President's Rule: What It Means - Polity And Governance | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
President's Rule: What It Means
Medium⏱️ 10 min read
polity and governance
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to President's Rule</h4><p><strong>President's Rule</strong>, also known as <strong>State Emergency</strong> or <strong>Constitutional Emergency</strong>, is a provision under the <strong>Indian Constitution</strong>. It allows the <strong>Central Government</strong> to take direct control of a state's administration. This is invoked when the <strong>constitutional machinery</strong> in a state breaks down.</p><h4>Constitutional Basis: Article 356</h4><p>The power to impose <strong>President's Rule</strong> is primarily derived from <strong>Article 356</strong> of the <strong>Indian Constitution</strong>. This article empowers the <strong>President of India</strong> to assume the functions of the state government. It is a critical aspect of India's quasi-federal structure, ensuring constitutional governance across all states.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Article 356:</strong> "Provisions in case of failure of constitutional machinery in States."</p></div><h4>Grounds for Imposition</h4><p><strong>President's Rule</strong> can be imposed in a state under specific circumstances, indicating a failure of constitutional governance. The <strong>President</strong> acts upon a report from the <strong>Governor</strong> or otherwise. This implies the <strong>President</strong> can also act on their own assessment.</p><ul><li><strong>Recommendation of Governor:</strong> The <strong>Governor</strong> of a state reports to the <strong>President</strong> that the state's government cannot be carried on in accordance with constitutional provisions.</li><li><strong>Failure of Constitutional Machinery:</strong> If a <strong>state legislature</strong> or executive is unable to function as per the <strong>Constitution</strong>. This could include a hung assembly or a government losing majority.</li></ul><h4>Duration and Extension</h4><p>Once proclaimed, <strong>President's Rule</strong> has a specific duration, subject to parliamentary approval. It is not intended to be a permanent arrangement but a temporary measure to restore constitutional order.</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li><strong>Initial Duration:</strong> A proclamation of <strong>President's Rule</strong> is initially valid for <strong>six months</strong>.</li><li><strong>Maximum Duration:</strong> It can be extended for a maximum period of <strong>three years</strong>.</li><li><strong>Parliamentary Approval:</strong> Each extension beyond the initial <strong>six months</strong> requires approval from <strong>Parliament</strong>, typically after every <strong>six months</strong>.</li></ul></div><h4>Termination of President's Rule</h4><p>The <strong>President</strong> holds the power to revoke <strong>President's Rule</strong> at any time. This decision does not require the approval of <strong>Parliament</strong>. It can be terminated as soon as the conditions for its imposition cease to exist, or a stable government can be formed.</p><h4>Executive Authority During President's Rule</h4><p>During the period of <strong>President's Rule</strong>, the executive authority of the state is directly exercised by the <strong>Central Government</strong>. The <strong>President</strong> takes over all functions of the state government. The <strong>Governor</strong>, who is a centrally appointed representative, plays a crucial role.