Decline of Private Members' Bills in Indian Parliament - Polity And Governance | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
Decline of Private Members' Bills in Indian Parliament
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
polity and governance
📖 Introduction
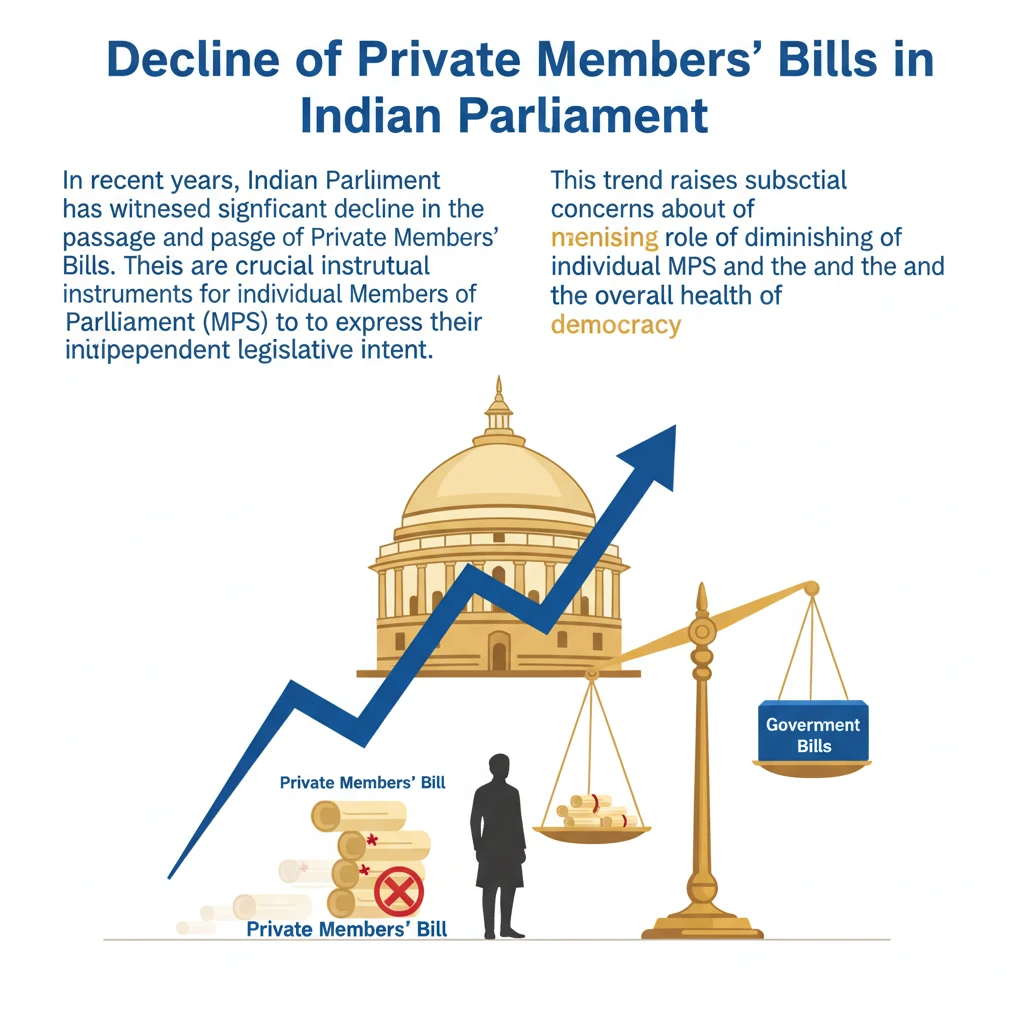
<h4>Decline of Private Members' Bills in Indian Parliament</h4><p>In recent years, the Indian Parliament has witnessed a significant decline in the consideration and passage of <strong>Private Members' Bills</strong>. These bills are crucial instruments for individual Members of Parliament (MPs) to express their independent legislative intent.</p><p>This trend raises substantial concerns about the diminishing role of individual MPs and the overall health of <strong>parliamentary democracy</strong> in India. It highlights a potential shift in legislative priorities and time allocation.</p><h4>Context of the Decline</h4><p>The issue gained prominence due to the limited time allocated for these bills in Parliament. This sidelining effect has been particularly noticeable in recent parliamentary sessions, impacting the legislative opportunities for non-ministerial MPs.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>17th Lok Sabha</strong> (June 2019 to February 2024) saw a sharp decline in the time spent on debating and considering <strong>Private Members' Bills</strong>. This period intensified concerns regarding their efficacy.</p></div><h4>What is a Private Members' Bill?</h4><p>A <strong>Private Members' Bill</strong> is a legislative proposal introduced by any Member of Parliament (MP) who is not a Minister. This distinction is vital as Ministers represent the government, while private members act independently.</p><p>These bills allow MPs to introduce new laws or amendments to existing ones. They typically focus on issues important to their constituencies or matters of public interest that the government might not prioritize.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Key Distinction:</strong> A bill introduced by a <strong>Minister</strong> is a <strong>Government Bill</strong>. A bill introduced by any other <strong>MP</strong> is a <strong>Private Members' Bill</strong>.</p></div><h4>Key Features of Private Members' Bills</h4><ul><li><strong>Independent Proposals:</strong> Only <strong>non-government MPs</strong> can introduce these bills, providing a platform for independent legislative initiatives.