Efficacy of Liquid Nano Urea - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
Efficacy of Liquid Nano Urea
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
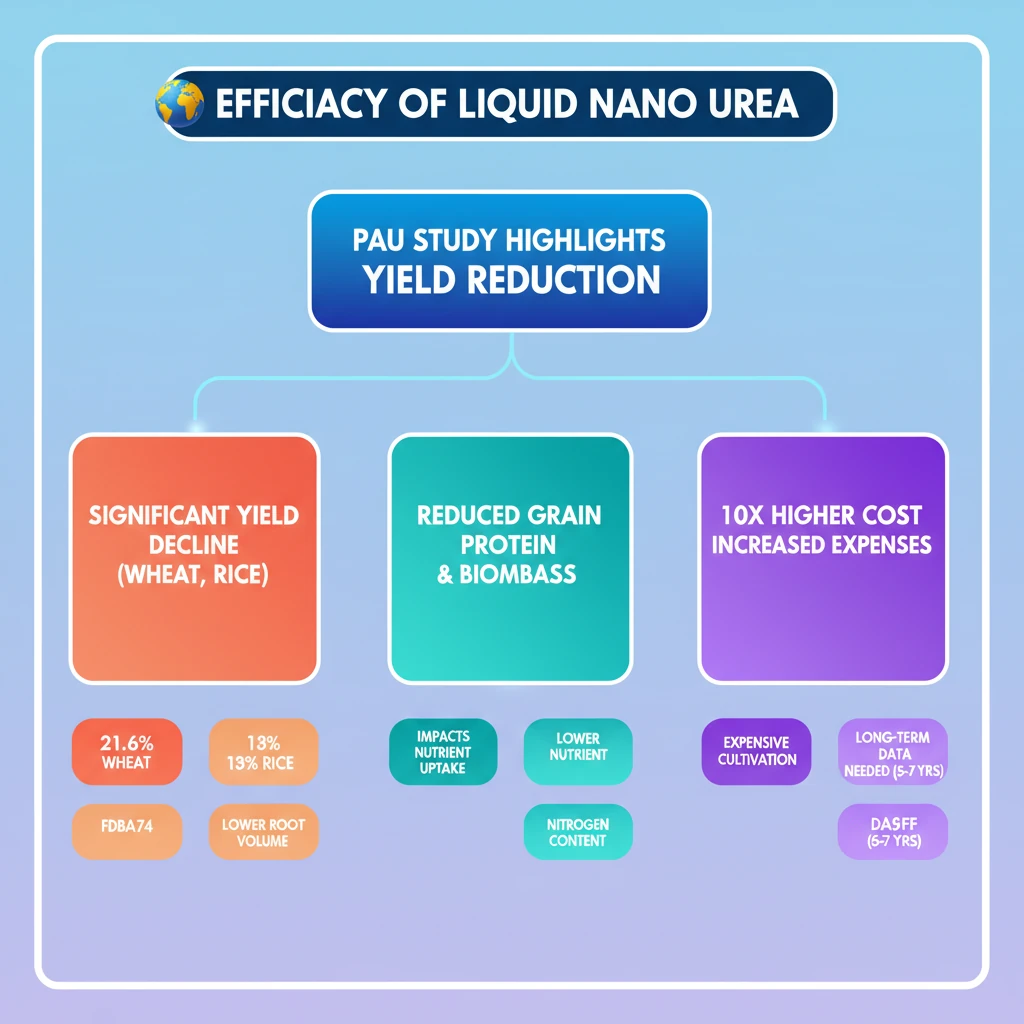
<h4>Introduction to Liquid Nano Urea Efficacy</h4><p>A recent <strong>two-year field experiment</strong> conducted by scientists from <strong>Punjab Agricultural University (PAU)</strong> has shed light on the efficacy of <strong>Liquid Nano Urea</strong>. The study compared its performance against <strong>conventional nitrogen (N) fertiliser application</strong>, revealing significant findings.</p><p>The results underscore the critical need for more extensive <strong>long-term field evaluations</strong>, ideally spanning <strong>5-7 years</strong>. Such prolonged studies are essential to definitively determine if <strong>nano urea</strong> can truly match the performance of <strong>conventional urea</strong> and sustain <strong>crop yields</strong> over time.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Key Insight:</strong> The initial findings suggest that <strong>Liquid Nano Urea</strong> may not be a direct substitute for <strong>conventional urea</strong> without further rigorous, long-term validation. This impacts future agricultural policy and farmer adoption.</p></div><h4>Significant Yield Reduction</h4><p>The PAU study observed a substantial decrease in <strong>crop yields</strong> when <strong>nano urea</strong> was utilized in comparison to <strong>conventional nitrogen fertilizers</strong>. This reduction raises concerns about its immediate applicability for maintaining agricultural productivity.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Specific Yield Decreases:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Wheat yield:</strong> A significant <strong>21.6% decrease</strong> was recorded.</li><li><strong>Rice yield:</strong> A notable <strong>13% decrease</strong> was observed.</li></ul></div><h4>Decline in Grain Nitrogen Content</h4><p>Beyond just yield, the application of <strong>nano urea</strong> also led to a reduction in the <strong>grain nitrogen content</strong> in both <strong>rice</strong> and <strong>wheat crops</strong>. This is a critical factor influencing the nutritional quality of staple foods.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Grain Nitrogen Content Reduction:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Rice:</strong> A <strong>17% decrease</strong> in grain N content.</li><li><strong>Wheat:</strong> An <strong>11.5% decrease</strong> in grain N content.