23rd Law Commission Set Up and History - Polity And Governance | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

23rd Law Commission Set Up and History
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
polity and governance
📖 Introduction
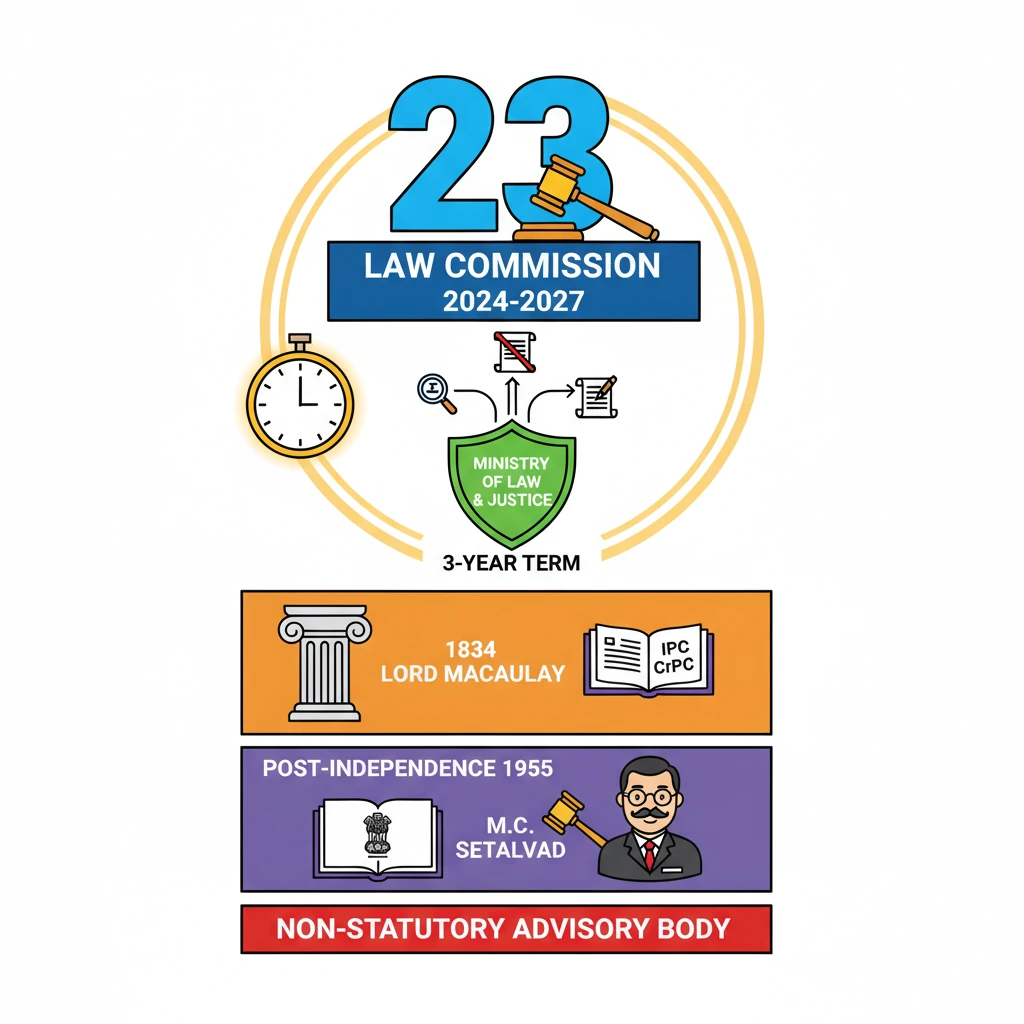
<h4>Introduction to the 23rd Law Commission</h4><p>The <strong>Ministry of Law and Justice</strong> recently announced the establishment of the <strong>23rd Law Commission</strong>. This commission is set for a <strong>three-year term</strong>, commencing from <strong>September 1, 2024</strong>, and concluding on <strong>August 31, 2027</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Dates:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Establishment:</strong> Recently announced by Ministry of Law and Justice</li><li><strong>Term Duration:</strong> 3 years</li><li><strong>Start Date:</strong> September 1, 2024</li><li><strong>End Date:</strong> August 31, 2027</li></ul></div><h4>Understanding the Law Commission of India</h4><p>The <strong>Law Commission of India</strong> is a significant body responsible for legal reforms. It operates as a <strong>non-statutory body</strong>, meaning it is not created by an Act of Parliament but rather through a <strong>notification</strong> from the Government of India.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Nature of the Body:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Non-statutory:</strong> Established by government notification, not by law.</li><li><strong>Advisory:</strong> Its recommendations are not binding on the government.</li><li><strong>Fixed Tenure:</strong> Appointed for a specific period, typically three years.</li></ul></div><h4>Core Functions of the Law Commission</h4><p>The primary role of the Law Commission is to undertake <strong>research in the field of law</strong> to facilitate legal reforms. This involves a wide array of responsibilities aimed at modernizing and improving the Indian legal system.</p><ul><li><strong>Review and Repeal of Obsolete Laws:</strong> It identifies and recommends the repeal of laws that are outdated, irrelevant, or have lost their utility in the current societal context.</li><li><strong>Law and Poverty:</strong> The Commission examines laws that have a significant impact on the poor and conducts post-audits of socio-economic legislation to assess their effectiveness and implications.</li><li><strong>Propose New Laws:</strong> It proposes new legislative frameworks to implement the <strong>Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP)</strong> and achieve the objectives outlined in the <strong>Preamble to the Constitution of India</strong>.</li><li><strong>Judicial Administration:</strong> The Commission reviews and provides recommendations on various issues related to law and judicial administration, particularly those referred to it by the Government of India.</li></ul><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding the <strong>non-statutory</strong> and <strong>advisory</strong> nature of the Law Commission is crucial. While its recommendations are not binding, they carry significant weight in legal policy-making and often influence legislative action. Mentioning specific functions can enhance your answers in <strong>GS Paper II (Polity and Governance)</strong>.</p></div><h4>Important Reports Submitted by the Law Commission</h4><p>Over its tenure, the Law Commission has submitted numerous reports addressing diverse legal issues. These reports often serve as foundational documents for legislative changes and policy reforms.</p><p>So far, the Law Commission of India has submitted <strong>289 reports</strong> on various critical issues. Some notable recent reports include:</p><ul><li><strong>Report No. 283 (September 2023):</strong> Focused on the <strong>Age of Consent</strong> under <strong>The Protection of Children From Sexual Offences Act, 2012 (POCSO Act)</strong>.</li><li><strong>Report No. 271 (July 2017):</strong> Dealt with the intricacies of <strong>Human DNA Profiling</strong>.</li><li><strong>Report No. 273 (October 2017):</strong> Addressed the <strong>Implementation of the United Nations Convention against Torture</strong> in India.</li><li><strong>Report No. 274 (April 2018):</strong> Provided a comprehensive <strong>Review of the Contempt of Courts Act, 1971</strong>.</li></ul>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •The 23rd Law Commission is a non-statutory, advisory body set for a 3-year term (2024-2027) by the Ministry of Law and Justice.
- •Its primary role is legal research, recommending repeal of obsolete laws, proposing new legislation, and advising on judicial administration.
- •The first Law Commission was established in 1834 under Lord Macaulay, leading to codification of IPC and CrPC.
- •Post-independence, the first Law Commission was set up in 1955 with M.C. Setalvad as Chairman.
- •The Commission's reports, like those on POCSO's age of consent or DNA profiling, significantly influence legal reforms and policy-making.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Official website of the Law Commission of India (for cross-referencing report numbers and dates)