What are Obelisks? - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
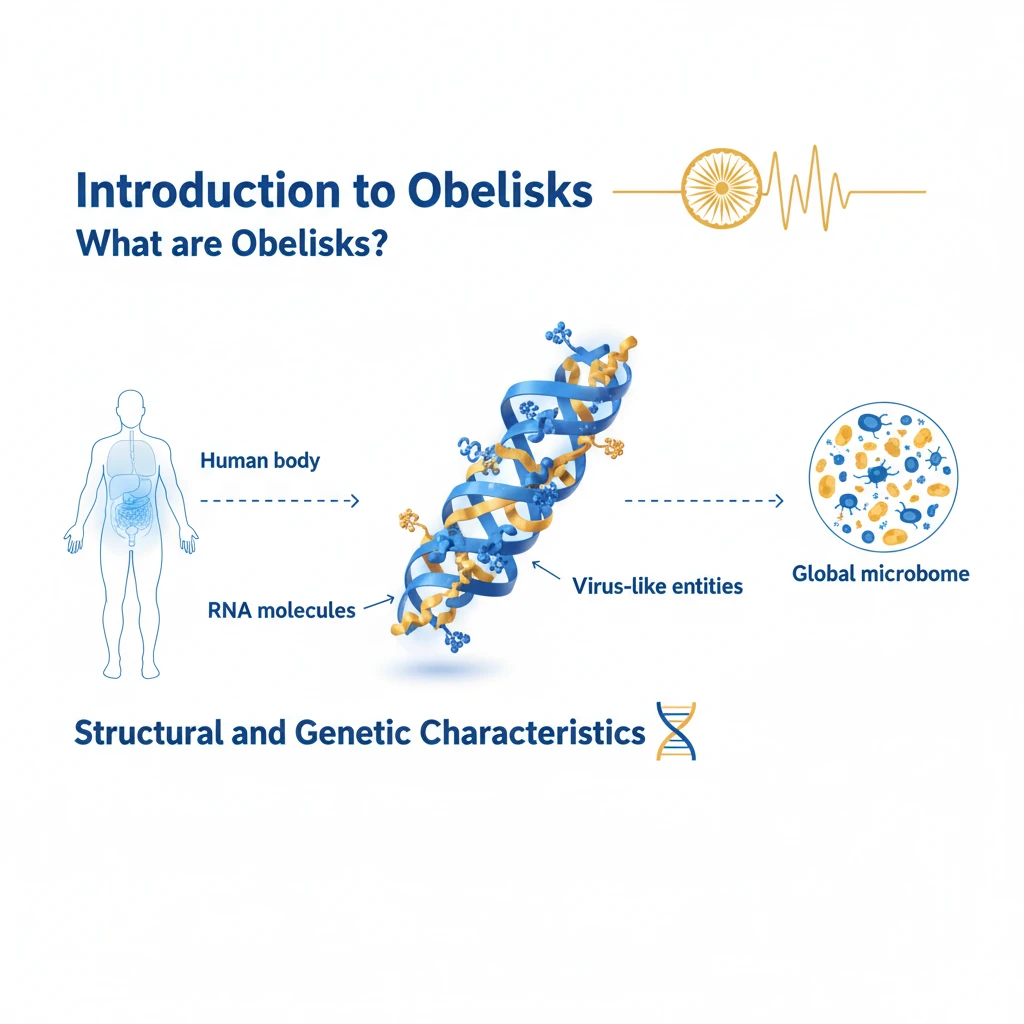
What are Obelisks?
Medium⏱️ 5 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to Obelisks</h4><p><strong>Obelisks</strong> represent a novel category of <strong>virus-like entities</strong>. They are primarily composed of diverse <strong>RNA molecules</strong>, distinguishing them from traditional viruses.</p><p>These entities have been identified residing within the <strong>human body</strong> and across the vast <strong>global microbiome</strong>, indicating a widespread, yet previously undetected, presence.</p><h4>Structural and Genetic Characteristics</h4><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Obelisks</strong> are characterized by their highly <strong>symmetrical, rod-like structures</strong>. This distinctive shape visually resembles the ancient monumental obelisks, inspiring their name.</p></div><p>Their <strong>genetic sequences</strong> are notably short, typically around <strong>1,000 nucleotides long</strong>. A significant finding is the absence of any detectable similarities to previously known <strong>biological agents</strong>, highlighting their unique nature.</p><h4>Discovery and Potential Host</h4><p>The initial study involved analyzing <strong>RNA data</strong> obtained from both <strong>gut and oral bacteria</strong>. However, researchers could not definitively pinpoint which specific bacteria hosted a given obelisk.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>Initial findings suggest a possible association with the bacterial species <strong><em>Streptococcus sanguinis</em></strong>. This bacterium is commonly found within the <strong>human mouth</strong>, hinting at a potential oral microbiome connection.</p></div><h4>Unanswered Questions and Future Research</h4><p>The discovery of <strong>Obelisks</strong> has opened a new frontier in microbiology, posing numerous critical questions regarding their fundamental biology and ecological role.</p><ul><li>How do they achieve <strong>genome replication</strong>?</li><li>What are their mechanisms of <strong>transmission</strong> between hosts?</li><li>Do they exhibit <strong>pathogenicity</strong> (ability to cause disease) in humans or other organisms?</li><li>How have they undergone <strong>evolution</strong>, and what are their evolutionary relationships?</li><li>What are their potential roles in overall <strong>human health and disease</strong>, and do they contribute to specific conditions?</li></ul><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Further research is crucial to unravel the mysteries surrounding <strong>Obelisks</strong>. This will shed light on their <strong>ecological significance</strong> and their broader <strong>impact on human health</strong>, a topic potentially relevant for <strong>UPSC Mains GS-III Science & Technology</strong> and <strong>Public Health</strong>.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Obelisks are newly discovered virus-like entities composed of diverse RNA molecules.
- •They are found in the human body and global microbiome, particularly associated with gut and oral bacteria.
- •Characterized by highly symmetrical, rod-like structures and short (~1,000 nucleotides) genetic sequences with no known biological similarities.
- •Initial research suggests a possible link to the oral bacterium Streptococcus sanguinis.
- •Their mechanisms of genome replication, transmission, pathogenicity, evolution, and specific roles in human health and disease are currently unknown and are subjects of ongoing research.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content