</li><li><strong>Addressing Constituencies:</strong> They offer a chance for MPs to address specific issues relevant to their <strong>constituencies</strong> or broader national concerns.</li><li><strong>Resolutions:</strong> Besides bills, MPs can also introduce <strong>resolutions</strong> to call attention to specific matters of public importance, which are non-legislative but serve a similar purpose of highlighting issues.</li></ul><h4>Procedure for Private Members' Bills</h4><ol><li><strong>Drafting and Notice:</strong> An MP first drafts the bill and submits it to the parliamentary secretariat. A minimum of <strong>one month's notice</strong> is required before its introduction.</li><li><strong>Introduction:</strong> Once approved, the bill is introduced in either the <strong>Lok Sabha</strong> or <strong>Rajya Sabha</strong>. This is usually followed by initial discussions on its merits.</li><li><strong>Debate and Discussion:</strong> If selected, these bills are debated in Parliament. Traditionally, specific slots are reserved for them, most commonly during <strong>limited Friday afternoon sessions</strong>.</li><li><strong>Decision:</strong> After debate, a bill may either be <strong>withdrawn</strong> by the introducing MP or proceed to a <strong>vote</strong>. Passage requires a majority vote in both Houses and presidential assent.</li></ol><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding the procedure for <strong>Private Members' Bills</strong> is crucial for questions on parliamentary functioning (<strong>GS-II Polity</strong>). Note the difference in success rate compared to Government Bills.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
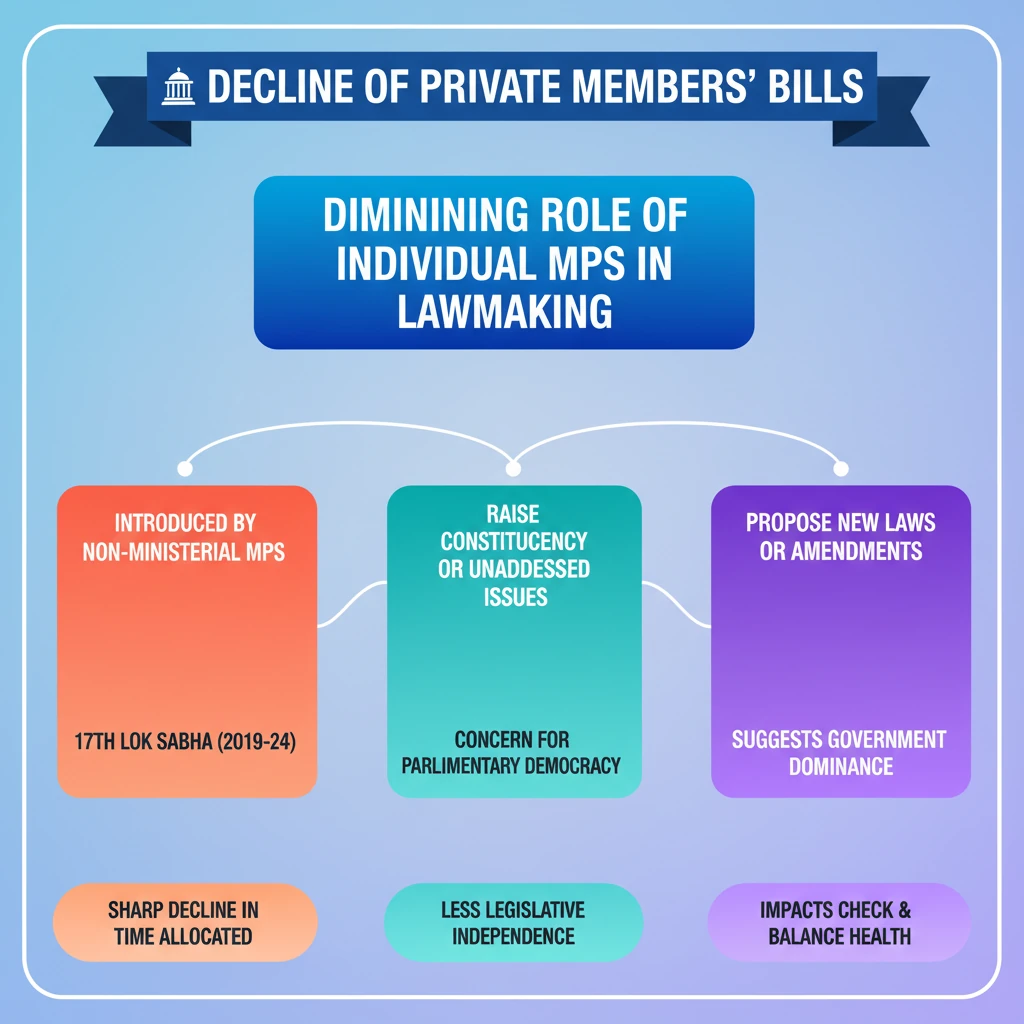
- •Private Members' Bills are introduced by non-ministerial MPs to propose new laws or amendments.
- •They allow MPs to raise issues important to their constituencies or not on the government's agenda.
- •The 17th Lok Sabha (2019-2024) witnessed a sharp decline in time allocated for these bills.
- •This decline raises concerns about the diminishing role of individual MPs in the legislative process.
- •It impacts the health of parliamentary democracy and legislative independence, suggesting government dominance.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content