Spices Board of India - Polity And Governance | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
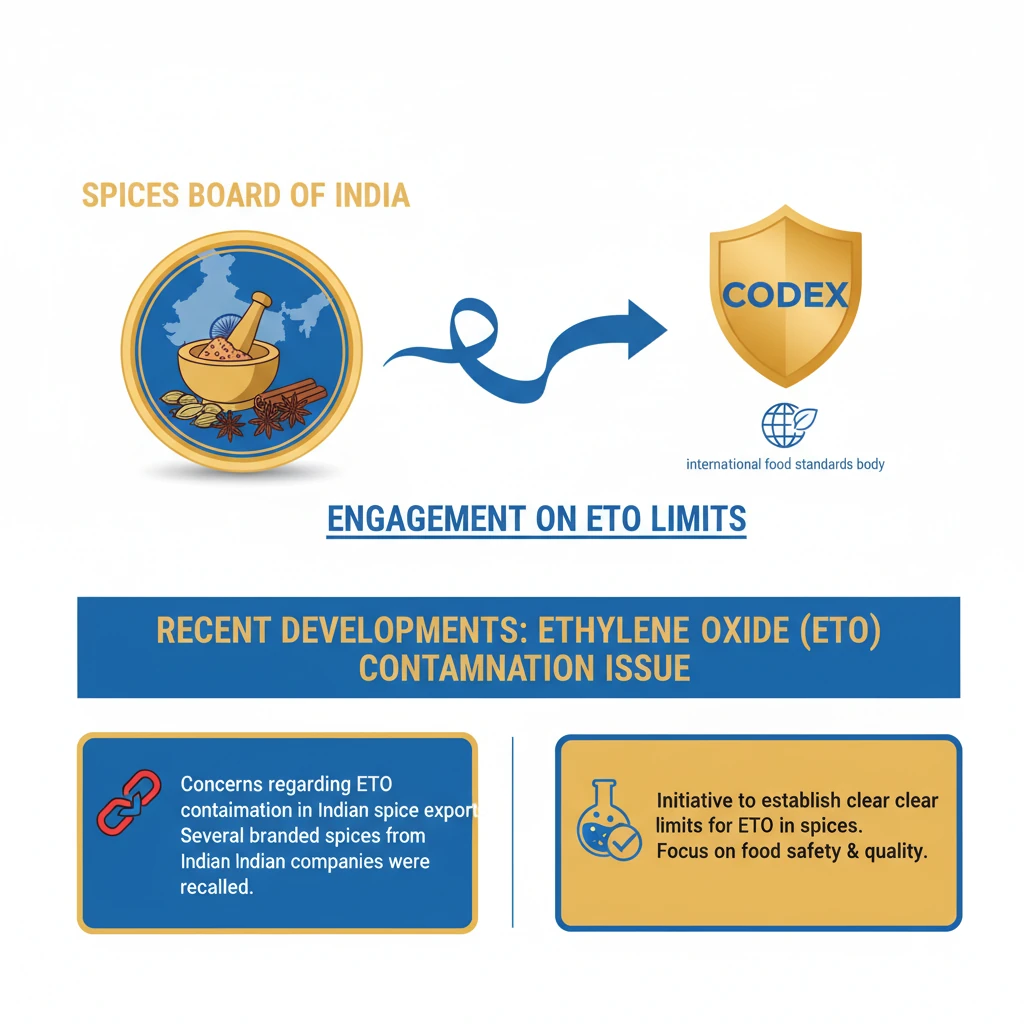
Spices Board of India
Medium⏱️ 5 min read
polity and governance
📖 Introduction
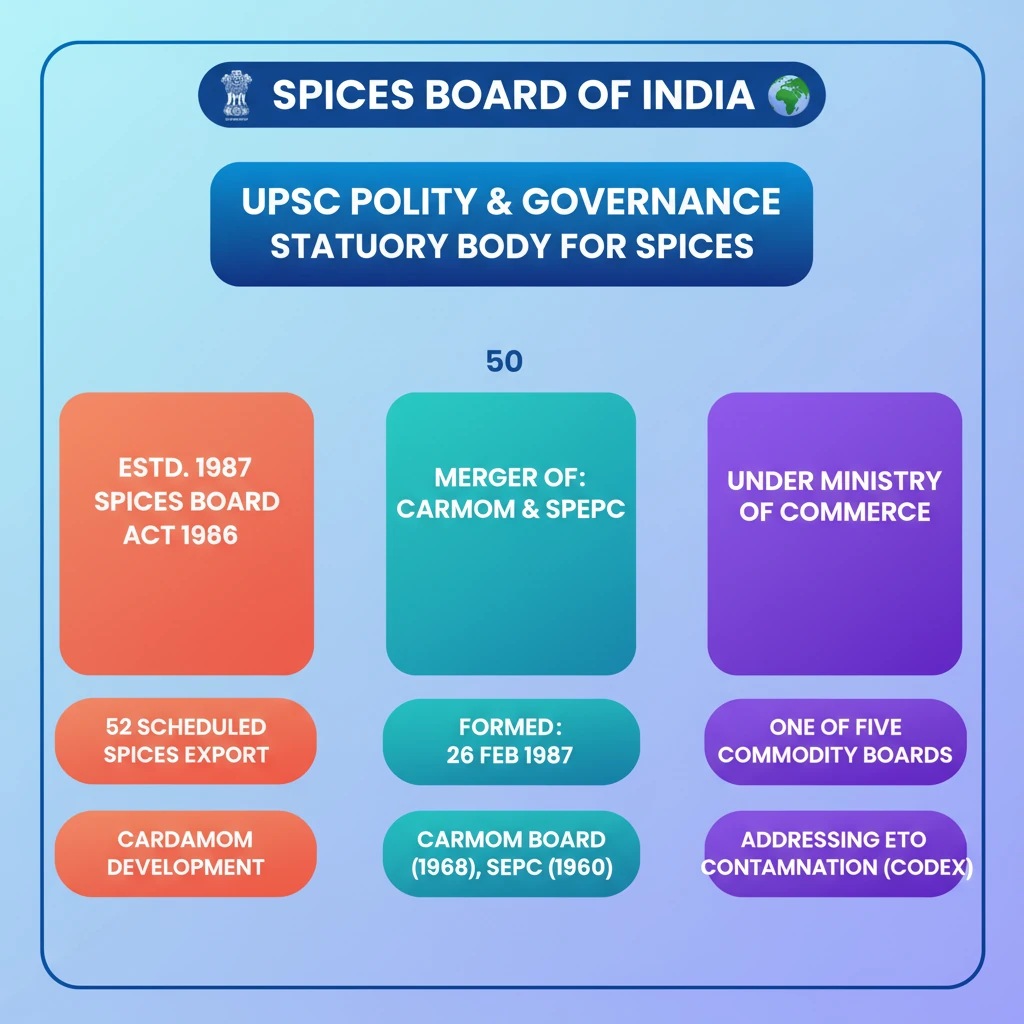
<h4>Recent Developments: Ethylene Oxide (ETO) Contamination Issue</h4><p>The <strong>Spices Board of India</strong> has recently engaged with <strong>CODEX</strong>, the international food standards body. This engagement focuses on establishing clear limits for the use of <strong>Ethylene Oxide (ETO)</strong> in spices.</p><p>This initiative follows significant concerns regarding <strong>ETO contamination</strong> in Indian spice exports. Several branded spices from Indian companies were recalled in <strong>Hong Kong</strong> and <strong>Singapore</strong> due to these issues.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Following the international recalls, <strong>Nepal</strong> also imposed a ban on the sale and import of certain spice-mix products. This ban was enacted due to similar concerns about potential <strong>ETO contamination</strong>, highlighting the global impact of such quality control issues.</p></div><h4>Understanding the Spices Board of India</h4><p>The <strong>Spices Board of India</strong> was formally constituted on <strong>February 26, 1987</strong>. Its establishment was mandated under the <strong>Spices Board Act, 1986</strong>, signifying its status as a statutory body.</p><p>This formation involved the merger of two existing entities: the erstwhile <strong>Cardamom Board (1968)</strong> and the <strong>Spices Export Promotion Council (1960)</strong>. This consolidation aimed to create a unified authority for spice development and promotion.