Precision Medicine and Biobanks - Science And Technology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Precision Medicine and Biobanks
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
science and technology
📖 Introduction
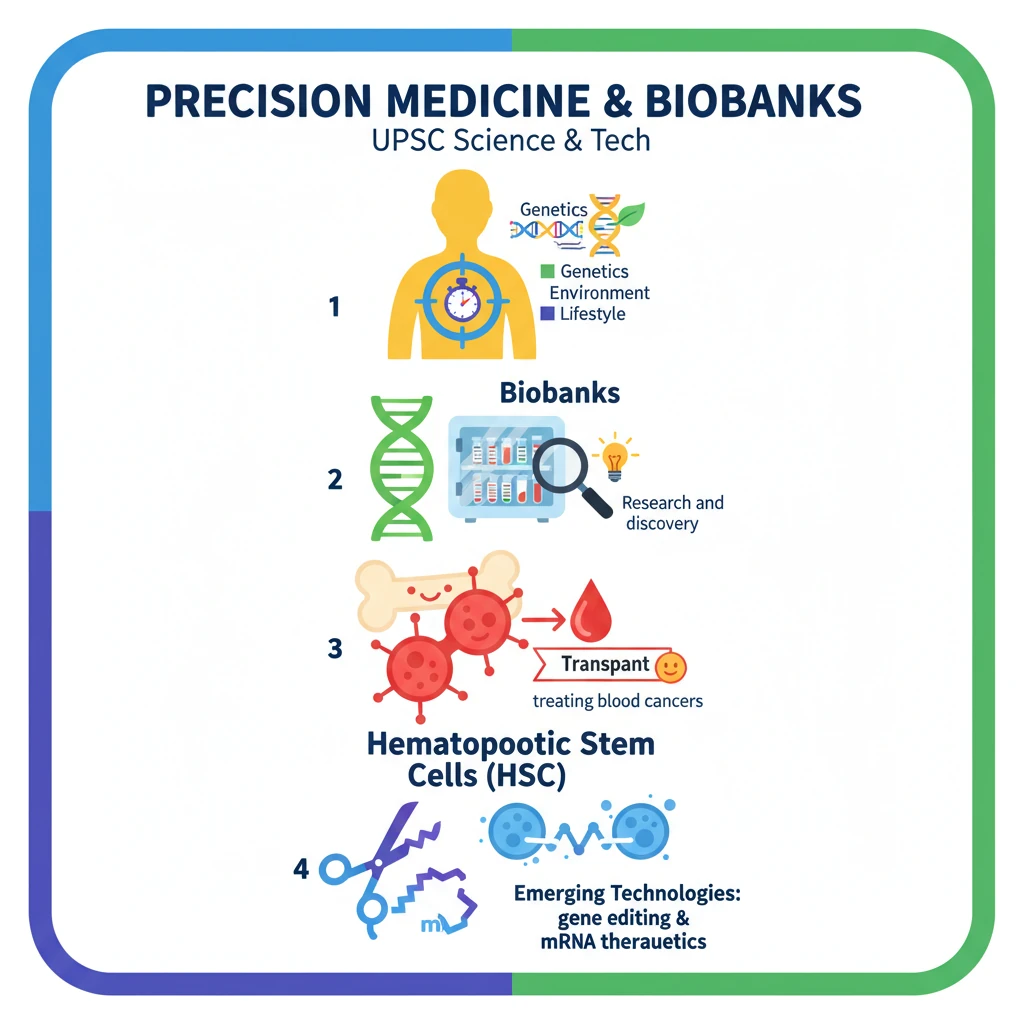
<h4>Introduction to Precision Medicine and Biobanks</h4><p><strong>Precision medicine</strong> is revolutionizing healthcare by offering a personalized approach to disease treatment and prevention. This field gained significant momentum with the completion of the <strong>Human Genome Project (HGP)</strong>, which laid the groundwork for understanding individual genetic variations.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The core idea is to move beyond a one-size-fits-all medical strategy, focusing instead on treatments tailored to each patient's unique biological makeup.</p></div><h4>What is Precision Medicine?</h4><p><strong>Precision medicine</strong> is an innovative strategy that considers individual differences in <strong>genetics</strong>, <strong>environment</strong>, and <strong>lifestyle</strong> to treat and prevent diseases. It emphasizes tailoring medical care to the unique characteristics of each patient.</p><p>This approach allows healthcare professionals and researchers to more accurately predict which treatments and preventive measures will be effective for specific groups of individuals.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Scope:</strong> Precision medicine now encompasses genomics for diagnosing and treating a wide range of conditions, including <strong>cancers</strong>, <strong>chronic diseases</strong>, <strong>immunological disorders</strong>, <strong>cardiovascular diseases</strong>, and <strong>liver diseases</strong>.</p></div><h4>The Role of Biobanks in Precision Medicine</h4><p><strong>Biobanks</strong> are essential repositories that store various <strong>biological samples</strong>, such as <strong>DNA</strong>, <strong>cells</strong>, and <strong>tissues</strong>, for research purposes. Their diversity is crucial for ensuring that precision medicine benefits a broader spectrum of populations.</p><p>Recent studies utilizing data from biobanks have been instrumental in identifying previously undiagnosed <strong>rare genetic disorders</strong>, highlighting their critical role in advancing medical knowledge.</p><h4>Emerging Technologies Driving Precision Medicine</h4><p>Several cutting-edge technologies are accelerating the progress and application of precision medicine.</p><h5>Gene Editing Technologies</h5><p>Techniques like <strong>CRISPR</strong> (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) have opened new avenues for correcting <strong>genetic defects</strong>. These advancements offer potential cures for conditions that were previously considered untreatable.</p><h5>mRNA Therapeutics</h5><p>The <strong>Covid-19 pandemic</strong> significantly demonstrated the power and versatility of <strong>mRNA technology</strong>. It allowed for the rapid development of highly effective vaccines, proving its potential for quick responses to global health crises.