Public Accounts Committee (PAC) - Polity And Governance | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Public Accounts Committee (PAC)
Medium⏱️ 6 min read
polity and governance
📖 Introduction
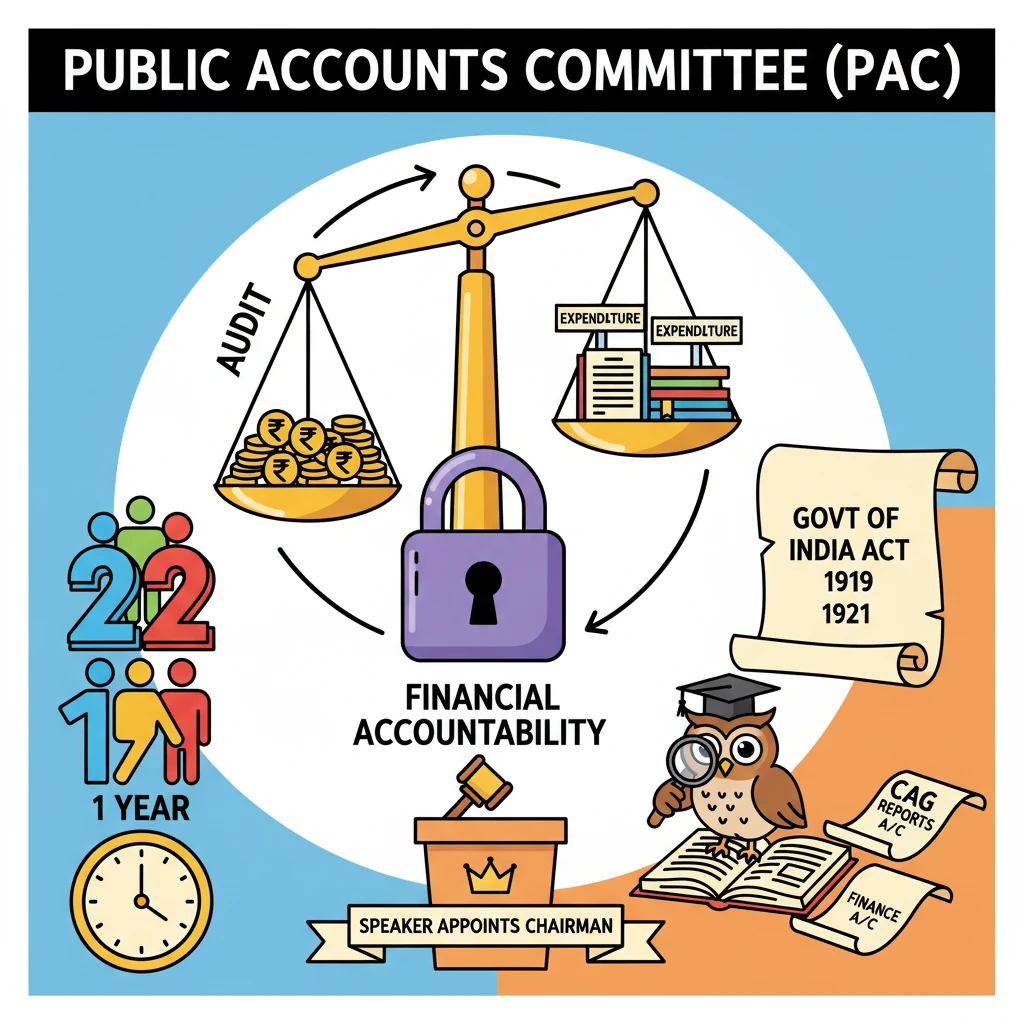
<h4>Introduction to the Public Accounts Committee (PAC)</h4><p>The <strong>Public Accounts Committee (PAC)</strong> is a crucial parliamentary body in India. It is composed of selected members of <strong>Parliament</strong> and is constituted specifically to audit the <strong>revenue</strong> and <strong>expenditure</strong> of the <strong>Government of India</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Purpose:</strong> To scrutinize government accounts and ensure financial accountability.</p></div><h4>Constitutional Basis and Nature</h4><p><strong>Parliamentary committees</strong>, including the PAC, derive their authority from <strong>Article 105</strong> (powers, privileges, etc., of members of Parliament) and <strong>Article 118</strong> (rules of procedure) of the <strong>Constitution of India</strong>.</p><p>The PAC is one of the three significant <strong>Financial Parliamentary Committees</strong>. The other two are the <strong>Estimates Committee</strong> and the <strong>Committee on Public Undertakings</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Key Restriction:</strong> No member of the PAC can hold a position as a <strong>government minister</strong>. This ensures impartiality in its oversight functions.</p></div><h4>Historical Background and Formation</h4><p>The establishment of the <strong>PAC</strong> dates back to <strong>1921</strong>. Its first mention was in the <strong>Government of India Act, 1919</strong>, famously known as the <strong>Montford Reforms</strong>.</p><p>The Committee is constituted <strong>every year</strong>. This annual formation is done under <strong>Rule 308</strong> of the <strong>Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha</strong>.</p><h4>Composition of the Committee</h4><p>Presently, the <strong>Public Accounts Committee</strong> comprises a total of <strong>22 members</strong>. These members serve for a term of <strong>one year only</strong>.</p><ul><li><strong>15 members</strong> are elected by the <strong>Lok Sabha Speaker</strong> from among its members.</li><li><strong>7 members</strong> are elected by the <strong>Rajya Sabha Chairman</strong> from among its members.</li></ul><p>The <strong>Chairman</strong> of the Committee is appointed by the <strong>Speaker of Lok Sabha</strong>. Traditionally, the Chairman is from the opposition party, reinforcing its oversight role.</p><h4>Powers and Functions of the PAC</h4><p>The PAC performs several critical functions to ensure financial propriety and accountability:</p><ul><li>It examines the <strong>accounts showing the appropriation of funds</strong> granted by the House for expenditure.</li><li>It reviews the <strong>annual Finance Accounts</strong> of the government.</li><li>The Committee also reviews other accounts presented to the House that it deems appropriate. However, it excludes those related to <strong>Public Undertakings</strong>, as these are assigned to the <strong>Committee on Public Undertakings</strong>.</li><li>A significant function involves reviewing various <strong>Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) Audit Reports</strong>. These reports cover revenue receipts, government expenditure by different Ministries/Departments, and accounts of autonomous bodies.</li></ul><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Crucial Assistance:</strong> The <strong>Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG)</strong> actively assists the committee during its investigations, providing expert insights and audit findings.</p></div><h4>Nature of Recommendations</h4><p>The recommendations made by the <strong>PAC</strong> are <strong>advisory</strong> in nature. They are <strong>not binding</strong> on the government.</p><p>This is because the PAC is an executive body that cannot issue direct orders. Ultimately, only <strong>Parliament</strong> as a whole can take a final decision on the committee's findings and recommendations.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding the <strong>advisory nature</strong> of PAC recommendations is crucial. While not binding, they carry significant moral and political weight, often leading to corrective action by the government.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •PAC audits government revenue and expenditure, ensuring financial accountability.
- •Established in 1921 under the Government of India Act, 1919.
- •Comprises 22 members (15 Lok Sabha, 7 Rajya Sabha) for a one-year term; Chairman appointed by Lok Sabha Speaker.
- •Examines CAG audit reports, appropriation accounts, and finance accounts.
- •Recommendations are advisory, not binding on the government.
- •No minister can be a member, ensuring impartiality.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content