National Commission for Scheduled Castes (NCSC): Composition & Functions - Polity And Governance | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

National Commission for Scheduled Castes (NCSC): Composition & Functions
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
polity and governance
📖 Introduction
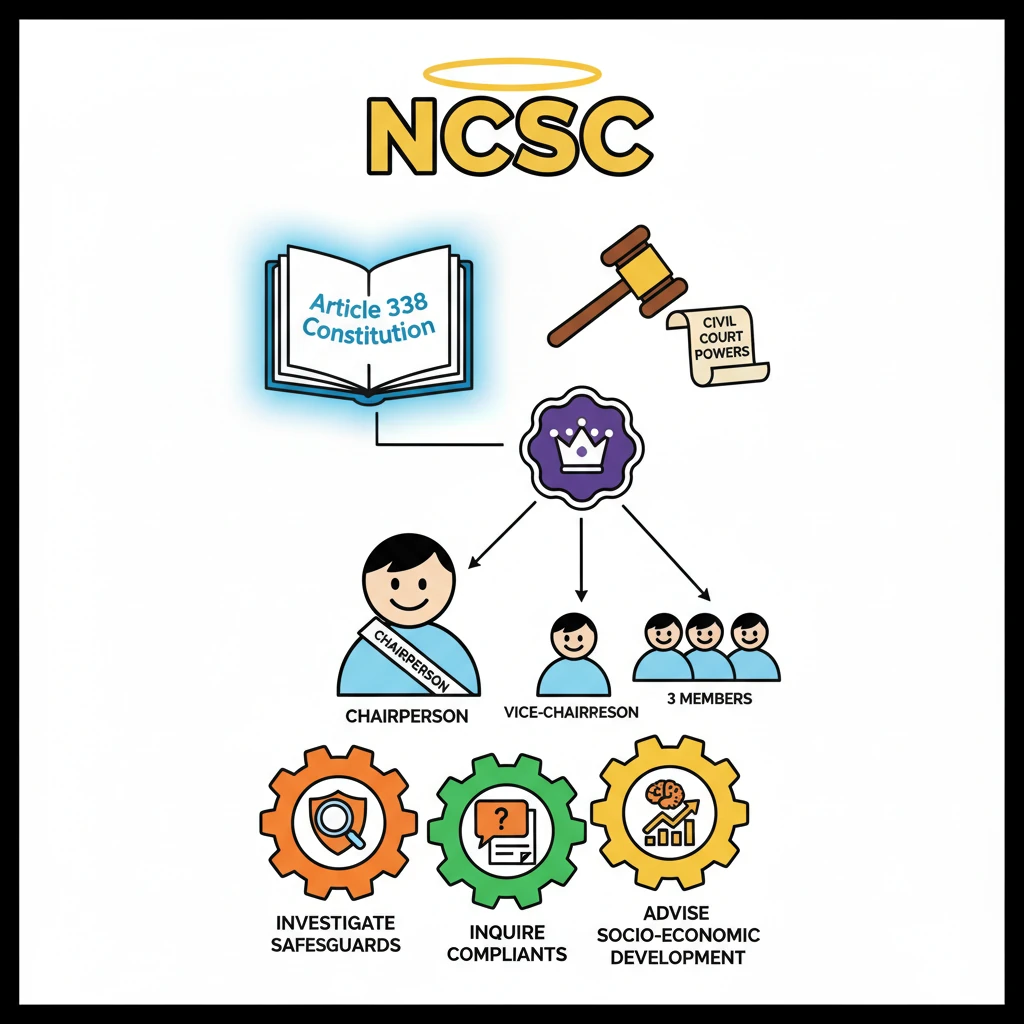
<h4>Introduction to the National Commission for Scheduled Castes (NCSC)</h4><p>The <strong>National Commission for Scheduled Castes (NCSC)</strong> is a crucial <strong>constitutional body</strong> in India. Established with the primary objective of safeguarding the interests of the <strong>Scheduled Castes (SCs)</strong>, it plays a pivotal role in ensuring their protection and development.</p><p>Its mandate extends to investigating, monitoring, and advising on matters related to the constitutional and legal safeguards provided for the SC community.</p><h4>Composition of the NCSC</h4><p>The Commission is structured to ensure comprehensive representation and effective functioning. It consists of a specific number of members, each appointed by the President of India.</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li><strong>Chairperson</strong>: Leads the Commission.</li><li><strong>Vice-Chairperson</strong>: Assists the Chairperson.</li><li><strong>Three additional Members</strong>: Contribute to the Commission's work.</li></ul><p>All members are appointed by the <strong>President of India</strong> through a <strong>warrant under his hand and seal</strong>.</p><p>The <strong>conditions of service</strong> and <strong>tenure of office</strong> for the Chairperson, Vice-Chairperson, and Members are also determined by the <strong>President</strong>.</p></div><h4>Key Functions of the NCSC</h4><p>The NCSC is entrusted with a broad range of responsibilities aimed at protecting and promoting the welfare of Scheduled Castes. These functions are critical for monitoring the implementation of various safeguards.</p><ul><li>To <strong>investigate and monitor</strong> all matters relating to the <strong>constitutional and other legal safeguards</strong> for the <strong>Scheduled Castes</strong> and to evaluate their working.</li><li>To <strong>inquire into specific complaints</strong> concerning the <strong>deprivation of rights and safeguards</strong> of the <strong>Scheduled Castes</strong>.</li><li>To <strong>participate and advise</strong> on the <strong>planning process of socio-economic development</strong> of the <strong>Scheduled Castes</strong> and to evaluate the progress of their development under the <strong>Union or a state</strong>.</li><li>To <strong>present to the President</strong>, annually and at such other times as it may deem fit, <strong>reports</strong> upon the working of those safeguards.