What is the Silk Road? - International Relations | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
What is the Silk Road?
Medium⏱️ 4 min read
international relations
📖 Introduction
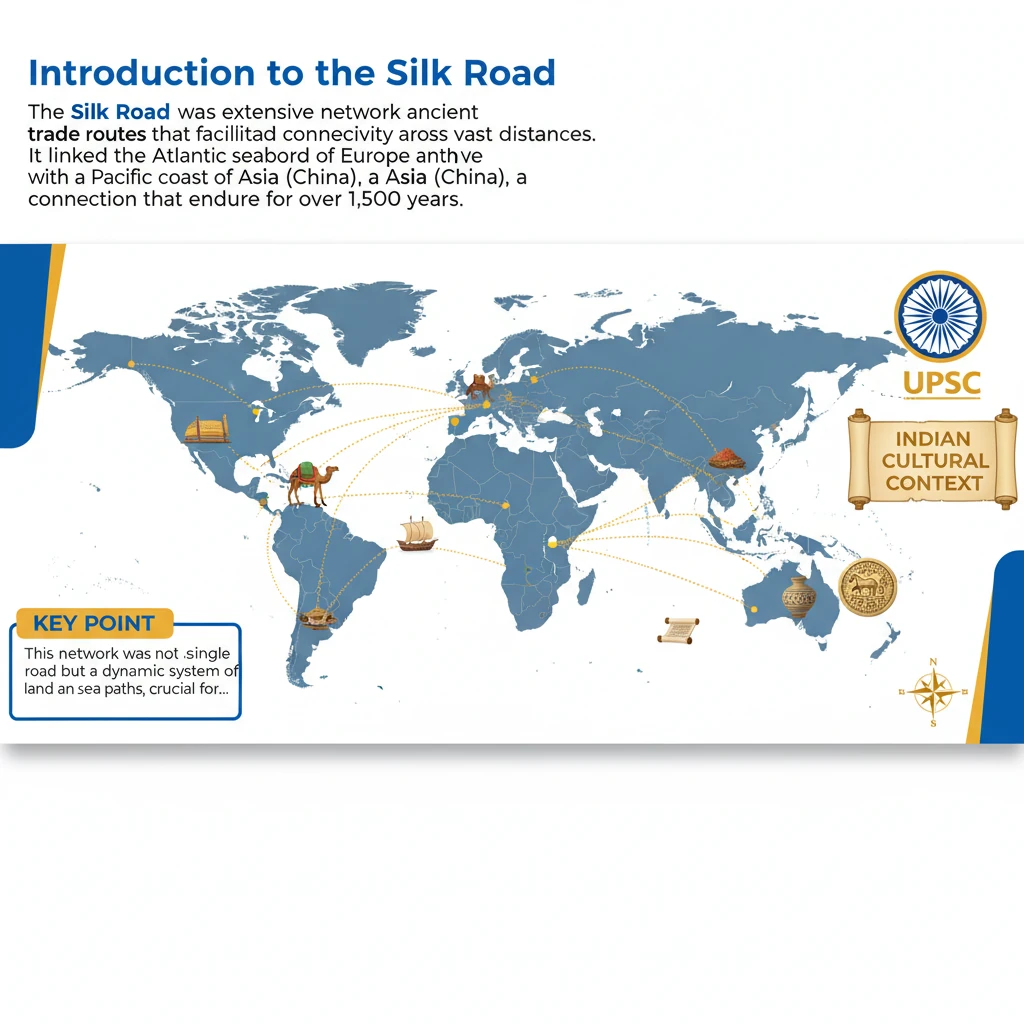
<h4>Introduction to the Silk Road</h4><p>The <strong>Silk Road</strong> was an extensive network of ancient <strong>trade routes</strong> that facilitated connectivity across vast distances.</p><p>It linked the <strong>Atlantic seaboard of Europe</strong> with the <strong>Pacific coast of Asia (China)</strong>, a connection that endured for over <strong>1,500 years</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>This network was not a single road but a dynamic system of land and sea paths, crucial for ancient globalization.</p></div><h4>Origin of the Name</h4><p>The name <strong>"Silk Road"</strong> was coined due to the highly lucrative <strong>silk trade</strong> originating from <strong>China</strong>.</p><p>China, located at the far eastern end of these routes, was the primary producer and exporter of this prized commodity.</p><h4>Key Goods Traded</h4><p>While <strong>silk</strong> was the most famous commodity, the routes transported a diverse array of goods, fostering extensive economic exchange.</p><ul><li><strong>Spices</strong>: Essential for cuisine, medicine, and preservation.</li><li><strong>Gold</strong>: A universal medium of exchange and symbol of wealth.</li><li><strong>Precious Stones</strong>: Valued for their beauty and rarity, including jade and rubies.</li><li>Other goods included textiles, ceramics, tea, horses, and various technologies.</li></ul><h4>Major Cities and Kingdoms Along the Route</h4><p>The Silk Road traversed numerous significant urban centers and powerful kingdoms, serving as vital hubs for trade and cultural interaction.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Key cities and regions along the route included:</p><ul><li><strong>Samarkand</strong>: A major Central Asian hub, known for its strategic location.</li><li><strong>Babylon</strong>: An ancient Mesopotamian city, connecting routes to the Middle East.</li><li><strong>Constantinople</strong>: The capital of the Byzantine Empire, a critical bridge between East and West.</li></ul></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Understanding the <strong>geographic span</strong>, <strong>diversity of goods</strong>, and <strong>key urban centers</strong> is crucial for Mains answers on ancient trade, cultural exchange, and economic history in <strong>GS Paper I</strong>.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •The Silk Road was a vast network of trade routes connecting the Atlantic seaboard of Europe with the Pacific coast of Asia (China) for over 1,500 years.
- •It was named for the lucrative silk trade from China but also transported spices, gold, and precious stones.
- •Key cities along its path included Samarkand, Babylon, and Constantinople.
- •Its formal establishment is linked to Emperor Wu of the Chinese Han Dynasty in the 2nd century BCE.
- •Diplomat Zhang Qian is credited as the 'Father of the Silk Road' for his expeditions that opened the Tarim Basin route.
- •Beyond trade, it facilitated significant cultural, religious, and technological exchange between diverse civilizations.
- •The historical Silk Road serves as an inspiration and context for modern connectivity projects like China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
🧠 Memory Techniques

100% Verified Content