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The <strong>Governor</strong> acts as the <strong>President's agent</strong> in the state, carrying out the administration on behalf of the <strong>Union Government</strong>. The <strong>state legislative assembly</strong> may be suspended or dissolved.</p></div><h4>Role of Parliament</h4><p><strong>Parliament's</strong> approval is essential for the imposition and continuation of <strong>President's Rule</strong>. This ensures a democratic check on the executive's power to intervene in state affairs. It underscores the principle of parliamentary oversight.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Every proclamation of <strong>President's Rule</strong> must be approved by both Houses of <strong>Parliament</strong> within <strong>two months</strong> from the date of its issue. Failure to secure approval leads to the cessation of the proclamation.</p></div><h4>The 44th Constitutional Amendment (1978)</h4><p>The <strong>44th Constitutional Amendment Act of 1978</strong> introduced significant restrictions on the extension of <strong>President's Rule</strong>. This amendment was a response to concerns about the potential misuse of <strong>Article 356</strong> for political purposes. It aimed to safeguard the federal structure.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The <strong>44th Amendment</strong> mandates that <strong>President's Rule</strong> cannot be extended beyond <strong>one year</strong> unless two specific conditions are met:</p><ul><li>A <strong>Proclamation of National Emergency</strong> (under <strong>Article 352</strong>) is in operation in the whole of India, or in the whole or any part of the state concerned.</li><li>The <strong>Election Commission of India</strong> certifies that the continuance of <strong>President's Rule</strong> is necessary due to difficulties in holding <strong>Assembly elections</strong> in the state.</li></ul></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Remember the <strong>44th Amendment Act, 1978</strong> is crucial for understanding the limitations on the duration of <strong>President's Rule</strong>. It's a frequently tested concept in <strong>UPSC Prelims</strong> and <strong>Mains</strong>.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
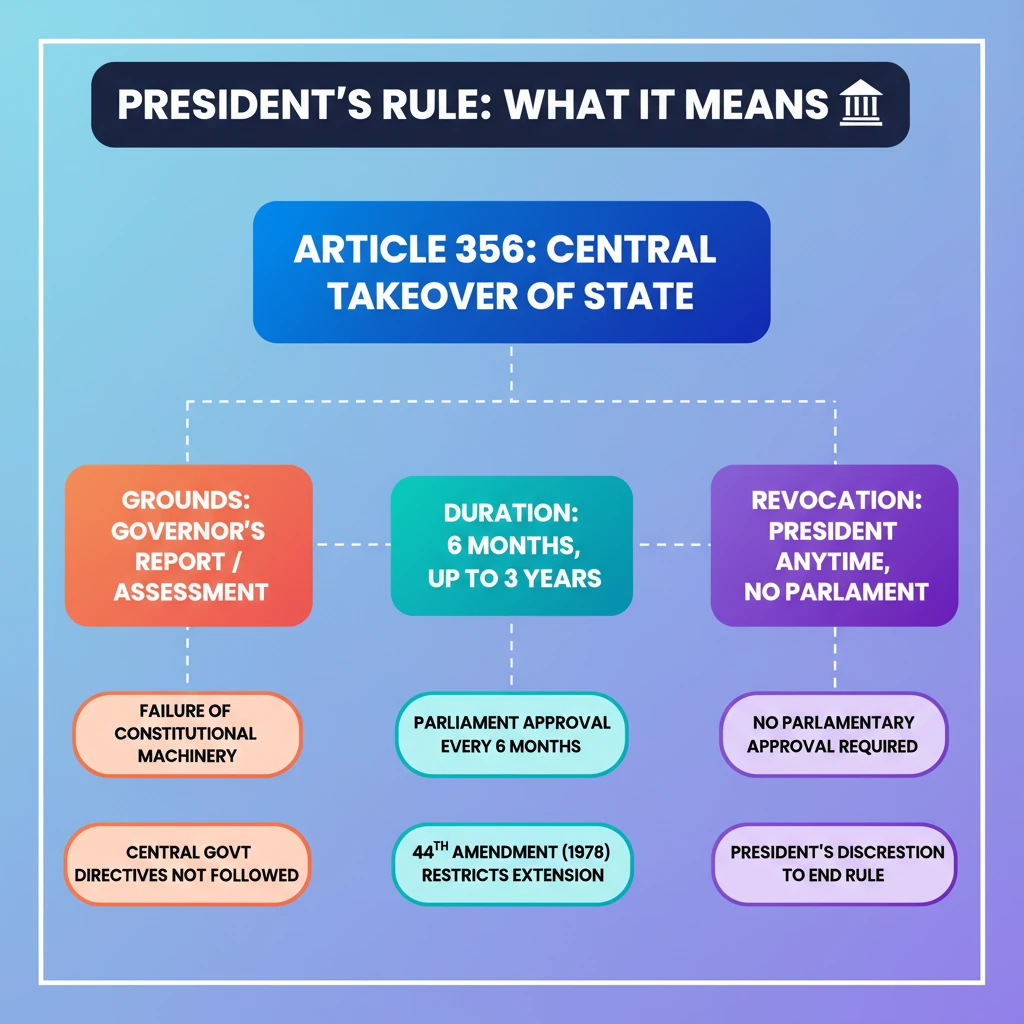
- •President's Rule (Article 356) allows central takeover of state administration due to failure of constitutional machinery.
- •It can be imposed on the Governor's report or the President's own assessment.
- •Initial duration is 6 months, extendable up to 3 years with parliamentary approval every 6 months.
- •The 44th Amendment (1978) restricts extension beyond 1 year, unless National Emergency is active or EC certifies election difficulties.
- •The President can revoke it anytime without parliamentary approval.
- •During President's Rule, executive authority is exercised through the Governor, acting as the President's agent.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•D.D. Basu's Commentary on the Constitution of India
•M. Laxmikanth, 'Indian Polity'
•Sarkaria Commission Report on Centre-State Relations (1988)
•Punchhi Commission Report on Centre-State Relations (2010)
•Supreme Court Judgement in S.R. Bommai v. Union of India (1994)