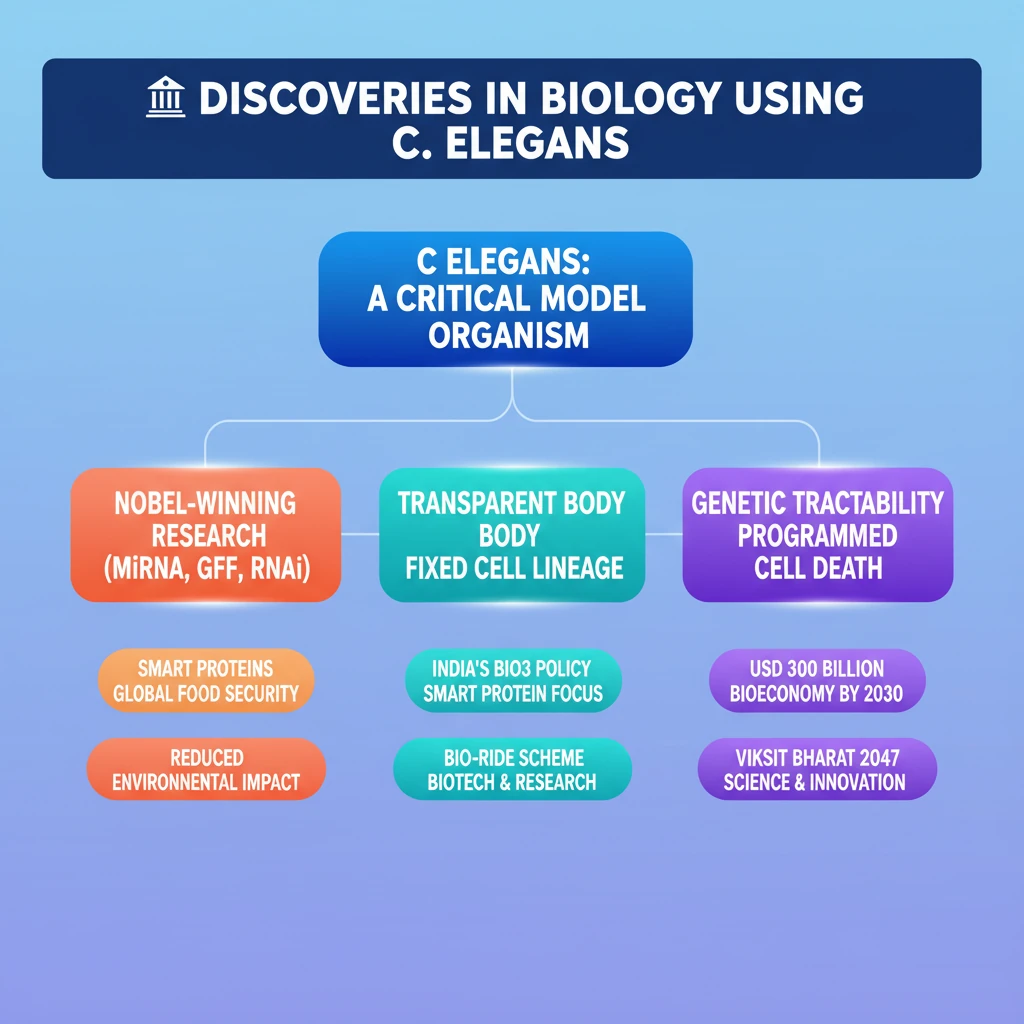
<h4>Introduction to C. elegans and its Scientific Significance</h4><p>The tiny roundworm <strong>Caenorhabditis elegans</strong>, often abbreviated as <strong>C. elegans</strong>, has emerged as a crucial model organism in biological research.</p><p>This transparent nematode, measuring only <strong>1 mm</strong> in length, has been instrumental in numerous groundbreaking discoveries, several of which have been recognized with <strong>Nobel Prizes</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>What is C. elegans?</strong></p><ul><li>A <strong>transparent nematode</strong> (roundworm).</li><li>Length: Approximately <strong>1 mm</strong>.</li><li>An <strong>invertebrate</strong>, commonly found in soil.</li></ul></div><h4>C. elegans: A Nobel Prize Powerhouse</h4><p>The simplicity and genetic tractability of <strong>C. elegans</strong> have made it an ideal subject for studying fundamental biological processes, leading to significant advancements across various fields.</p><p>Its contributions span genetics, developmental biology, neurobiology, and cell biology, often revealing mechanisms conserved across species, including humans.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Why C. elegans is a Model Organism:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Transparent body</strong>: Allows direct observation of internal processes.</li><li><strong>Simple nervous system</strong>: Exactly 302 neurons, fully mapped.</li><li><strong>Short life cycle</strong>: Rapid generation time for genetic studies.</li><li><strong>Fixed cell lineage</strong>: Every cell division and fate is known.</li><li><strong>Genetic tractability</strong>: Easy to manipulate genes.</li></ul></div><p>Several Nobel Prizes have been awarded for discoveries made using or significantly advanced by research on <strong>C. elegans</strong>:</p><table class='info-table'><tr><th>Nobel Laureates</th><th>Year</th><th>Prize Category</th><th>Discovery/Contribution</th></tr><tr><td><strong>Victor Ambros</strong> and <strong>Gary Ruvkun</strong></td><td><strong>2024</strong></td><td>Physiology or Medicine</td><td>Discovered <strong>microRNAs</strong></td></tr><tr><td><strong>Osamu Shimomura</strong>, <strong>Martin Chalfie</strong>, <strong>Roger Tsien</strong></td><td><strong>2008</strong></td><td>Chemistry</td><td>Developed <strong>Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP)</strong></td></tr><tr><td><strong>Andrew Fire</strong> and <strong>Craig Mello</strong></td><td><strong>2006</strong></td><td>Medicine</td><td>Discovered <strong>RNA interference (RNAi)</strong></td></tr><tr><td><strong>Sydney Brenner</strong></td><td><strong>2002</strong></td><td>Medicine</td><td>Research on understanding <strong>programmed cell death</strong></td></tr></table><h4>The Rise of Smart Proteins: Food of the Future</h4><p>Beyond model organisms, biotechnology is revolutionizing food production, with <strong>smart proteins</strong> emerging as a sustainable solution to global food security and environmental challenges.</p><p>The Indian government has recognized this potential through policies like the <strong>Biotechnology for Economy, Environment, and Employment (Bio3) Policy</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>What are Smart Proteins?</strong></p><ul><li>Also known as <strong>alternative proteins</strong>.</li><li>Derived from <strong>unconventional sources</strong>: algae, fungi, insects.</li><li>Produced using <strong>advanced methods</strong>: fermentation, lab-grown cells.