</li><li>To make <strong>recommendations</strong> as to the measures that should be taken by the <strong>Union or a state</strong> for the effective implementation of those safeguards and other measures for the <strong>protection, welfare, and socio-economic development</strong> of the <strong>Scheduled Castes</strong>.</li></ul><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Historical Mandate Change (102nd Amendment)</strong>:</p><p>Till <strong>2018</strong>, the Commission was also required to discharge similar functions with regard to the <strong>Other Backward Classes (OBCs)</strong>. However, it was relieved from this responsibility by the <strong>102nd Amendment Act, 2018</strong>. A separate <strong>National Commission for Backward Classes (NCBC)</strong> was established with constitutional status by this amendment.</p></div><h4>Powers of the NCSC</h4><p>To effectively carry out its functions, the NCSC is vested with significant powers, enabling it to conduct thorough investigations and inquiries.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The Commission is empowered to <strong>regulate its own procedure</strong>, ensuring operational autonomy.</p><p>While investigating any matter or inquiring into any complaint, the Commission possesses all the <strong>powers of a civil court</strong> trying a suit. These powers include:</p><ul><li><strong>Summoning and enforcing the attendance</strong> of any person and examining him on oath.</li><li><strong>Receiving evidence on affidavits</strong>.</li><li><strong>Requisitioning any public record</strong> from any court or office.</li></ul></div><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Mandatory Consultation</strong>:</p><p>The <strong>Central and state governments</strong> are legally required to <strong>consult the Commission</strong> on all <strong>major policy matters affecting the Scheduled Castes</strong>. This provision underscores the NCSC's advisory and oversight role in governance.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •The NCSC is a constitutional body established under Article 338 for Scheduled Castes.
- •It comprises a Chairperson, Vice-Chairperson, and three members, all appointed by the President.
- •Key functions include investigating safeguards, inquiring into complaints, and advising on SC socio-economic development.
- •The NCSC holds powers equivalent to a civil court for inquiries and investigations.
- •The 102nd Amendment Act, 2018, relieved NCSC of its responsibilities towards OBCs, focusing solely on SCs.
- •Central and state governments must consult NCSC on major policy matters affecting SCs.
🧠 Memory Techniques
98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•National Commission for Scheduled Castes (NCSC) official website
•Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, Government of India publications
•Drishti IAS Summary (provided source material)