72nd Plenary of the North Eastern Council (NEC) - Polity And Governance | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
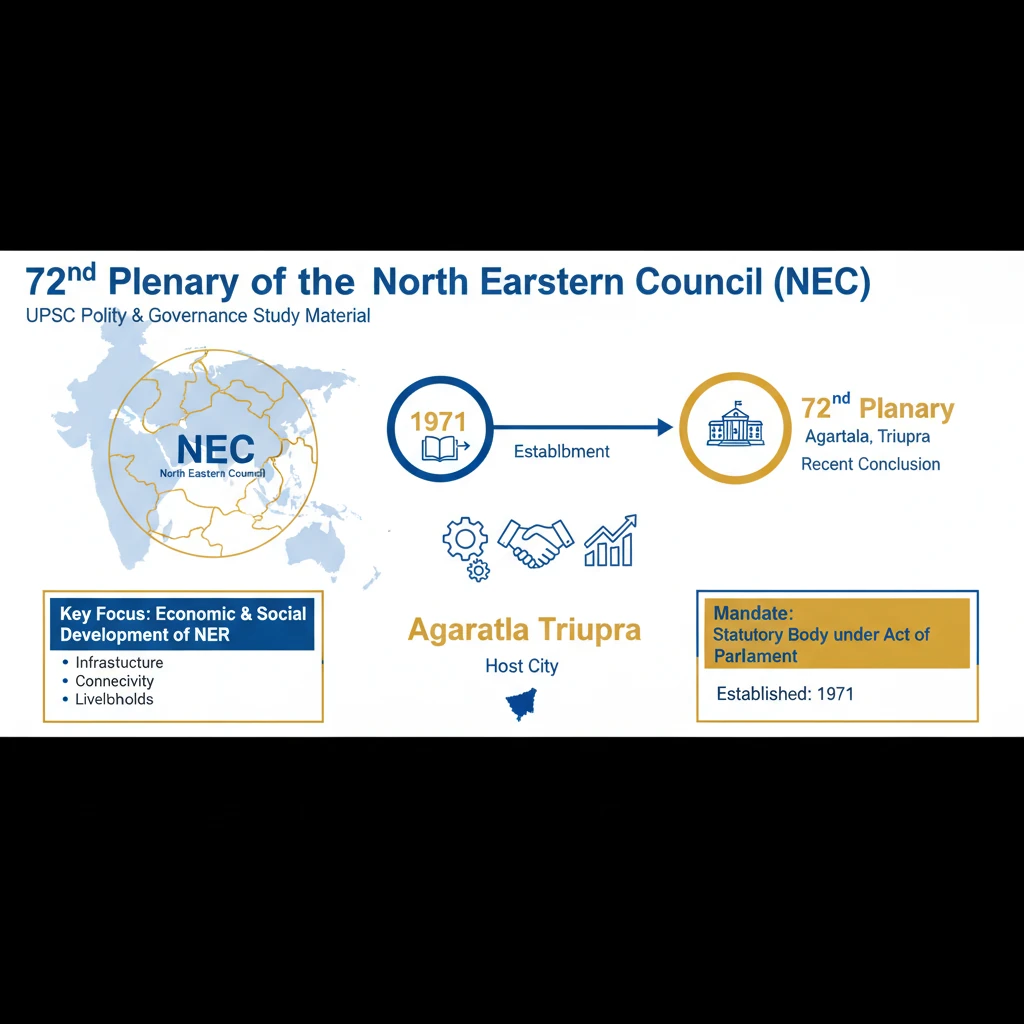
72nd Plenary of the North Eastern Council (NEC)
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
polity and governance
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to the 72nd NEC Plenary</h4><p>The <strong>72nd Plenary</strong> of the <strong>North Eastern Council (NEC)</strong> recently concluded in <strong>Agartala, Tripura</strong>. This significant event brought together key stakeholders to discuss the economic and social development of the <strong>North Eastern Region (NER)</strong>.</p><h4>Establishment and Mandate of NEC</h4><p>The <strong>North Eastern Council (NEC)</strong> was established in <strong>1971</strong> through an <strong>Act of Parliament</strong>. It serves as the <strong>nodal agency</strong> dedicated to the <strong>economic and social development</strong> of the entire North Eastern Region.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Member States:</strong> The NEC comprises <strong>eight states</strong> of the North East: <strong>Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, and Tripura</strong>.</p></div><p>Its primary objective is to address the unique <strong>developmental challenges</strong> faced by the region and to actively work towards unlocking its immense <strong>potential</strong> for growth and progress.</p><h4>Key Achievements of the NEC</h4><p>Over the decades, the NEC has played a pivotal role in transforming the North Eastern Region. Its efforts have led to substantial advancements across various sectors.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Transformative Role:</strong> The NEC has evolved from merely an <strong>advisory body</strong> to a crucial <strong>Regional Planning Agency</strong>. This transformation highlights its critical role in strategic decision-making and project implementation for the region's development.</p></div><ul><li><strong>Infrastructure Development:</strong> The NEC has overseen the construction of over <strong>11,500 kilometers of roads</strong>, significantly enhancing <strong>connectivity</strong> throughout the NER.</li><li><strong>Power Sector Growth:</strong> It has boosted <strong>power generation capacity</strong> through various projects, notably those led by the <strong>North Eastern Electric Power Corporation (NEEPCO)</strong>.</li><li><strong>Institutional Building:</strong> The Council has been instrumental in setting up foundational institutions. This includes the establishment of the <strong>Regional Institute of Medical Sciences (RIMS)</strong> and various other <strong>educational and technical hubs</strong>, fostering human resource development.</li></ul><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> When discussing regional development in GS-II or GS-III, citing the <strong>NEC's achievements</strong> provides concrete examples of institutional impact. Note its dual role as a <strong>nodal agency</strong> and <strong>regional planning body</strong>.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •The 72nd NEC Plenary was held in Agartala, Tripura.
- •NEC, established in 1971 by an Act of Parliament, is the nodal agency for NE Region's socio-economic development.
- •It covers Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, and Tripura.
- •Key achievements include 11,500 km of roads, boosted power generation (NEEPCO), and foundational institutions like RIMS.
- •NEC evolved from an advisory body to a critical Regional Planning Agency.
- •It addresses developmental challenges and aims to unlock the region's potential.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•North Eastern Council (NEC) official website
•The North Eastern Council Act, 1971