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Nobel Prize:</strong> This innovative approach earned a <strong>Nobel Prize</strong>, underscoring its profound significance and transformative impact on modern medicine.</p></div><h4>Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs) and their Therapeutic Role</h4><p><strong>Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs)</strong> are immature cells with the remarkable ability to develop into all types of blood cells. This includes <strong>white blood cells</strong>, <strong>red blood cells</strong>, and <strong>platelets</strong>.</p><p>The therapeutic potential of HSCs was first explored for human use in the <strong>1950s</strong>, marking an early milestone in regenerative medicine.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Location:</strong> <strong>Hematopoietic stem cells</strong> are primarily found in the <strong>peripheral blood</strong> and <strong>bone marrow</strong>, often referred to simply as <strong>blood stem cells</strong>.</p></div><h5>HSC Transplants</h5><p>An <strong>HSC transplant</strong> involves administering healthy hematopoietic stem cells to patients whose bone marrow is either dysfunctional or depleted. This procedure is critical for restoring the body's ability to produce blood cells.</p><p>These transplants are life-saving interventions, particularly for individuals suffering from various <strong>blood cancers</strong>. After a successful transplant, the donated stem cells help to re-establish the recipient’s blood cell production system.</p><h4>Precision Medicine in India: A Unique Approach</h4><p>India is actively contributing to the field of precision medicine, recognizing the unique genetic diversity of its vast population.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The <strong>Indian Human Genome Project (HGP)</strong> aims to identify and catalog genetic variations across various Indian groups. It plans to sequence the entire genomes of <strong>10,000 healthy individuals</strong> from all major ethnic communities nationwide.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding India's specific initiatives like the <strong>Indian HGP</strong> and its policy frameworks (e.g., <strong>BioE3</strong>) is crucial for questions on science and technology in <strong>GS Paper 3</strong>.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Precision medicine tailors healthcare based on individual genetics, environment, and lifestyle.
- •Biobanks are crucial repositories of biological samples, enabling research and discovery of genetic disorders.
- •Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs) are vital for treating blood cancers and disorders through transplants.
- •Emerging technologies like gene editing (CRISPR) and mRNA therapeutics are transforming disease treatment and prevention.
- •India is actively advancing in precision medicine with initiatives like the Indian HGP, BioE3 policy, and indigenous CAR-T cell therapy (NexCAR19).
🧠 Memory Techniques
100% Verified Content