</li></ul></div><p>The lowered <strong>grain nitrogen content</strong> directly implies reduced <strong>protein levels</strong> in the harvested crops. For a country like <strong>India</strong>, where <strong>rice</strong> and <strong>wheat</strong> are primary staple foods providing essential <strong>protein</strong> and <strong>carbohydrates</strong>, this decline is a significant public health concern.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Relevance:</strong> The impact of reduced <strong>protein content</strong> in staple foods can be linked to <strong>food security</strong>, <strong>malnutrition</strong>, and public health challenges in India (<strong>GS-II Social Justice, GS-III Food Security</strong>). This highlights the socio-economic implications of agricultural research findings.</p></div><h4>Elevated Cost Considerations</h4><p>The study also highlighted the economic implications for farmers. The <strong>cost of nano urea formulation</strong> was found to be significantly higher than that of traditional granular urea.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Cost Comparison:</strong> The cost of <strong>nano urea</strong> was approximately <strong>10 times higher</strong> than that of <strong>granular urea</strong>.</p></div><p>This substantial price difference means that adopting <strong>nano urea</strong> could considerably increase the <strong>cost of cultivation</strong> for farmers, potentially impacting their profitability and economic viability.</p><h4>Reduced Crop Biomass and Root Volume</h4><p>Another key finding was the negative effect of <strong>nano urea</strong> on the physical development of crops. Its application resulted in a reduction in both <strong>above-ground biomass</strong> and <strong>root volume</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Impact on Plant Structure:</strong> Decreased <strong>root volume</strong> leads to a smaller <strong>root-surface area</strong>, which is crucial for efficient <strong>nutrient uptake processes</strong> by the roots. This can impair the plant's overall health and productivity.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •PAU study shows significant yield reduction (21.6% wheat, 13% rice) with Liquid Nano Urea compared to conventional urea.
- •Grain nitrogen content also declined, impacting protein levels in staple foods.
- •Liquid Nano Urea is 10 times more expensive than granular urea, increasing cultivation costs.
- •Reduced crop biomass and root volume observed, affecting nutrient uptake.
- •Long-term field evaluations (5-7 years) are crucial to confirm nano urea's equivalence and sustainability.
- •Findings highlight a need for cautious adoption and further research before widespread implementation.
🧠 Memory Techniques

90% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Reference to Punjab Agricultural University (PAU) research findings.