What are the Different Organs of the UN? - International Relations | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What are the Different Organs of the UN?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
international relations
📖 Introduction
<h4>The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA)</h4><p>The <strong>United Nations General Assembly (UNGA)</strong> stands as the primary <strong>policy-making organ</strong> of the entire <strong>United Nations Organisation</strong>.</p><p>It serves as a unique global forum, bringing together all <strong>Member States</strong> for multilateral discussions.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>UNGA</strong> comprises <strong>all 193 Member States</strong> of the <strong>UN</strong>. Each of these nations holds an <strong>equal vote</strong>, ensuring democratic representation in its deliberations.</p></div><p>Its mandate covers the full spectrum of international issues as outlined in the <strong>Charter of the UN</strong>.</p><h4>The United Nations Security Council (UNSC)</h4><p>The <strong>United Nations Security Council (UNSC)</strong> is entrusted with the primary responsibility for the maintenance of <strong>international peace and security</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>UNSC</strong> is composed of <strong>15 members</strong>. This includes <strong>five permanent members</strong> and <strong>ten non-permanent members</strong>.</p></div><p>The <strong>five permanent members</strong> hold veto power and are <strong>China</strong>, <strong>France</strong>, the <strong>Russian Federation</strong>, the <strong>United Kingdom</strong>, and the <strong>United States</strong>.</p><p>The <strong>ten non-permanent members</strong> are elected by the <strong>General Assembly</strong> for a term of <strong>two years</strong>.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>India's</strong> significant role in global affairs is highlighted by its election as a <strong>non-permanent member</strong> of the <strong>UNSC</strong> for <strong>eight terms</strong>, a crucial fact for <strong>UPSC Mains GS-II</strong>.</p></div><h4>The United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC)</h4><p>The <strong>United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC)</strong> is a central platform for debate and innovative thinking on sustainable development.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>ECOSOC</strong> consists of <strong>54 Members</strong> of the <strong>UN</strong>, who are elected by the <strong>UN General Assembly</strong>.</p></div><p>It is the principal body for <strong>coordination</strong>, <strong>policy review</strong>, <strong>policy dialogue</strong>, and making <strong>recommendations</strong> on crucial <strong>economic</strong>, <strong>social</strong>, and <strong>environmental issues</strong>.</p><h4>The United Nations Trusteeship Council</h4><p>The <strong>Trusteeship Council</strong> was established as one of the main organs of the <strong>UN</strong> with a specific, historical mandate.</p><p>Its primary role was to <strong>supervise the administration of Trust Territories</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The Council's objective was to ensure these territories were prepared for <strong>self-governance</strong> or <strong>independence</strong>, transitioning them from <strong>colonies</strong> to <strong>sovereign nations</strong>.</p></div><h4>The International Court of Justice (ICJ)</h4><p>The <strong>International Court of Justice (ICJ)</strong>, often referred to as the <strong>World Court</strong>, is the principal judicial organ of the <strong>United Nations</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>ICJ</strong> is the <strong>only international court</strong> that settles legal disputes between the <strong>193 UN Member States</strong>.</p></div><p>The Court has the authority to rule on two distinct types of cases.</p><ul><li><strong>Contentious cases:</strong> These involve <strong>legal disputes between states</strong> that have agreed to submit to the Court's jurisdiction.</li><li><strong>Advisory proceedings:</strong> These are requests for <strong>advisory opinions</strong> on legal questions, referred to the <strong>ICJ</strong> by <strong>UN organs</strong> and certain <strong>specialized agencies</strong>.</li></ul>
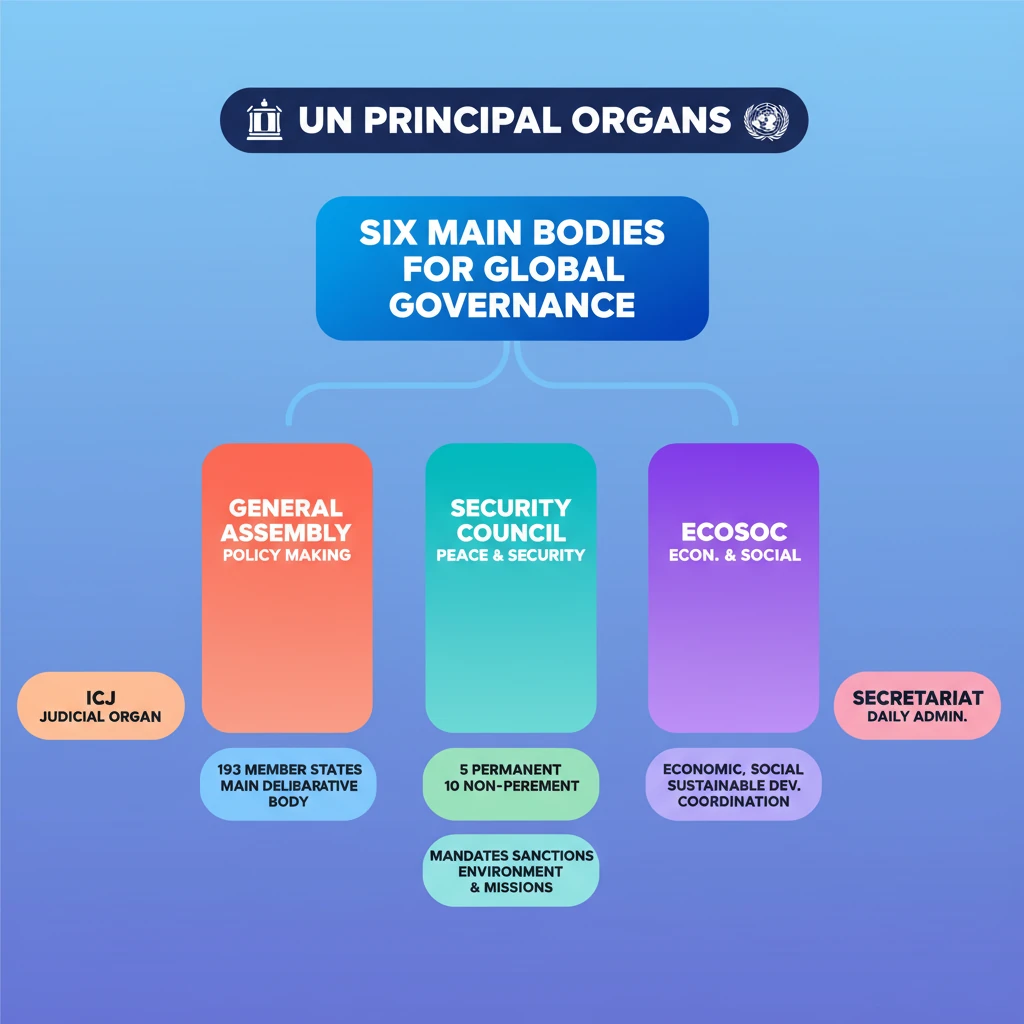
💡 Key Takeaways
- •The UN has six principal organs, each with distinct functions for global governance.
- •The General Assembly is the main policy-making body, representing all 193 member states with equal vote.
- •The Security Council maintains international peace and security, comprising 5 permanent and 10 non-permanent members.
- •ECOSOC coordinates economic, social, and environmental issues, vital for sustainable development.
- •The ICJ is the primary judicial organ, settling disputes between states.
- •The Trusteeship Council fulfilled its mandate of overseeing territories to independence.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Official UN Website (for general structure and functions)