Does Anti-Defection Law Apply to Rajya Sabha Elections? - Polity And Governance | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Does Anti-Defection Law Apply to Rajya Sabha Elections?
Medium⏱️ 6 min read
polity and governance
📖 Introduction
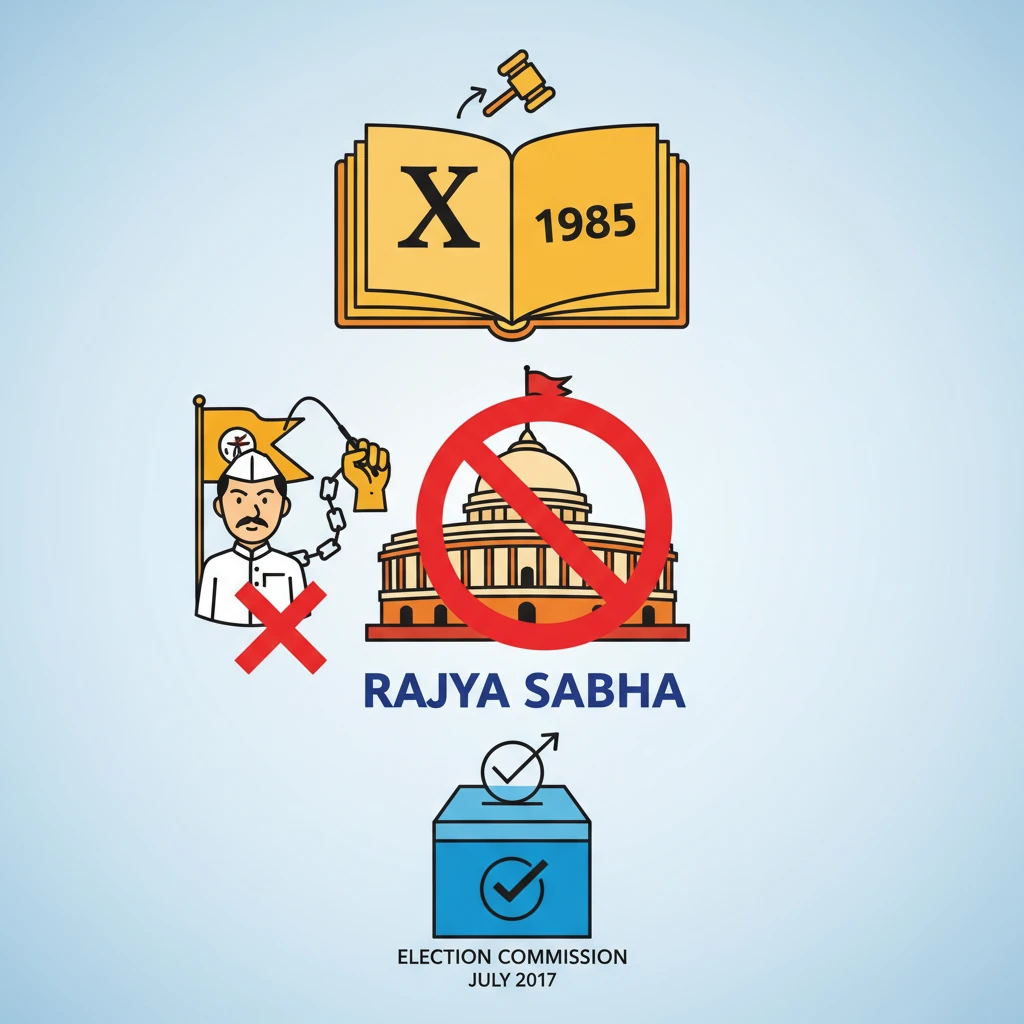
<h4>Introduction to the Anti-Defection Law</h4><p>The <strong>Anti-Defection Law</strong> is a crucial provision in the Indian Constitution designed to prevent political defections. It aims to bring stability to governments by discouraging legislators from changing parties for personal gain.</p><p>This law ensures that members remain loyal to their political party's ideology and instructions, especially during crucial votes in the legislature.</p><h4>The Tenth Schedule and its Provisions</h4><p>The <strong>Tenth Schedule</strong> of the Indian Constitution contains the specific provisions related to the <strong>Anti-Defection Law</strong>. It was incorporated into the Constitution through the <strong>52nd Constitutional Amendment Act</strong> in <strong>1985</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Date:</strong> The <strong>52nd Constitutional Amendment Act</strong> was enacted in <strong>1985</strong>.</p><p><strong>Purpose:</strong> To combat the 'Aaya Ram Gaya Ram' phenomenon and ensure political stability.</p></div><p>Under this schedule, a member of Parliament (MP) or a state legislature (MLA/MLC) can be disqualified from their House on specific grounds.</p><h4>Grounds for Disqualification</h4><p>There are two primary grounds for disqualification under the <strong>Tenth Schedule</strong>:</p><ul><li><strong>Voluntarily Giving Up Membership:</strong> If a legislator voluntarily gives up the membership of their political party. This can be explicit (resignation) or implicit (acting against party interests).</li><li><strong>Voting Against Party Instructions:</strong> If a legislator votes or abstains from voting in the House contrary to any direction issued by their political party. Such directions are typically issued by the <strong>party whip</strong>.</li></ul><div class='key-point-box'><p>The <strong>party whip</strong> is an official who ensures the attendance and voting of party members according to the party's instructions.</p></div><h4>Applicability to Rajya Sabha Elections</h4><p>A significant clarification regarding the <strong>Anti-Defection Law</strong> pertains to its applicability during <strong>Rajya Sabha elections</strong>. The <strong>Election Commission of India (ECI)</strong> has explicitly stated its position on this matter.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>ECI Clarification Date:</strong> <strong>July 2017</strong>.</p><p><strong>Key Ruling:</strong> The <strong>Tenth Schedule</strong> and the <strong>Anti-Defection Law</strong> are <strong>not applicable</strong> to <strong>Rajya Sabha elections</strong>.</p></div><p>This means that political parties <strong>cannot issue a whip</strong> to their members for voting in <strong>Rajya Sabha elections</strong>. Consequently, members are <strong>not bound</strong> by party instructions in these specific elections.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> This distinction is crucial for both Prelims (factual recall) and Mains (analytical questions on electoral reforms or party discipline). Understanding why the law doesn't apply here reflects a deeper understanding of the electoral process for <strong>Rajya Sabha</strong>.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •The Anti-Defection Law is enshrined in the Tenth Schedule of the Indian Constitution.
- •It was introduced by the 52nd Constitutional Amendment Act in 1985 to curb political defections.
- •Legislators can be disqualified for voluntarily giving up party membership or voting against the party whip.
- •The Election Commission clarified in July 2017 that the Anti-Defection Law does NOT apply to Rajya Sabha elections.
- •Therefore, political parties cannot issue a whip to members for Rajya Sabha elections, and members are not bound by party instructions.
🧠 Memory Techniques
98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•52nd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1985
•Election Commission of India's official clarifications (July 2017)
•Drishti IAS Summary on Anti-Defection Law