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>Spices Board</strong> is one of <strong>five statutory Commodity Boards</strong> operating under the administrative control of the <strong>Department of Commerce</strong>. These boards play a crucial role in overseeing specific agricultural commodities.</p></div><div class='key-point-box'><p>These <strong>Commodity Boards</strong> are collectively responsible for the <strong>production, development, and export</strong> of key agricultural products. The five commodities they cover are <strong>tea, coffee, rubber, spices, and tobacco</strong>.</p></div><p>Specifically, the <strong>Spices Board</strong> holds a dual mandate. It is responsible for the comprehensive <strong>export promotion</strong> of <strong>52 Scheduled spices</strong> listed under its purview.</p><p>Additionally, it has a dedicated role in the <strong>development</strong> and cultivation of <strong>Cardamom</strong>. This includes initiatives for improving quality, productivity, and market access for this specific spice.</p>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Spices Board of India was constituted on February 26, 1987, under the Spices Board Act, 1986.
- •It resulted from the merger of the Cardamom Board (1968) and Spices Export Promotion Council (1960).
- •It is one of five statutory Commodity Boards under the Department of Commerce.
- •Its primary responsibilities include export promotion of 52 Scheduled spices and development of Cardamom.
- •Currently, it is addressing the issue of Ethylene Oxide (ETO) contamination in spices with CODEX.
- •Plays a crucial role in maintaining India's reputation and competitiveness in the global spice market.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content