</li><li>Includes <strong>plant-based proteins</strong> designed to mimic animal products in taste and nutrition.</li></ul></div><p>These proteins offer a compelling alternative to conventional animal agriculture, addressing concerns related to environmental impact, food safety, and ethical consumption.</p><h4>Environmental and Health Benefits of Smart Proteins</h4><p>The production of <strong>alternative proteins</strong> significantly reduces the environmental footprint compared to traditional meat production.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Environmental Advantages:</strong></p><ul><li>Uses <strong>72-99% less water</strong>.</li><li>Requires <strong>47-99% less land</strong>.</li><li>Causes <strong>51-91% less water pollution</strong>.</li><li>Emits <strong>30-90% fewer greenhouse gases</strong>.</li></ul></div><p>From a public health perspective, <strong>smart proteins</strong> enhance <strong>food safety</strong> by mitigating the risk of <strong>zoonotic diseases</strong>, which are illnesses transmitted from animals to humans.</p><p>They also align with ethical consumption trends and can complement diverse dietary habits, including those prevalent in <strong>India</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>India's Protein Consumption:</strong></p><p>India's protein intake increased from <strong>9.7%</strong> of calories in <strong>1991</strong> to <strong>11%</strong> in <strong>2021</strong>, reflecting rising incomes and changing dietary patterns.</p></div><h4>BIO-RIDE Scheme: Boosting India's Bioeconomy</h4><p>To further bolster research and innovation in biotechnology, the <strong>Union Cabinet</strong> has approved the <strong>Biotechnology Research Innovation and Entrepreneurship Development (Bio-RIDE) scheme</strong>.</p><p>This scheme is a strategic initiative aimed at positioning <strong>India</strong> as a global leader in the biotechnology sector.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Objectives of Bio-RIDE:</strong></p><ul><li>Foster <strong>research, innovation, and entrepreneurship</strong> in biotechnology.</li><li>Achieve a <strong>USD 300 billion bioeconomy</strong> for India by <strong>2030</strong>.</li><li>Contribute to the broader vision of <strong>Viksit Bharat 2047</strong>.</li></ul></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understand how schemes like <strong>Bio-RIDE</strong> and policies like <strong>Bio3</strong> are crucial for India's economic growth, sustainable development, and global standing in the science and technology domain. Connect them to topics like <strong>food security</strong>, <strong>climate change mitigation</strong>, and <strong>public health</strong>.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •C. elegans is a critical model organism, instrumental in multiple Nobel Prize-winning discoveries (miRNAs, GFP, RNAi, programmed cell death).
- •Its transparent body, fixed cell lineage, and genetic tractability make it ideal for studying fundamental biological processes.
- •Smart Proteins (alternative proteins) are emerging as a sustainable solution for global food security, reducing environmental impact and zoonotic disease risks.
- •India's Bio3 Policy prioritizes smart protein production, while the Bio-RIDE scheme aims to boost biotechnology research and entrepreneurship.
- •India targets a USD 300 billion bioeconomy by 2030, aligning with the Viksit Bharat 2047 vision.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Nobel Prize official website (for laureates and discoveries)
•General knowledge of Indian government policies (Bio3, Bio-RIDE, Viksit Bharat)